Marketing
It is a process whereby people exchange goods and services for money or for something of value to them. Taking the social perspective, Phillip Kolter has defined marketing as, “a social process by which individual groups obtain what they need and want through creating offerings and freely exchanging products and services of value with others”.
Features of marketing:
- Needs and Wants: The process of marketing helps individuals and groups in obtaining what they need and want. Thus, the primary reason or motivation for people to engage in the process of marketing is to satisfy some of their needs or wants. In other words, the focus of the marketing process is on satisfaction of the needs and wants of individuals and organizations.
- Creating a Market Offering: On the part of the marketers, the effort involves creation of ‘market offering. Market offering refers to a complete offer for a product or service, having given features like size, quality, taste, etc.; at a certain price; available at a given outlet or location and so on.
- Customer Value: The process of marketing facilitates exchange of products and services between the buyers and the sellers. The buyers, however, make buying decisions on their perceptions of the value of the product or service in satisfying their need, in relation to its cost. A product will be purchased only if it is perceived to be giving greatest benefit or value for the money.
- Exchange Mechanism: The process of marketing works through the exchange mechanism. The individuals (buyers and sellers) obtain what they need and want through the process of exchange. In other words, the process of marketing involves exchange of products and services for money or something considered valuable by the people.
Marketing Management
Marketing management means management of the marketing function. In other words, marketing management refers to planning, organizing, directing and control of the activities which facilitate exchange of goods and services between producers and consumers of users of products and services. Thus the focus of marketing management is on achieving desired exchange outcomes with the target markets, Taking a management perspective, the term marketing has been defined as “the process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion and distribution of ideas, goods and services to create exchanges that satisfy individual and organizational goals” by American Management Association, similarly Philip kotler has defined Marketing management as the art and science of choosing target markets and getting, keeping and growing customers through creating, delivering and communicating superior customer values of management.
Marketing Management
Philosophies
Concept: In order to achieve desired exchange outcomes with target markets, it is important to decide what philosophy or thinking should guide the marketing efforts of an organization. An understanding of the philosophy or the concept to be adopted is important as it determines the emphasis or the weightage to be put on different factors, in achieving the organizational objectives. For example, whether the marketing efforts of an organization will focus on the product- say designing its features etc or on selling techniques or on customer’s needs or the social concerns.
The concept or philosophy of marketing has evolved over a period of time, and is discussed as follows.
- The Production concept: During the earlier days of industrial revolution, the demand for industrial goods started picking up but the number of producers were limited. As a result, the demand exceeded the supply. Selling was no problem. Anybody who could produce the goods was able to sell. The focus of business activities was, therefore, on production of goods. It was believed that profits at large scale, thereby reducing the average cost of production. availability and affordability of the product was considered to be the key to the success of the firm
- The Product Concept: As a result of emphasis on production capacity during the earlier days, the position of supply increased over period of time. Mere availability and low price of the product could not ensure increased sale and as such the survival and growth of the firm. Thus, with the increase in the supply of the products, customers started looking for products which were superior in quality, performance and features.
- The Selling Concept:. The product quality and availability did not ensure the survival and growth of firms because of the large number of sellers selling quality products. This led to greater importance to attracting and persuading customers to buy the product. The business philosophy changed. they must be motivated to buy .the firm must undertake aggressive selling and promotional effort to make customer buy their product such as advertisement, personal selling and sales promotions.
- The Marketing Concept: Marketing orientation implies that focus on satisfaction of customer’s needs is the key to the success of any organization in the market. It assumes that in the long run an organization can achieve its objective of maximization of profit by identifying the needs of its present and prospective buyers and satisfying them in an effective way. All the decisions in a firm are taken from the point of view of the customers.
- The Societal Marketing Concept: The marketing concept, as described in the preceeding section cannot be considered as adequate if we look at the challenges posed by social problems like environmental pollution, deforestation, shortage of resources, population explosion and inflation. It is so because any activity which satisfies human needs but is detrimental to the interests of the society at large cannot be justified. The business orientation should, therefore, not be short- sighted to serve only consumers’ needs.
Functions of Marketing
Marketing is concerned with exchange of goods and services from producers to consumers or users in such a way that maximizes the satisfaction of customers’ needs. From the view point of management function, number of activities are involved, which have been described as below:
1. Gathering and Analysing Market Information: One of the important functions of a marketer is to gather and analyse market information. This is necessary to identify the needs of the customers and take various decision for the successful marketing of the products and services. This is important for making an analysis of the available opportunities and threats as well as strengths and weaknesses of the organization and help in deciding what opportunities can best be pursued by it.
2. Marketing Planning: Another important activity or area of work of a marketer is to develop appropriate marketing plans so that the marketing objectives of the organization can be achieved. For example a marketer of colour TV, having 10 per cent of the current market share in the country, aims at enhancing his market share to 20 per cent, in the next three years.
3. Product Designing and Development: Another important marketing activity or decision area relates to product designing and development. The design of the product contributes to making the product attractive to the target customers. A good design can improve performance of a product and also give it a competitive advantage in the market. For example, when we plan to buy any product say a motorbike, we not only see its features like cost, mileage, but also the design aspects like its shape, style, etc.
4. Standardisation and Grading: Standardisation refers to producing good of predetermined specifications, which helps in achieving uniformity and consistency in the output. Standardisation ensures the buyers that goods conform to the predetermined standards of quality, price and packaging and reduces the need for inspection, testing and evaluation of the products. grading is the process of classification of product into different group , on the basis of some important characteristics like quality,size.
