Introduction
Service sector includes all those economic activities which are required for uninterrupted production and exchange of goods. In includes specialized services required for removing various hindrances of trade. Trade and industry is not possible without the various service sectors like banking, insurance, communication, transportation, warehousing, etc. In short, service sector is the backbone of every business and Industry.
Types of services:-
- Business Services: – Business services are those services which are used by business enterprises for the conduct of their activities. For example, banking, insurance and communication services.
Types-
- Banking:- Every business enterprise needs finance to carry on its operations. Banks provide funds to the business.
- Insurance:- In order to protect the businessman from damage to risk, there is a need to get the plant, machinery, goods, etc. insured.
- Communication:- Communication is needed to educate the consumer or potential user about the availability and utility of the product.
- Transportation:- Transportation is required to carry raw material and finished goods in good shape and on time.
- Warehousing:- Warehousing is needed to store the goods from the time of their production or purchase until they are sold or consumed.
Banking:-
Commercial banks are an important institution of the economy for providing institutional credit to its customer. A banking company in India is the one which transacts the business of banking which means accepting.
For the purpose of lending and investment of deposits of money from the public, repayable on demand or otherwise and withdrawable by cheques, draft, order or otherwise .
In simple terms, a bank accepts money on deposit, repayable on demand and also earns a margin of profit by lending money. A bank stimulates economic activity in the market by dealing in money. It mobilizes the savings of people and makes funds available to business financing their capital and revenue expenditure.
Types of Banks:-
- Commercial Banks:-Commercial Banks are institutions dealing in money. These are governed by Indian banking regulation Act 1949 and according to it banking means accepting deposits of money from the public for the purpose of lending or investment. These are two types of commercial banks, public sector and private sector banks. Public sector banks are those in which the government has a major are a number of public sector banks likes SBI, PNB, etc. And other private sector banks represented by HDFC bank, ICICI bank, etc.
2. Cooperative Banks:- Cooperative banks are governed by the provisions of state cooperative societies Act and meant essentially for providing cheap credit to their members. It is an important source of rural credit, i.e., agricultural financing in India.
3. Specialized Banks:- Specialized Banks are foreign exchange bank, industrial banks, development banks, export-import banks catering to specific needs of these unique activities. These banks provide financial aid to industries, heavy turnkey projects and foreign trade.
4. Central Bank:-The central bank of any country supervise. Controls and regulates the activities of all the commercial banks of that country. It also acts as a government banker. It controls and coordinates currency and credit policies of any country. The Reserve Bank of India is the central bank of our country.
Type of bank account
There are mainly four types of account –
- Current Account – These accounts are mainly owned by business firms or enterprises and individual with frequent financial transaction. The money with these accounts is liquid cash. There can be as many transactions through this account. No interest is paid on the sum of money in this account. Current account provide checkbook, debit card and online banking facilities.
2. Saving Account – Saving account as its name says this account holding money. It offer a safe place to deposit funds while providing easy accessibility. This account can be owned by a working-class, pensioners or the students. Saving account are suitable for emergency fund, short term goal or general purpose saving .The rate of interest in these accounts lies between 4% to 6% in India.
3. Fixed deposit Account – This account works with a certain sum of the money. The amount of money is deposited and withdrawal at once. A fixed deposit account works with the time specification and the money can be withdrawn before it. the interest rate amount remain fixed for the entire tenure, ensuring predictable growth of fund.
4. Recurring Deposit Account – It is designed for individual who want to save a fixed amount regularly over a specific period. This account pays off the high rates of interest. This account helps with regular saving. The total of money withdrawn after a time is the increment amount.
5. Multiple option deposit account- A multiple option deposit account (MODA) is a type of savings account. Multiple option deposit accounts are becoming more popular as they offer the convenience of managing your money without opening numerous accounts. In addition, they can be beneficial for individuals who want to save for specific goals like retirement or college tuition. Many banks offer MODAs. The most common type is an online bank that provides online banking and mobile apps. Other types include credit unions and community banks.
Banking services with particular reference to Bank Draft, Bank Overdraft, Cash credit
Bank draft
Bank draft is an order issued by a bank on any branch of the same bank to pay the specified amount to the person named in it.
- A requisition slip has to be filled in by the customer for the issue of bank draft.
- It is drawn by one branch of a bank on another branch of the same bank at some other place.
- There is full guarantee by the issuing bank branch about the payment of the draft to the payee. So, there is no risk of bank draft getting dishonoured.
- It must be noted that a bank draft is always payable on demand.
- It is also known as ‘Demand Draft’ or ‘ Banker’s Draft’.
Bank overdraft
It refers to a facility in which a customer is allowed to overdraw his current account up to an agreed limit.
- Banks give this facility after taking security or personal guarantee. This facility is extended by the bank to its regular customer who enjoy good financial status.
- This overdraft is a kind of temporary loan and bank charges interest on actual amount which is overdrawn by the account holder.
Cash credit
Cash Credit refers to a loan given to the borrower against his current assets like shares, stocks, bonds, etc.
- A Credit limit is sanctioned and the amount is credited in his account. The borrower may withdraw any amount within his credit limit.
- Cash Credit facility is helpful in meeting day-to-day working capital needs.
- Interest is charged on the amount actually withdrawn.
Features of a Cash Credit
- Borrowing limit.
- Minimum commitment charge.
- Interest on the running balance only.
- Validity of the credit period.
- Security.
E-Banking:-
The Growth of internet and e-commerce is dramatically changing everyday life, with the world wide web and e-commerce transforming the world into a digital global village. The latest wave in information technology is internet banking. It is a part of virtual banking and another delivery channel for customers.
In simple terms, internet banking means any user with a PC and a browser can get connected to the banks website to perform any of the virtual banking function and avail of any of the bank services.
There is no human operator to respond to the needs of the customer. The bank has a centralized data base that is web-enable. All the services that the bank has permitted on the internet are displayed on a menu. Any service can be selected and further interaction is dictated by the nature of service.
Benefits:-
- E-banking facilitates digital payments and promotes transparency in financial statements.
- E-banking provides 24 hours, 365 days a year services to the customers of the bank.
- It inculcates a sense of financial discipline by recording each and every transaction.
- Customers can make some of the permitted transaction from office or house or while travelling via mobile telephone.
Insurance:-
Life is full of uncertainties. The chances of occurrence of an event causing losses are quite uncertain. There are risks of death and disability for human life. when it happened , the individuals and/or organisation may suffer a great loss, sometime beyond their capacities to bear the same. It into minimize the impact of such uncertainties that there is a need for insurance.
Investment in factory building or other assets is not possible unless there is arrangement for covering the risks, with the help of insurance. Keeping this in mind, people facing common risks come together an make small contributions to a common fund, which help to spread the loss caused to an individual by a particular risk over a number of persons who are exposed to it.
Function of Insurance:-
- Providing certainty:- Insurance provides certainity of payment for the risk of loss. There are uncertainties of happening of time and amount of loss. Insurance removes these uncertainties and the assured receives payment of loss. The insurer changes premium for providing the certainty.
- Protection:- The second main function of insurance is to provide protection from probable chances of loss. Insurance cannot stop the happening of a risks or event but can compensate for losses arising out of it.
- Risk Sharing:- On the happening of a risk event, the loss is shared by all the persons exposed to it. The share is obtained from every insured member by way of premiums.
- Assist in capital formation:- The accumulated funds of the insurer received by way of premium payments made by the insured are invested in various income generating schemes.
Principles of insurance:-
- Utmost good faith:- A contract of insurance is a contract of good faith. Both the insurer and the insured should display good faith towards each other in regard to the contract.
- Insurance Interest:- The interest must have an insurable interest in the subject matter of insurance. Insurable interest refer to an investment that protects anything subject to financial loss . a person or entity may have an insurable interest in an event, item or action when the loss or damage of insured object can cause of financial loss.
- Indemnity:- All Insurance contracts of fire or marine insurance are contracts of indemnity. According to it, the insurer undertakes to put the insured, in the event of loss, in the same position that he occupied immediately before the happening of the event insured against. In other words the insurer undertakes to compensate the insured for the loss caused to him/her due to damage of property insured. The compensation payable and the loss suffered are to be measured in terms of money. The principle of indemnity is not applicable to life insurance.
- Proximate Cause:- According to this principle, an insurance policy is designed to provide compensation only for such losses as are caused by the risk which are stated in the policy. When the loss is the result of two or more causes, the proximate cause means the direct , the most dominant and most effective cause of which the loss is the natural consequence.
- Subrogation:- It refers to the right of the insurer to stand in the place of the insured, after settlement of a claim, as far as the right of insured in respect of recovery from an alternative source is involved. After the insured is compensation for the loss or damage to the property insured by him/her the right of ownership of such property passes on to the insurer. This is because the insured should not be allowed to make any profit, by selling the damaged property or in the case of lost property being recovered.
- Contribution:- As per this principle it is the right of an insurer who has paid claim under an insurance, to call upon other liable insurers to contribute for the loss of payment. It implies, that in case of double insurance, the insurers are to share the losses in proportion to the amount assured by each of them. In case there is a loss, when there is more than one policy on the same property, the insured will have no right to recover more than the full amount of his loss.
- Mitigation:– According to this principle, it is the duty of the insured to take reasonable steps to minimize the loss or damage to the insured property.
For example:- If goods kept in a warehouse are covered by a fire policy and the warehouse catches fire, then the insured must try to recover the goods and save them from fire to minimize the loss or damage.