5. Packaging and Labelling: Packaging refers to designing and developing the package for the products. Labelling refers to designing and developing the label to be put on the package. The label may vary from a simple tag to complex graphics.
Packaging and labeling have become so important in modern day marketing that these are considered as the pillar of marketing
6. Branding: A very important decision area for marketing of most consumer products is whether to sell the product in its generic name (name of the category of the product, say Fan, Pen, etc.) or to sell them in a brand name (such as Pollar Fan or Rottamac Pen). Brand name helps in creating product differentiation, i.e., providing basis for distinguishing the product of a firm with that of the competitor, which in turn, helps in building customer’s loyality and in promoting its sale.
7. Customer Support Services: A veery important function of the marketing management relates to developing customer support services such as after sales services, handling customer complaints and adjustments, procuring credit services, maintenance services, technical services and consumer information. All these services aim at providing maximum satisfaction to the customers, which is the key to marketing success in modern days. Customer support services are very effective in bringing repeat sales from the customers and developing brand loyality for a product.
8. Pricing of Product: Price of product refers to the amount of money customers have to pay to obtain a product. Price is an important factor affecting the success or failure of a product in the market. The demand for a product or service is related to its price. Generally lower the price, higher would be the demand for the product and vice-versa.
Marketing Mix
The marketing mix consists of various elements, which have been classified into four categories, popularly known as four Ps of marketing. These are: (i) Product, (ii) Price, (iii) Place, and (iv) Promotion. These are briefly discussed as follows:
- Product: Product means goods or services or ‘anything of value’, which is offered to the market for sale. For example, Hindustan lever offers number of consumer products like toiletries (Close-Up toothpaste, Lifebuoy soap, etc.), detergent powder (Surf, Wheel), food products (Refined Vegetable Oil); Tata offers Tata Steel, Trucks, Salt and a large number of other products; LG electronics offers televisions, refrigerators, colour monitors for computers, etc; Amul offers a number of food products (Amul milk, ghee, butter, cheese, chocolates, etc.).
- Price: Price is the amount of money customers have to pay to obtain the product. In case of most of the products, level of price affects the level of their demand. The marketers have not only to decide about the objectives of price setting but to analyse the factors determining the price and fix a price for the firm’s products. Decisions have also to be taken in respect of discounts to customers, traders and credit terms, etc., so that customers perceive the price to be in line with the value of the produt.
- Place: Place or Physical Distribution include activities that make firm’s products available to the target customers. Important decision areas in this respect include selection of dealers or intermediaries to reach the customers, providing support to the intermediaries (by way of discounts, promotional campaigns, etc.). The intermediaries in turn keep inventory of the firm’s products, demonstrate them to potential buyers, negotiate price with buyers, close sales and also service the products after the sale.
- Promotion: Promotion of products and services include activities that communicate availability, features, merits, etc., of the products to the target customers and persuade them to buy it. Most marketing organisations, undertake various promotional activities and spend substantial amount of money on the promotion of their goods through using number of tools such as advertising, personal selling and sales promotion techniques (like price discounts, free samples, etc.).
Products
A product is a bundle of utilities, which is purchased because of its capability to provide satisfaction of certain need.
A buyer buys a product or service for what it does for her or the benefit it provides to her. There can be three types of benefits a customer may seek to satisfy from the purchase of a product, viz.,
- Functional benefits,
- Psychological benefits, and
- Social benefits.
For example-
The purchase of a motorcycle provides functional utility of transportation, but at the same time satisfies the need for prestige and esteem and provides social benefit by the way of acceptance from a group, by riding a motorbike. Thus, all these aspects should be considered while planning for a product.
Classification of Products
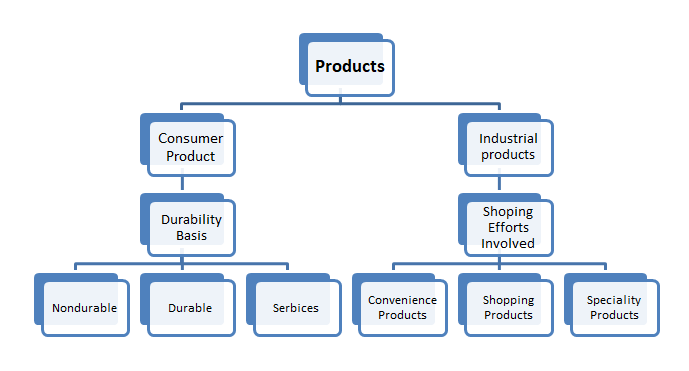
Products may broadly be classified into two categories-
- Consumers’ products, and
- Industrial products.
The consumer products may further be classified into different groups, as detailed below:
(I) Consumer Products
Products, which are purchased by the ultimate consumers or users for satisfying their personal needs and desires are referred to as consumer products. For example, soap, edible oil, eatables, textiles, toothpaste, fans, etc. which we use for our personal and non-business use are consumer goods. We can classify the consumer product into the following three categories as here under:
Classification of Products
- Convenience Products: Those consumer products, which are purchased frequently, immediately and with least time and efforts are referred to as convenience goods, Examples of such products are cigarettes, ice creams, medicines, newspaper, stationery items toothpaste etc. These products have low unit-value and are bought in small qualities.
- Shopping Products: Shopping products are those consumer goods where buyers devote considerable time, to compare the quality, price, style, suitability, etc., at several stores, before making final purchase. Some of the examples of shopping products are clothes, shoes, jewellery, furniture, radio, television, etc.
- Speciality Products: Speciality products are those consumer goods which have certain special features because of which people make special efforts in their purchase. These products are such, which have reached a brand loyalty of the highest order, with a significant number of buyers. The buyers are willing to spend a lot of time and efforts on the purchase of such products.