Types of insurance:-
- Life Insurance:– Since life itself is uncertain, all individuals try to assure themselves of a certain sum of money in the future to take care of unforeseen event or happenings. Individuals in the course of their life are always exposed to some kind of risks. The risk may be of an event which is certain that is death.
It that case, what will happen to the other member of the family who are dependent on a particular individual income. The other risk may be living too long in which an individual may become too old to earn retirement. In this case also, the earnings will decline or end. under such circumstances, individual seek protection against these risks and life insurance companies offer protection against such risks.
Types of life insurance policies:-
The document containing the written contract between the insurer and the insured along with the terms and conditions of insurance is called the policy. After the proposal form is filled by the insured (or the proposer) and the insurer (insurance company) accepts the form and the premium, a policy is issued to the insurer. People have different requirements and therefore they would like a policy to fulfill all their needs.
The needs of people for life insurance can be family needs, children’s needs. Old age and special needs. To meet the needs of people the insurers have developed different types of products such as whole Life Assurance. Endowment type plans, combination of Whole life and Endowment type plans, children’s Assurance plans and Annuity plans. Some of these are explained below:-
- Endowment Life Assurance Policy:- The insurer (Insurance Company) undertakes to pay a specified sum when the insured attains a particular age or on his death which ever Is earlier. The sum is payable to his legal heir/s or nominee named therein in case of death of the assured. Otherwise, the sum will be paid to the assured after a fixed period I.e., till he/she attains a particular age. Thus, the endowment policy matures after a limited number of years.
- Children’s Endowment Policy:- This policy is taken by a person for his/her children to meet the expenses of their education or marriage. The agreement states that a certain sum will be paid by the insurer when the children attain a particular age. The premium is paid by the person entering into the contract. However, no premium will be paid, if he dies before the maturity of the policy.
- Whole Life Policy:- In this kind of policy, the amount payable to the insured will not be paid before the death of the assured. The sum then becomes payable only to the beneficiaries or heir of the deceased. The premium will be payable for a fixed period (20 or 30 years) or for the whole life of the assured. If the premium is payable for a fixed period, the policy will continue till the death of the assured.
- Annuity Policy:- Under this policy the assured sum or policy money is payable after the assured attains a certain age in monthly, quarterly, half yearly or annual installments. The premium is paid in installments over a certain period or single premium may be paid by the assured. This is useful to those who prefer a regular income after a certain age.
- Joint Life Policy:- This policy is taken up two or more persons. The premium is paid jointly or by either of them in instalment or lump sum. The assured sum or policy money is payable upon the death of any one person to the other survivor or survivors. Usually this policy is taken up by husband and wife jointly or by two partners in a partnership firm where the amount is payable to the survivor on the death of either of the two.
2. Health insurance;- Health insurance is a type of insurance coverage that pays for medical and surgical expenses incurred by the insured. Health insurance can reimburse such expenses to the insured or pay the care provider directly.
Types of Health Insurance;-
- Individual Mediclaim
- Family Floater policy
- Unit linked health plans
3. Fire Insurance:- Fire insurance is a contract whereby the insurer in consideration of the premium paid, undertakes to make good any loss or damage caused by fire during a specified in the policy normally, the fire insurance policy is for a period of one year after which it is to be renewed from time-to-time. The premium may be paid either in lump sum or installments. A claim for loss by fire must satisfy the two following condition:-
- There must be actual loss
- Fire must be accidental and non-intentional.
The risk covered by a fire insurance contract is the loss resulting from fire or some other cause, and which is the proximate cause of the loss. If overheating without ignition causes damage, it will not be regarded as a fire insurance and the loss will not be recoverable from the insurer.
4. Marine Insurance:- A marine insurance contract is an agreement whereby the insurer undertakes to indemnify the insured in the manner and to the extent thereby agreed against marine losses. Marine insurance provides protection against loss by marine Risk or risk of the sea. Marine risk and collision of ship with the rock, or ship attacked by the enemies, fire and captured by pirates and actions of the captains and crew of the ship. These perils cause damage, destruction or disappearance of the ship and cargo and non-payment of freight.
Types
- Ship or hull insurance:- Since the ship is exposed to many dangers at sea, the insurance policy is for indemnifying the insured for losses caused by damage to the ship.
- Cargo insurance:- The cargo while being transported by ship is subject to many risks. These may be at port i.e., risk of theft, lost goods etc. Thus, an insurance policy can be issued to cover against such risks to cargo.
- Freight Insurance:- If the cargo does not reach the destination due to damage or loss in transit, the shipping company is not paid freight charges. Freight insurance is for reimbursing the loss of freight to the shipping company the insured.
Postal services:-
The Indian Postal and Telegraph Department provides a variety of postal services throughout the country. The numerous services supplied by the postal department are essentially classified into the following categories as a result of their regional and divisional level arrangement:-
- Mail Facilities:- Mail services include parcel services, which is the transmission of articles from one location to another, registration services, which ensures the security of the transmitted articles and insurance services, which provide coverage for any dangers faced during postal transmission.