Durability of Products
On the basis of their durability, the consumer products have been classified into three categories- Durable, Non-durable and Services.
- Non-durable Products: The consumer products which are normally consumed in one or few ues are called non-durable products. For example, bathing soap and stationary products etc. From the marketing point of view, these products generally command a small margin, should be made available in many locations and need to be heavily advertised.
- Durable Products: Those tangible consumer products which normally survive many years, for example, refrigerator, radio, bicycle, sewing machine and kitchen gadgets are referred to as durable products. These goods are generally used for a longer period, commond a higher personal- selling efforts, guarantees and after sales services, on the part of the seller.
- Services: By services we mean those intangible activities, benefits which are offered for sale, e.g., dry cleaning, watch repairs, hair cutting, postal services, services offered by a doctor, an architect and a lawyer.
(II) Industrial Products
Industrial products are those products, which are used as inputs in producing other products. The examples of such products are raw materials, engines, lubricants, machines, tools, etc. In other words, industrial products are meant for non-personal and business use for producing other products.
The market for industrial products consists of manufacturers, transport agencies, banks and insurance companies, mining companies and public utilities.
Classification
The industrial goods are classified into the following major categories:
I. Materials and Parts: These include goods that enter the manufacture’s products completely. Such goods are of two types:
- Raw material: including farm products like cotton, sugar cane, oil seed and natural products such as minerals (say crude petroleum, iron ore), fish and lumber; and
- Manufactured material and parts
These are again of two types- component materials like glass, iron, plastic and component parts such as tyre, electric bulb, steering, and battery.
II. Capital Items: These are such goods that are used in the production of finished goods. These include: (a) installations like elevators, mainframe Computers, and
b. Equipments like Hand Tools, Personal Computer, Fax Machines, etc.
III. Supplies and Business Services: These are short lasting goods and services that facilitate developing or managing the finished product. These include:
- Maintenance and repair items like Paint, Nails, etc., and
- Operating supplies like Lubricant, Computer Stationary, Writing Paper, etc.
Branding
One of the most important decisions that a marketer has to take in the area of ‘product’ is in respect of branding. He has to decide whether the firm’s products will be marketed under a brand name or a generic name. Generic name refers to the name of the whole class of the product. For example, a book, a wristwatch, tyre, camera, toilet soap, etc. We know that a camera is a lens surrounded by plastic or steel from all sides and having certain other features such as a flash gun and so on.
The various terms relating to branding are as follows:
- Brand: A brand is a name, term, sing, symbol, design or some combination of them, used to identify the products- goods or services of one seller or group of sellers and to differentiate them from those of the competitors. For example, some of the common brands are Bara, Lifebuoy, Dunlop, and Parker. Brand is a comprehensive term, which has two components- brand name and brand mark.
- Brand Name: That part of a brand, which can be spoken, is called a brand name. In other words, brand name is the verbal component of a brand.
- Brand Mark: That part of a brand which can be recognized but which is not utterable is called brand mark. It appears in the form of a symbol, design, distinct colour scheme or lettering.
- Trade Mark: A brand or part of a brand that is given legal protection is called trademark. The protection is given against its use by other firms. Thus the firm, which got its brand registered, gets the exclusive right for its use. In that case, no other firm can use such name or mark in the country.
Packaging
One of the most important developments affecting the business world in recent years has been in the area of packaging. Many products, which we thought could never lend themselves to packing because of their nature, have been successfully packed e.g., Pulses, Ghee, Milk, Salt, Cold Drinks, etc. Packaging refers to the act of designings and producing the container or wrapper of a product.
Levels of Packaging
There can be three different levels of packaging. These are as below:
- Primary Package: It refers to the product’s immediate container. In some cases, the primary package is kept till the consumer is ready to use the product (e.g., plastic packet for socks); whereas in other cases, it is kept throughout the entire life of the product (e.g., a toothpaste tube, a match box, etc.).
- Secondary Packaging: It refers to additional layers of protection that are kept till the product is ready for use, e.g., a tube of shaving cream usually comes in a card board box. When consumers start using the shaving cream, they will dispose off the box but retain the primary tube.
- Transportation Packaging: It refers to further packaging components necessary for storage, identification or transportation. For example, a toothpaste manufacturer may send the goods to retailers in corrugated boxes containing 10, 20, or 100 units.
Importance of Packaging
Packaging has acquired great significance in the marketing of goods and services, because of following reasons:
- Rising Standards of Health and Sanitation: Because of the increasing standards of living in the country, more and more people have started purchasing packed goods as the chances of adulteration in such goods are minimized.
- Self Service Outlets: The self-service retail outlets are becoming very popular, particularly in major cities and towns. Because of this, some of the traditional role assigned to personal selling in respect of promotion has gone to packaging.
- Innovational Opportunity: Some of the recent developments in the area of packaging have completely changed the marketing scene in the country. For example, mild can now be stored for 4-5 days without refrigeration in the recently developed packing materials. Similarly, in the area of pharmaceuticals, soft drinks, etc., lots of new innovations have come in respect of packaging. As a result, the scope for the marketing of such products has increased.
- Product Differentiation: Packaging is one of the very important means of creating product differentiation. The colour, size, material, etc., of package makes real difference in the perception of customers about the quality of the product. For example, by looking at the package of a product say Paint or Hair Oil, one can make some guess about quality of the product contained in it.
Functions of Packaging
As stated above, packaging performs a number of functions in the marketing of goods. Some of the important functions are as follows:
- Product Identification: Packaging greatly helps in identification of the products. For example, Colgate in red colour, or Ponds cream jar can be easily identified by its package.
- Product Protection: Packaging protects the contents of a product from spoilage, breakage, leakage, pilferage, damage, climatic effect, etc. This kind of protection is required during storing, distribution and transportation of the product.
- Facilitating Use of the Product: The size and shape of the package should be such that it should be convenient to open, handle and use for the consumers. Cosmetics, medicines and tubes of toothpastes are good example of this.
- Product Promotion: Packaging is also used for promotion purposes. A startling colour scheme, photograph or typeface may be used to attract attention of the people at the point of purchase. Sometimes it may work even better than advertising. In self-service stores, this role of packaging becomes all the more important.
Labelling
A simple looking but important task in the marketing of goods relates to designing the label to be put on the package. The label may vary from a simple tag attached to the product (such as in case of local unbranded products like sugar, wheat, pulses, etc.) indicating some information about the quality or price, to complex graphics that are part of the package, like the ones on branded products. Lables are useful in providing detailed information about the product, its contents, method of use, etc. The various functions performed by a lable are as follows:
- Describe the Product and specify its contents: Let us look at some of the labels of the products used by us in our day to day life. The label on the package of a local tea company describes the company as ‘Mohini Tea Company, and ISO 9001:200C Certified Company’; a popular brand of Prickly Heat Powder, describes how the product provides relief from prickly heat and controls bacterial growth and infection, giving caution forbidding its application on cuts and wounds. Thus, one of the most important functions of lables is to describe the product, its usage, caution in use, etc. and specify its contents.
- Identification of the Product or brand: The other important function performed by lables is to help in identifying the product or brand. For example, the brand name of any product, say Biscuits or Potato Chips imprinted on its package helps us to identify, from number of packages, which one is our favorite brand. Other common identification information provided by the labels include name and address of the manufacturer, net weignt when packed, manufacturing date, maximum retail price and Batch number.
- Grading of Products: Another important function performed by labels is to help grading the products into different categories. Sometimes marketers assign different grades to indicate different features or quality of the product. For example, a popular brand of Hair Conditioners comes in different categories for different hair, say for ‘normal hair’ and for other categories. Different type of tea is sold by some brands under Yellow, red and Green Label categories.
- Helps in Promotion of Products: An important function of label is to aid in promotion of the products. A carefully designed label can attract attention and give reason to purchase. We see many product labels providing promotional messages for example, the pack of a popular Amla Hair Oil states, ‘Baalon mein Dum, Life mein Fun’. The label on the package of a brand of Detergent Powder says, ‘keep cloth look good and your machine in top condition’.
- Providing Information Required by Law: Another important function of labeling is to provide information required by law. For example, packaged food articles must have list of ingredients declaration regarding vegetarian or non-vegetarian food additives and date of manufacturing of packing on the label. Such information is required on processed foods, drugs and tobacco products. In case of hazardous or poisonous material, appropriate safety-warning need to be put on the label.
Pricing
When a product is bought, some money is paid for it. This money represent the sum of values that consumers exchange for the benefit of having or using the product and is referred to as the price of the product. Similarly, money paid for the services such as fare for the transport service, premium for an insurance policy, and fee to a doctor for his medical advise represent the price of these services. Price may therefore be defined at the amount of money paid by a buyer (or received by a seller) in consideration of the purchase of a product or a services.
Factors affecting Price Determination
There are number of factors which affect the fixation of the price of a product. Some of the important factors in this regard are discussed as below:
- Product cost: One of the most important factor affecting price of a product or service is its cost. This includes the cost of producing, distributing and selling the product. The cost sets the minimum level or the floor price at which the product may be sold. Generally all marketing firms strive to cover all their costs, at least in the long run.
- The Utility and Demand: While the product costs set the lower limits of the price, the utility provided by the product and the intensity of demand of the buyer sets the upper limit of price, which a buyer would be prepared to pay. In fact the price must reflect the interest of both the parties to the transaction- the buyer and the seller. The buyer may be ready to pay up to the point where the utility from the product is at least equal to the sacrifice made in term of the price paid. The seller would , however, try to at least cover the costs. According to the law of demand, consumers usually purchase more unit at a low price than at a high price.
- Extent of Competition in the Market: Between the lower limit and the upper limit where would the price settle down? This is affected by the nature and the degree of competition. The price will tend to reach the upper limit in case there is lesser degree of competition while under conditions of free competition, the price will tend to be set at the lowest level.
- Government and Legal Regulations: In order to protect the interest of public against unfair practices in the field of price fixing, Government can intervene and regulate the price of commodities. Government can declare a product as essential product and regulate its price. For example, the cost of a drug manufactured by a company having monopoly in the production of the same come to 20 per strip of ten and the buyer is prepared to pay any amount for it, say 200.
- Pricing Objectives: Pricing objectives are another important factor affecting the fixation of the price of a product or a service. Generally the objective is stated to be maximize the profits. But there is a difference in maximizing profit in the short run and in the long run. If the firm decides to maximize profits in the short run, it would tend to charge maximum price for its products. But if it is to maximize it total profit in the long run, it would opt for a lower per unit price so that it can capture larger share of the market and earn greater profits through increased sales.
- Marketing Methods Used: Price fixation process is also affected by other elements of marketing such as distribution system, quality of salesmen employed, quality and amount of advertising, sales promotion efforts, the type of packaging, product differentiation, credit facility and customer services provided. For example, if a company provided free home delivery, it has some of flexibility in fixing prices. Similarly, uniqueness of any of the elements mentioned above gives the company a competitive freedom in fixing prices of its products.