- Registered Post: This facility ensures the sender of the mail that in case the mail is not delivered to the addressee , it comes back to the seeder.
- Parcel Post: Under this facility, the parcels of specified size and weight can be sent across the country as well as outside the country on the payment of parcel charges.
- Speed Post: Under it, the post and telegraph department guarantees that all the internet mail received up to 5 p.m. at the specified post offices will be delivered within 24 hours and if it fails to do so, the extra fee changed will be refunded.
- Courier Services: Letters, documents, parcels etc. can be sent through the courier service. It being a private service the employees work with more responsibility.
Other postal services
- Greeting post:- Greeting cards can be sent through post offices to people on different occasions.
- Media post:- Business enterprise can advertise their brands through post cards, envelops, aerograms, etc.
- Direct post:- Direct advertising can be done through addressed and unaddressed direct post.
- International Money Transfer:- Postal department has collaborated with Western Union financial services, USA, for remittance of money from 185 countries to India.
- Passport facilities:- Postal department has entered into partnership with the ministry of external affairs.
- E-bill post:- The post offices collect bill payments on behalf of BSNL, Airtel and other organizations.
Telecom Services
Telecom services involve use of electronic devices for exchange of information. It provides faster, cheaper and more reliable means of communication. Telecom service are widely used by business organizations.
Types
- Cellular mobile services:- These are used to provide voice and non-voice messages, data services and PCO services by utilizing any type of network equipment within the service area.
- Fixed line services:- It provides voice and non-voice messages and data services to establish linkages for long distance traffic.
- Cable Services:- It is one-way transmission of entertainment related services to the subscribes within a licensed area of operation.
- Very Small Aperture Terminal Services:- It offers a highly flexible and reliable communication solution that is better than land-based services.
- Direct to Home Services:- It is a satellite based media services, which is received through a satellite with the help of a small dish antenna and a set top box.
COMMUNICATION SERVICES:-
Communication services are helpful to the business for establishing links with the outside world suppliers, customers, competitions etc. Business does not exit in isolation, it has to communicate with others for transmission of ideas and information . communication services need to be very efficient, accurate and fast for them to be effective. In this fast moving and competitive world it is essential to have advanced technology for quick exchange of information. The electronic media is mainly responsible for this transformation. The main service which helps business can be classified into postal and telecom.
Types of Communication services :-
- Telecommunication Services:- The key to the country’s rapid economic and social development is world-class telecommunication infrastructure
- Cellular mobile services:- These are all types of mobile telecom services including voice and non-voice message, data services and PPO services utilising any type of network equipment within their service area.
- Cable Services:- These are linkages and switched services within a licensed area of operation hoe to operate media services, which are essentially one-way entertainment related services.
- Fixed line services:- All sorts of fixed services, including voice and non-voice communication, as well as data services, are used to establish linkage for long-distance traffic. These make use of any form of network equipment, which is typically connected by fibre optic cables.
- VSAT services:- VSAT (very small aperture terminal) is a satellite based communication service. In both urban and rural location, it provides business and government organisation with a highly flexible and reliable communication solution.
- DTH services:- DTH (direct to home) services are another satellite-based media service offered by cellular provides. With the help of tiny dish antenna and a set top box, one can receive media services directly from a satellite.
2. Postal services:- The Indian Postal and Telegraph Department provides a variety of postal services throughout the country. The numerous services supplied by the postal department are essentially classified into the following categories as a result of their regional and divisional level arrangement:-
- Financial facilities:- These facilities are provided through the post office’s saving schemes like Public Provident Fund (PPF), kisan vikas patra, and National Saving Certificate.
- Mail Facilities:- Mail services include parcel services, which is the transmission of articles from one location to another, registration services, which ensures the security of the transmitted articles and insurance services, which provide coverage for any dangers faced during postal transmission.
- Additional Services:-Greeting cards, media mail, international money transfers, speed mail, passport services and e-billing.
TRANSPORTATION SERVICES:-
Transportation includes freight services as well as supporting and auxiliary services, provided by all means of transportation, including rail, road, air and sea for the movement of commodities and international passenger transportation. Transportation removes the barrier of location, that means the production and consumption of goods may not take place at the same place, hence to avoid the distance between the production and consumption location, transportation comes to rescue. Both government and industry must be proactive and consider the efficient operation of this service as a need for providing a lifeline to a business.
WAREHOUSING:-
Storage has always been an important aspect of economic development. The warehouse was initially viewed as a static unit for keeping and storing goods in a scientific and systematic manner so as to maintain their original quality, value and usefulness. The typical warehouse received merchandise by rail, truck or bullock cart. The items were moved manually to a storage within the warehousing and hand piled in stacks on floor. They are used by manufacturers, importers, exporters, wholesalers, transport business, customs etc. In India.