Physical Distribution
The fourth important element of marketing mix is the physical distribution of products and services. Through this component of marketing mix, the goods and services are made available at right place, at right time to right people without change.
Once goods are manufactured, packaged, branded, priced, and promoted, these must be made available to customers at the right time. For example, a person convinced about the quality, etc. of a product, say, a detergent bar, wants to purchase the same. He/She goes to a retail outlet and asks for the product. If that product is not available in that shop, he/she may purchase some of the alternative brand available. This way a sure sale is lost because goods were not available at the place where the customer wanted to purchase. Thus, it is an important responsibility of the marketers to make the product physically available at a place where the customers would like them to buy.
Components of Physical
Distribution
The main components of physical distribution are explained as follows:
- Order Processing: In a typical buyer-seller relationship, order placement is the first step. Products flow from manufactures to customers via channel members while orders flow in the revere direction, from customers to the manufactures. A good physical distribution system should provide for an accurate and speedy processing of orders, in the absence of which, goods would reach the customers late or in wrong result in customer dissatisfaction, with the danger of loss of business and goodwill.
- Transportation: Transportation is the means of carrying goods and raw materials from the point of production to the point of sale. It is one of the major elements in the physical distribution of goods. It is important because unless the goods are physically made available, the sale cannot be completed.
- Warehousing: Warehousing refers to the act of storing and assorting products in order to create time utility in them. The basic purpose of warehousing activities is to arrange placement of goods and provide facilities to store them. The need for warehousing arises because there may be difference between the time a product is produced and the time it is required for consumption. Generally the efficiency of a firm in serving its customers will depend on where these warehouses are located and where are these to be delivered.
- Inventory Control: Linked to warehousing decision are the inventory decisions which hold key to success for many manufacturers, especially those where the per unit cost is high. A very important decision in respect of inventory is deciding about the level of inventory. Higher the level of inventory, higher will be the level of service to customers but the cost of carrying the inventory will also be high because lot of capital would be tied up in the stock. Thus, a balance it to be maintained in respect of the cost and customer satisfaction.
Promotion
A company may produce a good quality product, price it appropriately and make it available at the selling points, which are convenient to customers. But in spite of all this, the product may not sell well in the market. There is a need for developing proper communication with the market. In the absence of communication, the customers would not be able to know about the product and how it can satisfy their needs and wants or may not be convinced about its utility and benefits.
Promotion is an important element in marketing mis which marketer makes use of various tool of communication to encourage exchange of goods and service in the market.
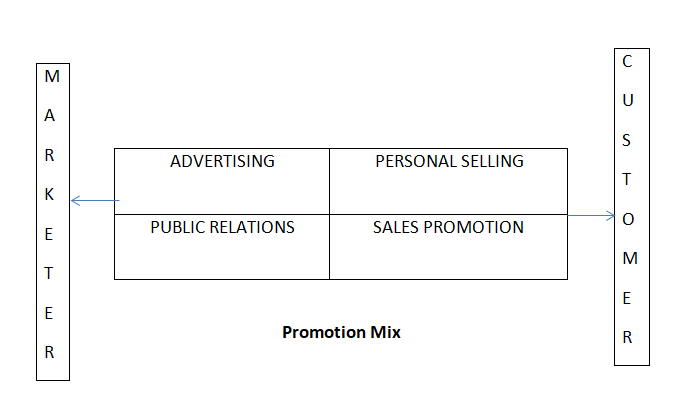
Promotion Mix
Promotion mix refers to combination of promotional tools used by an organization to achieve its communication objectives. Various tools of communication are used by the marketers to inform and persuade customers about their firm’s products. These include:
- Advertising
- Personal Selling
- Sales Promotion
- Publicity
These tools are also called elements of promotion mix and can be used in different combinations, to achieve the goals of promotion. For example, consumer goods firms may use more of advertising through mass media while the industrial goods firms may be using more of personal selling.
Advertising
We generally come across hundreds of advertising messages every day, which tell us about various products such as toilet soaps, detergent powder, soft drinks and services such as hotels, insurance policies, etc.
Advertising is perhaps the most commonly used tool of promotion. It is an impersonal form of communication, which is paid for by the marketers (sponsors) to promote some goods or service. The most common modes of advertising are ‘newspapers’, ‘magazines’, ‘television’, and ‘radio’. The important distinguishing features of advertising are as follows:
- Paid Form: Advertising is a paid form of communication. That is, the sponsor has to bear the cost of communicating with the prospects.
- Impersonality: There is no direct face-to face contact between the prospect and the advertiser. It is therefore, referred to as impersonal method of promotion. Advertising creates a monologue and not a dialogue.
- Identified Sponsor: Advertising is undertaken by some identified individual or company, who makes the advertising efforts and also bears the cost of it.
Merits of advertising
Advertising, as a medium of communication, has the following merits:
- Mass Reach: Advertising is a medium through which a large number of people can be reached over a vast geographical area. For example, an advertisement message placed in a national daily reaches lakhs of its subscribers.
- Enhancing Customer Satisfaction and Confidence: Advertising creates confidence amongst prospective buyers as they feel more comfortable and assured about the product quality and hence feel more satisfied.
- Expressiveness: With the developments in art, computer designs, and graphics, advertising has developed into one of the most forceful medium of communication. With the special effects that can be created, even simple products and messages can look very attractive.
- Economy: Advertising is a very economical mode of communication if large number of people are to be reached. Because of its wide reach, the overall cost of advertising gets spread over numerous communication links established. As a result the per-unit cost of reach come low.
Objections To Advertising
Though advertising is one of the most frequently used medium of promostion of goods and services, it attracts lot of criticism. The opponents of advertising say that the expenditure on advertising is a social waste as it adds to the cost, multiplies the needs of people and undermines social values. The proponents, however, argue that advertising is very useful as it increases the reach, brings the pay unit cost of production down and adds to the growth of the economy. It is therefore, important to examine the major criticisms against advertising and see the extent to which these are true. This is taken up as follows:
- Adds to Cost: The opponents of advertising argue that advertising unnecessarily adds to the cost of product, which is ultimately passed on to the buyers in the form of high prices. An advertisement on TV, for a few seconds, for example, costs the marketers several lakhs of rupees. Similarly an advertisement in print media say in a newspaper or a magazine costs the marketers a large amount of money. The money spent adds to the cost, which in an important factor in fixation of the price of a product.
- Undermines Social Values: Another important criticism of advertising is that it undermines social values and promotes materialism. It breeds discontent among people as they come to know about new products and feel dissatisfied with their present state of affairs. Some advertisements show new life styles, which don’t find social approval.
- Confuses the Buyers: Another criticism against advertisement is that so many products are being advertised which makes similar claims that the buyer gets confused as to which one is true and which one should be relied upon. For example, we may note similar claims of whiteness or stain removing abilities in competing brands detergent powder or claims of whiteness of tooth or ‘feelings of freshness’ in competing brands of toothpaste that it is sometimes confusing to us as to which one to buy.
- Encourages Sale of Inferior Products: Advertising does not distinguish between superior and inferior products and persuade people to purchase even the inferior products.
Personal Selling
Personal selling involves oral presentation of message in the form of conversation with one or more prospective customers for the purpose of making sales. It is a personal form of communication. Companies appoint salespersons to contact prospective buyers and create awareness about the product and develop product preferences with the aim of making sale.
Features of Personal selling
- Personal Form: In personal selling a direct face-to-face dialogue takes place that involves an interactive relationship between the seller and the buyer.
- Development of Relationship: Personal selling allows a salesperson to develop personal relationships with the prospective customers, which may become important in making sale.
Merits of Personal selling
- Flexibility: There is lot of flexibility in personal selling. The sales presentation can be adjusted to fit the specific needs of the individual customers.
- Direct Feedback: As there is direct face-to-face communication in personal selling, it is possible to take a direct feed back from the customer and to adapt the presentation according to the needs of the prospects.
- Minimum Wastage: The wastage of efforts in personal selling can be minimized as company can decide the target customers before making any contact with them.
Role Of Personal Selling
Personal selling plays a very important role in the marketing of goods and services. The importance of personal selling to businessmen, customers and society may be described as below.
Importance to Businessmen
Personal selling is a powerful tool for creating demand for a firm’s products and increasing their sale. The importance of personal selling to a business organization may be described as follows:
- Effective Promotional Tool: Personal selling is very effective promotional tool, which helps in influencing the prospects about the merits of a product and thereby increasing its sale.
- Flexible Tool: Personal selling is more flexible than other tools of promotion such as advertising and sales promotion. It helps business persons in adopting their offer in varying purchase situations.
- Minimises Wastage of Efforts: Compared with other tools of promotion, the possibility of wastage of efforts in personal selling is minimum. This helps the business persons in bringing economy in their efforts.
- Consumer Attention: There is an opportunity to detect the loss of consumer attention and interest in a personal selling situation. This helps a business person in successfully completing the sale.
- Lasting Retationship: Personal selling helps to develop lasting relationship between the sales persons and the customers, which is very important for achieving the objectives of business.
Importance to Customers
This role of personal selling becomes more important for the illiterate and rural customers, who do not have many other means of getting product information.
The customers are benefited by personal selling in the following ways:
- Help in Identifying Needs: Personal selling helps the customers in identifying their needs and wants and in knowing how these can best be satisfied.
- Latest Market Information: Customers get latest market information regarding price changes, product availability and shortages and new product introduction, which help them in taking the purchase decisions in a better way.
- Expert Advice: Customers get expert advice and guidance in purchasing various goods and services, which help them in making better purchase.
- Induces Customers: Personal selling induces customers to purchase new products that satisfy their needs in a better way and thereby helps in improving their standards of living.
Importance to Society
Personal selling plays a very productive role in the economic progress of a society. The more specific benefits of personal selling to a society are as follows:
- Converts Latest Demand: Personal selling converts latest demand into effective demand. It is through this cycle that the economic activity in the society is fostered, leading to more jobs, more incomes and more products and services. That is how economic growth is influenced by personal selling.
- Employment Opportunities: Personal selling offers greater income and employment opportunities to the unemployed youth.
- Career Opportunities: Personal selling provides attractive career with greater opportunities for advancement and job satisfaction as well as security, respect, variety, interest and independence to young men and women.
- Mobility of Sales People: There is a greater degree of mobility in sales people, which promote travel and tourism in the country.
- Product Standardisation: Personal selling increases product standardization and uniformity in consumption pattern in a diverse society.
Sales Promotion
Sales promotion refers to short-term incentives, which are designed to encourage the buyers to make immediate purchase of a product or service. These include all promotional efforts other than advertising, personal selling and publicity, used by a company to boost its sales. Sales promotion activities include offering cash discounts, sales contests, free gift offers, and free sample distribution. Sales promotion is usually undertaken to supplement other promotional efforts such as advertising and personal selling.
Merits of Sales Promotion
- Attention Value: Sales promotion activities attract attention of the people because of the use of incentives.