Types of Warehouses:-
- Private warehouses:- Private warehouses are operated, owned or leased by a company handling their own goods, such as retail chain stores or multi-brand multi-product companies. As a general rule an efficient warehouse is planned around a material handling system in order to encourage maximum efficiency of product movement. The benefit of private warehousing includes control, flexibility, and other benefits like improved dealer relations.
- Public Warehouses:- Public warehouses can be used for storage of goods by traders, manufacturers or any member of the public after the payment of a storage fee or charges. The government regulates the operation of these warehouses by issuing licenses for them to private parties. The owner of the warehouses stands as an agent of the owner of the goods and is expected to take appropriate care of the goods.
- Bonded Warehouses:- Bonded warehouses are licensed by the government to accept imported good prior to payment of tax and customs duty. These are goods which are imported from other countries. Importers are not permitted to remove goods from the docks or the airport till customs duty is paid. At times, importers are not in a position to pay the duty in full or does not require all the goods immediately. The goods are kept in bonded warehouses by the customs authorities till the customs duty is paid. These goods are said to be in bond.
- Government Warehouses:- These warehouses are fully owned and managed by the government. The government manages them through organisation set up in the public sector. For example, Food Corporation of India, Stet Trading Corporation, and Central Warehouses Corporation.
- Cooperative Warehouses:- Some marketing cooperative societies or agricultural cooperative societies have set up their own warehouses for members of their cooperative society.
Function of Warehousing:-
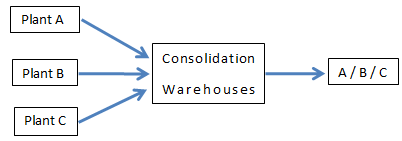
- Consolidation:- In this function the warehouse receives and consolidates, materials/goods from different production plants and dispatches the same to a particular customer on a single transportation shipment.
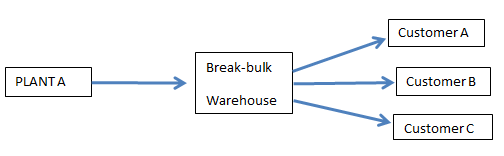
2. Break the bulk:- The warehouse performs the function of dividing the bulk quantity of goods received from the production plants into smaller quantities. These smaller quantities are then transported according to the requirements of clients to their places of business.
3. Stock piling:- The next function of warehousing is the seasonal storage of goods to select businesses. Goods or raw materials, which are not required immediately for sale or manufacturing, are stored in warehouses. They are made available to business depending on customers demand. Agricultural products which are harvested at specific times with subsequent consumption throughout the year also need to be stored and released in lots.
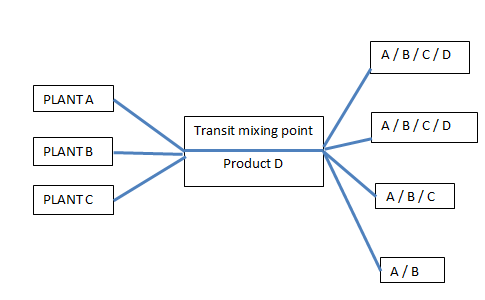
4. Value added services:- certain value added services are also provided by the warehouses, such as in transit mixing, packaging and labelling. Goods sometimes need to be opened and repackaged and labelled again at the time of inspection by prospective buyers. Grading according to quantity and dividing goods in smaller lots is another function.
5. Price stablization:- By adjusting the supply of goods with the demand situation, warehousing performs the function of stabilizing prices. Thus, prices are controlled when supply is increasing and demand is slack and vice versa.
6. Financing:- Warehouse owners advance money to the owners on security of goods and further supply goods on credit terms to customers.
question answer explanation
Short Answer Questions
1.Define services and goods
Answer:
Services:- Services are referred to as any intangible activity that involves interaction between the service provider and consumer. Purchasing the service does no result in ownership of any physical item. For example teaching service, communication service, legal services etc.
Goods:- Goods refer to objects that are tangible and have a physical appearance. The ownership of a good is transferred as soon as it is purchase for example mobile phone, books etc.
2.what is E-banking. What are the advantages of E-banking?
Answer:
E-banking:- The Growth of internet and e-commerce is dramatically changing everyday life, with the world wide web and e-commerce transforming the world into a digital global village. The latest wave in information technology is internet banking. It is a part of virtual banking and another delivery channel for customers.
There is no human operator to respond to the needs of the customer. The bank has a centralized data base that is web-enable. All the services that the bank has permitted on the internet are displayed on a menu. Any service can be selected and further interaction is dictated by the nature of service.
Benefits:-
- E-banking facilitates digital payments and promotes transparency in financial statements.
- E-banking provides 24 hours, 365 days a year services to the customers of the bank.
- It inculcates a sense of financial discipline by recording each and every transaction.