- Useful in New Product Launch: Sales promotion tools can be very effective at the time of introduction of a new product in the market. It induces people to break away from their regular buying behavior and try the new product.
- Synergy in Total Promotional Efforts: Sales promotion activities are designed to supplement the personal selling and advertising efforts used by a firm and add to the over all effectiveness of the promotional efforts of a firm.
Limitation of Sales Promotion
- Reflects Crisis: If a firm frequently rely on sales promotion, it may give the impression that it is unable to manage its sales or that there are no takers of its product.
- Spoils Product Image: Use of sales promotion tools may affect the image of a product. The buyers may start feeling that the product is not of good quality or is not appropriately priced.
Commonly used sales Promotion activities
- Rebate
- Discount
- Refunds
- Product combinations
- Quantity gift
- Instant Draws and Assigned
- Lucy Draw
- Usable Benefit
- Full finance @ 0%
- Sampling
- Contests
Public Relations
Managing public opinion of an organization is an important task which can be performed by the marketing department. The business needs to communicate effectively to customers, suppliers, and dealers, since they are instrumental in increasing the sales and profit. Besides those who come into direct contact with the organization or its products, there are other members of the general public whose voice or opinion is equally important.
Role of Public Relations
The role of public relations can be discussed with respect to the functions which the department performs. Public relations itself is an important tool in the hands of the marketing department, which can be used to the advantage of the business. The public relations department performs five functions:
- Publicity: Publicity is similar to advertising, in the sense that it is a non-personal form of communication. However, as against advertising it is a non-paid form of communication. Publicity generally takes place when favourable news is presented in the mass media about a product or service. For example, if a manufacturer achieves a breakthrough by developing a car engine, which runs on water instead of petrol, and this news is covered by television radio or newspapers in the form of a news item.
- Press release: Information about the organization needs to be presented in a positive manner in the press. Generating news requires skill in developing and researching a story and getting the media to accept press releases is a difficult task. The public relations department is in contact with the media to present true facts and a correct picture about the company. Otherwise news can get distorted if taken from other sources.
- Corporate communication: The image of the organization needs to be promoted through communicating with the public and the employees within the organization. This is usually done with the help of newsletter, annual reports, brochures, articles and audio-visual materials. Companies rely on these materials to reach and influence their target markets.
- Lobbying: The organization has to deal with government officials and different ministers in charge of corporate affairs, industry, finance with respect to policies relating to business and the economy.
- Counselling: The public relations department advise the management on general issues which affect the public and the position the company would like to the take on a particular issue. The company can build goodwill by contributing money and time to certain causes like environment, wildlife, children’s rights, education, etc.
Very Short Answer
- State any two advantages of branding to marketers of goods and services?
Ans.: Branding implies giving a unique name, sign, symbol, or term for the identification of a product. The following are the advantages of branding to marketers.
- Branding enables a firm to distinguish its product from the product of other firms.
- It facilitates the advertising of the product. Only when a product is given a brand, it can be advertised and thereby, attract customers. A product with a generic name cannot be advertised.
2. How does branding help in differential pricing?
Ans.: The brand name creates a perception about the quality of the product and helps consumers know about the quality of different brands offered by different firms when the customer is also to differentiate, a marketer can charge different prices from their competitor, and a good brand can charge a premium over the competitor.
3. What is the societal concept of marketing?
Ans:
The Societal Marketing Concept: The societal concept is the new concept of marketing that aims at satisfying customer needs by taking proper care of society and the environment. According to this concept customer satisfaction must be within the ethical and ecological aspects of society.
Societal marketing should consider the following things
- The consumer needs are most important
- Genuine modern and continuous development should be introduced in the product so as to increase its life and value
- The emphasis should be on building long-term customer relationships and not on doing business
- An organization should market the product keeping in mind the consumer organizational and societal long-term needs and welfare.
4. Enlist the advantages of packaging of consumer products.
Ans. The advantages of packaging are:
- It becomes easy to identify and differentiate the product.
- It helps in promotional activities
- It contributes to the convenience in handling the product
- It protects the product from all types of damages
5. List five shopping products purchased by you or your family during the last few months.
Ans. The five shopping products purchased during last few months are:
- Clothes
- Shoes
- Furniture
- Computer
- Books
6. A Marketer of color TV having 20% of the current market share of the country aims at enhancing the market share to 50 per cent in next three years. For achieving this objective he specified an action programme. Name the function of marketing being discussed above.
Ans. Marketing planning. An important activity or area of work of a marketer is to develop appropriate marketing plans so that the marketing objectives of the organization can be achieved. For example, a marketer of colour TV, having 10 percent of the current market share in the country, aims at enhancing his market share to 20 percent, in the next three years. He will have to develop a complete marketing plan covering various important aspects including the plan for increasing the level of production, promotion of the products, etc., and specify the action programs to achieve these objectives.
Short Answer
- What is marketing? What functions does it perform in the process of exchange of goods and services? Explain.
Ans:
Marketing
It is a process whereby people exchange goods and services for money or for something of value to them. Taking the social perspective, Phillip Kolter has defined marketing as, “a social process by which individual groups obtain what they need and want through creating offerings and freely exchanging products and services of value with others”.
Functions of Marketing
Marketing is concerned with exchange of goods and services from producers to consumers or users in such a way that maximizes the satisfaction of customers’ needs. From the view point of management function, number of activities are involved, which have been described as below:
Gathering and Analyzing Market Information: One of the important functions of a marketer is to gather and analyze market information. This is necessary to identify the needs of the customers and take various decision for the successful marketing of the products and services. This is important for making an analysis of the available opportunities and threats as well as strengths and weaknesses of the organization and help in deciding what opportunities can best be pursued by it.