- Customers can make some of the permitted transaction from office or house or while travelling via mobile telephone.
3.Write a note on various telecom services available for enhancing business.
Answer:
- Cellular mobile services:-These are all types of mobile telecom services including voice and non-voice message, data services and PPO services utilising any type of network equipment within their service area.
- Cable Services:- These are linkages and switched services within a licensed area of operation hoe to operate media services, which are essentially one-way entertainment related services.
- Fixed line services:-All sorts of fixed services, including voice and non-voice communication, as well as data services, are used to establish linkage for long-distance traffic. These make use of any form of network equipment, which is typically connected by fiber optic cables.
- VSAT services:- VSAT (very small aperture terminal) is a satellite based communication service. In both urban and rural location, it provides business and government organisation with a highly flexible and reliable communication solution.
- DTH services:- DTH (direct to home) services are another satellite-based media service offered by cellular provides. With the help of tiny dish antenna and a set top box, one can receive media services directly from a satellite.
- 4 Explain briefly the principles of insurance with suitable examples.
Answer:
- Utmost good faith:- A contract of insurance is a contract of good faith. Both the insurer and the insured should display good faith towards each other in regard to the contract.
- Insurance Interest:- The interest must have an insurable interest in the subject matter of insurance. Insurable interest refer to an investment that protects anything subject to financial loss . a person or entity may have an insurable interest in an event, item or action when the loss or damage of insured object can cause of financial loss.
- Indemnity:- All Insurance contracts of fire or marine insurance are contracts of indemnity. According to it, the insurer undertakes to put the insured, in the event of loss, in the same position that he occupied immediately before the happening of the event insured against. In other words the insurer undertakes to compensate the insured for the loss caused to him/her due to damage of property insured. The compensation payable and the loss suffered are to be measured in terms of money. The principle of indemnity is not applicable to life insurance.
- Proximate Cause:- According to this principle, an insurance policy is designed to provide compensation only for such losses as are caused by the risk which are stated in the policy. When the loss is the result of two or more causes, the proximate cause means the direct , the most dominant and most effective cause of which the loss is the natural consequence.
- Subrogation:- It refers to the right of the insurer to stand in the place of the insured, after settlement of a claim, as far as the right of insured in respect of recovery from an alternative source is involved. After the insured is compensation for the loss or damage to the property insured by him/her the right of ownership of such property passes on to the insurer. This is because the insured should not be allowed to make any profit, by selling the damaged property or in the case of lost property being recovered.
5.Explain warehouse and its functions.
Answer: WAREHOUSING:- Storage has always been an important aspect of economic development. The warehouse was initially viewed as a static unit for keeping and storing goods in a scientific and systematic manner so as to maintain their original quality, value and usefulness. The typical warehouse received merchandise by rail, truck or bullock cart. The items were moved manually to a storage within the warehousing and hand piled in stacks on floor. They are used by manufacturers, importers, exporters, wholesalers, transport business, customs etc. In India.
- Consolidation:-In this function the warehouse receives and consolidates, materials/goods from different production plants and dispatches the same to a particular customer on a single transportation shipment.
- Break the bulk:- The warehouse performs the function of dividing the bulk quantity of goods received from the production plants into smaller quantities. These smaller quantities are then transported according to the requirements of clients to their places of business.
- Stock piling:-The next function of warehousing is the seasonal storage of goods to select businesses. Goods or raw materials, which are not required immediately for sale or manufacturing, are stored in warehouses. They are made available to business depending on customers demand. Agricultural products which are harvested at specific times with subsequent consumption throughout the year also need to be stored and released in lots.
- Value added services:-certain value added services are also provided by the warehouses, such as in transit mixing, packaging and labelling. Goods sometimes need to be opened and repackaged and labelled again at the time of inspection by prospective buyers. Grading according to quantity and dividing goods in smaller lots is another function
Long Answer Types:
1.What are services? Explain their distinct characteristics.
Answer: Services:- Services are referred to as any intangible activity that involves interaction between the service provider and consumer. Purchasing the service does no result in ownership of any physical item. For example teaching service, communication service, legal services etc.
- Intangibility:- Services are intangible they cannot be touched. They are experiential in nature. One cannot taste a doctor’s treatment, or touch entertainment. One can only experience it.
- Inconsistency:- The second important characteristic of service is inconsistency. Since there is no standard tangible product, service have to be performed exclusively each time. Different customers have different demand and expectations. Service providers need to have an opportunity to alter their offer to closely meet the requirement of the customer. This is happening, for example in the case of mobile services.
- Inseparability:- Another important characteristic of services is the simultaneous activity of production and consumption being performed. This makes the production and consumption of service seem to be inseparable. While we can manufacture a car today and sell if after, say a month this is often not possible with service that have to be consumed as and when they are produced.
- Inventory loss:- Services have little or no tangible components and therefore, Cannot be stored for a future use. This means that the demand and supply need to be managed as the service has to be performed as and when the customer asks for it.
- Involvement:- One of the most important characteristics of services is the participation of the Customer in the service delivery process. A customer has the opportunity to get the services modified according to specific requirements.
- 2. Explain the function of commercial banks with an examples of each.
Answer:
Function of Commercial Bank:
The functions of commercial banks are classified into two main divisions.
(a) Primary functions
- Accepts deposit : The bank takes deposits in the form of saving, current, and fixed deposits. The surplus balances collected from the firm and individuals are lent to the temporary requirements of the commercial transactions.
- Provides loan and advances : Another critical function of this bank is to offer loans and advances to the entrepreneurs and business people, and collect interest. For every bank, it is the primary source of making profits. In this process, a bank retains a small number of deposits as a reserve and offers (lends) the remaining amount to the borrowers in demand loans, overdraft, cash credit, short-run loans, and more such banks.
- Credit cash: When a customer is provided with credit or loan, they are not provided with liquid cash. First, a bank account is opened for the customer and then the money is transferred to the account. This process allows the bank to create money.
(b) Secondary functions
- Discounting bills of exchange: It is a written agreement acknowledging the amount of money to be paid against the goods purchased at a given point of time in the future. The amount can also be cleared before the quoted time through a discounting method of a commercial bank.
- Overdraft facility: It is an advance given to a customer by keeping the current account to overdraw up to the given limit.
- Purchasing and selling of the securities: The bank offers you with the facility of selling and buying the securities.
- Locker facilities: A bank provides locker facilities to the customers to keep their valuables or documents safely. The banks charge a minimum of an annual fee for this service.
- Write a detailed note on various facilities offered by Indian Postal Department.
Answer:
The Indian Postal and Telegraph Department provides a variety of postal services throughout the country. The numerous services supplied by the postal department are essentially classified into the following categories as a result of their regional and divisional level arrangement:-
- Mail Facilities:- Mail services include parcel services, which is the transmission of articles from one location to another, registration services, which ensures the security of the transmitted articles and insurance services, which provide coverage for any dangers faced during postal transmission.
- Registered Post: This facility ensures the sender of the mail that in case the mail is not delivered to the addressee , it comes back to the seeder.
- Parcel Post: Under this facility, the parcels of specified size and weight can be sent across the country as well as outside the country on the payment of parcel charges.
- Speed Post: Under it, the post and telegraph department guarantees that all the internet mail received up to 5 p.m. at the specified post offices will be delivered within 24 hours and if it fails to do so, the extra fee changed will be refunded.
- Courier Services: Letters, documents, parcels etc. can be sent through the courier service. It being a private service the employees work with more responsibility.
- Describe various types of insurance and examine the nature of risks protected by each type of insurance.
Answer:
- Life Insurance:Sinc li-fe itself is uncertain, all individuals try to assure themselves of a certain sum of money in the future to take care of unforeseen event or happenings. Individuals in the course of their life are always exposed to some kind of risks. The risk may be of an event which is certain that is death.
It that case, what will happen to the other member of the family who are dependent on a particular individual income. The other risk may be living too long in which an individual may become too old to earn retirement. In this case also, the earnings will decline or end. under such circumstances, individual seek protection against these risks and life insurance companies offer protection against such risks.
Types of life insurance policies:-
- Endowment Life Assurance Policy:- The insurer (Insurance Company) undertakes to pay a specified sum when the insured attains a particular age or on his death which ever Is earlier. The sum is payable to his legal heir/s or nominee named therein in case of death of the assured. Otherwise, the sum will be paid to the assured after a fixed period I.e., till he/she attains a particular age. Thus, the endowment policy matures after a limited number of years.
- Children’s Endowment Policy:- This policy is taken by a person for his/her children to meet the expenses of their education or marriage. The agreement states that a certain sum will be paid by the insurer when the children attain a particular age. The premium is paid by the person entering into the contract. However, no premium will be paid, if he dies before the maturity of the policy.
- Whole Life Policy:-In this kind of policy, the amount payable to the insured will not be paid before the death of the assured. The sum then becomes payable only to the beneficiaries or heir of the deceased. The premium will be payable for a fixed period (20 or 30 years) or for the whole life of the assured. If the premium is payable for a fixed period, the policy will continue till the death of the assured.
- Annuity Policy:- Under this policy the assured sum or policy money is payable after the assured attains a certain age in monthly, quarterly, half yearly or annual installments. The premium is paid in installments over a certain period or single premium may be paid by the assured. This is useful to those who prefer a regular income after a certain age.
- Joint Life Policy:- This policy is taken up two or more persons. The premium is paid jointly or by either of them in instalment or lump sum. The assured sum or policy money is payable upon the death of any one person to the other survivor or survivors. Usually this policy is taken up by husband and wife jointly or by two partners in a partnership firm where the amount is payable to the survivor on the death of either of the two.
- Fire Insurance:- Fire insurance is a contract whereby the insurer in consideration of the premium paid, undertakes to make good any loss or damage caused by fire during a specified in the policy normally, the fire insurance policy is for a period of one year after which it is to be renewed from time-to-time. The premium may be paid either in lump sum or installments. A claim for loss by fire must satisfy the two following condition:-
- There must be actual loss
- Fire must be accidental and non-intentional.
The risk covered by a fire insurance contract is the loss resulting from fire or some other cause, and which is the proximate cause of the loss. If overheating without ignition causes damage, it will not be regarded as a fire insurance and the loss will not be recoverable from the insurer.
- Marine Insurance:- A marine insurance contract is an agreement whereby the insurer undertakes to indemnify the insured in the manner and to the extent thereby agreed against marine losses. Marine insurance provides protection against loss by marine Risk or risk of the sea. Marine risk and collision of ship with the rock, or ship attacked by the enemies, fire and captured by pirates and actions of the captains and crew of the ship. These perils cause damage, destruction or disappearance of the ship and cargo and non-payment of freight.
- Ship or hull insurance:- Since the ship is exposed to many dangers at sea, the insurance policy is for indemnifying the insured for losses caused by damage to the ship.
- Cargo insurance:- The cargo while being transported by ship is subject to many risks. These may be at port i.e., risk of theft, lost goods etc. Thus, an insurance policy can be issued to cover against such risks to cargo.
- Freight Insurance:- If the cargo does not reach the destination due to damage or loss in transit, the shipping company is not paid freight charges. Freight insurance is for reimbursing the loss of freight to the shipping company the insured.
- Explain in detail the warehousing services.
Answer:
WAREHOUSING:-
Storage has always been an important aspect of economic development. The warehouse was initially viewed as a static unit for keeping and storing goods in a scientific and systematic manner so as to maintain their original quality, value and usefulness. The typical warehouse received merchandise by rail, truck or bullock cart. The items were moved manually to a storage within the warehousing and hand piled in stacks on floor. They are used by manufacturers, importers, exporters, wholesalers, transport business, customs etc. In India.
Types of Warehouses:-
- Private warehouses:-Private warehouses are operated, owned or leased by a company handling their own goods, such as retail chain stores or multi-brand multi-product companies. As a general rule an efficient warehouse is planned around a material handling system in order to encourage maximum efficiency of product movement. The benefit of private warehousing includes control, flexibility, and other benefits like improved dealer relations.
- Public Warehouses:- Public warehouses can be used for storage of goods by traders, manufacturers or any member of the public after the payment of a storage fee or charges. The government regulates the operation of these warehouses by issuing licenses for them to private parties. The owner of the warehouses stands as an agent of the owner of the goods and is expected to take appropriate care of the goods.
- Bonded Warehouses:- Bonded warehouses are licensed by the government to accept imported good prior to payment of tax and customs duty. These are goods which are imported from other countries. Importers are not permitted to remove goods from the docks or the airport till customs duty is paid. At times, importers are not in a position to pay the duty in full or does not require all the goods immediately. The goods are kept in bonded warehouses by the customs authorities till the customs duty is paid. These goods are said to be in bond.
- Government Warehouses:- These warehouses are fully owned and managed by the government. The government manages them through organisation set up in the public sector. For example, Food Corporation of India, Stet Trading Corporation, and Central Warehouses Corporation.
- Cooperative Warehouses:-Some marketing cooperative societies or agricultural cooperative societies have set up their own warehouses for members of their cooperative society.
Function of Warehousing:-
- Consolidation:-In this function the warehouse receives and consolidates, materials/goods from different production plants and dispatches the same to a particular customer on a single transportation shipment.
- Break the bulk:- The warehouse performs the function of dividing the bulk quantity of goods received from the production plants into smaller quantities. These smaller quantities are then transported according to the requirements of clients to their places of business.
- Stock piling:-The next function of warehousing is the seasonal storage of goods to select businesses. Goods or raw materials, which are not required immediately for sale or manufacturing, are stored in warehouses. They are made available to business depending on customers demand. Agricultural products which are harvested at specific times with subsequent consumption throughout the year also need to be stored and released in lots.
- Value added services:-certain value added services are also provided by the warehouses, such as in transit mixing, packaging and labelling. Goods sometimes need to be opened and repackaged and labelled again at the time of inspection by prospective buyers. Grading according to quantity and dividing goods in smaller lots is another function.
- Price stablisation:- By adjusting the supply of goods with the demand situation, warehousing performs the function of stabilising prices. Thus, prices are controlled when supply is increasing and demand is slack and vice versa.
- Financing:-Warehouse owners advance money to the owners on security of goods and further supply goods on credit terms to customers.