2. Marketing Planning: Another important activity or area of work of a marketer is to develop appropriate marketing plans so that the marketing objectives of the organization can be achieved. For example a marketer of colour TV, having 10 per cent of the current market share in the country, aims at enhancing his market share to 20 per cent, in the next three years.
3. Product Designing and Development: Another important marketing activity or decision area relates to product designing and development. The design of the product contributes to making the product attractive to the target customers. A good design can improve performance of a product and also give it a competitive advantage in the market. For example, when we plan to buy any product say a motorbike, we not only see its features like cost, mileage, but also the design aspects like its shape, style, etc.
4. Standardisation and Grading: Standardisation refers to producing good of predetermined specifications, which helps in achieving uniformity and consistency in the output. Standardisation ensures the buyers that goods conform to the predetermined standards of quality, price and packaging and reduces the need for inspection, testing and evaluation of the products.
5. Packaging and Labelling: Packaging refers to designing and developing the package for the products. Labelling refers to designing and developing the label to be put on the package. The label may vary from a simple tag to complex graphics.
6. Branding: A very important decision area for marketing of most consumer products is whether to sell the product in its generic name (name of the category of the product, say Fan, Pen, etc.) or to sell them in a brand name (such as Pollar Fan or Rottamac Pen). Brand name helps in creating product differentiation, i.e., providing basis for distinguishing the product of a firm with that of the competitor, which in turn, helps in building customer’s loyality and in promoting its sale.
7. Customer Support Services: A veery important function of the marketing management relates to developing customer support services such as after sales services, handling customer complaints and adjustments, procuring credit services, maintenance services, technical services and consumer information. All these services aim at providing maximum satisfaction to the customers, which is the key to marketing success in modern days. Customer support services are very effective in bringing repeat sales from the customers and developing brand loyality for a product.
8. Pricing of Product: Price of product refers to the amount of money customers have to pay to obtain a product. Price is an important factor affecting the success or failure of a product in the market. The demand for a product or service is related to its price. Generally lower the price, higher would be the demand for the product and vice-versa.
2. Distinguish between the product concept and production concept of marketing.
Ans:
The Production concept: During the earlier days of industrial revolution, the demand for industrial goods started picking up but the number of producers were limited. As a result, the demand exceeded the supply. Selling was no problem. Anybody who could produce the goods was able to sell. The focus of business activities was, therefore, on production of goods. It was believed that profits at large scale, thereby reducing the average cost of production.
The Product Concept: As a result of emphasis on production capacity during the earlier days, the position of supply increased over period of time. Mere availability and low price of the product could not ensure increased sale and as such the survival and growth of the firm. Thus, with the increase in the supply of the products, customers started looking for products which were superior in quality, performance and features.
3. Product is a bundle of utilities. Explain.
Ans. When a customer decides to buy a product, his/her main focus lies on the utility which he/she receives while consuming it. A customer seeks different types of satisfaction from the product. Benefits derived from a product can be of three types- functional benefits, psychological benefits, and social benefits. For instance, when a consumer purchases a car, it provides him functional utility as a means of transport. Besides, he also receives a psychological benefit in the form of pride and self- esteem that he has bought a car. Along with it comes the social benefit in the form of acceptance by peers. Thus, a product is said to be a bundle of utilities, and a buyer while buying a product values all such kinds of utilities.
4. What are industrial products? How are they different from consumer products? Explain.
Ans:
Industrial Products
Industrial products are those products, which are used as inputs in producing other products. The examples of such products are raw materials, engines, lubricants, machines, tools, etc. In other words, industrial products are meant for non-personal and business use for producing other products.
The market for industrial products consists of manufacturers, transport agencies, banks and insurance companies, mining companies and public utilities.
Consumer Products
Products, which are purchased by the ultimate consumers or users for satisfying their personal needs and desires are referred to as consumer products. For example, soap, edible oil, eatables, textiles, toothpaste, fans, etc. which we use for our personal and non-business use are consumer goods. We can classify the consumer product into the following three categories as here under:
5. Distinguish between convenience product and shopping product.
Ans:
- Convenience Products: Those consumer products, which are purchased frequently, immediately and with least time and efforts are referred to as convenience goods, Examples of such products are cigarettes, ice creams, medicines, newspaper, stationery items toothpaste etc. These products have low unit-value and are bought in small qualities.
- Shopping Products: Shopping products are those consumer goods where buyers devote considerable time, to compare the quality, price, style, suitability, etc., at several stores, before making final purchase. Some of the examples of shopping products are clothes, shoes, jewellery, furniture, radio, television, etc.
6. Describe the functions of labeling in the marketing of products.
Ans:
Labeling
A simple looking but important task in the marketing of goods relates to designing the label to be put on the package. The label may vary from a simple tag attached to the product (such as in case of local unbranded products like sugar, wheat, pulses, etc.) indicating some information about the quality or price, to complex graphics that are part of the package, like the ones on branded products. Lables are useful in providing detailed information about the product, its contents, method of use, etc.
The various functions performed by a label are as follows:
- Describe the Product and specify its contents: Let us look at some of the labels of the products used by us in our day to day life. The label on the package of a local tea company describes the company as ‘Mohini Tea Company, and ISO 9001:200C Certified Company’; a popular brand of Prickly Heat Powder, describes how the product provides relief from prickly heat and controls bacterial growth and infection, giving caution forbidding its application on cuts and wounds. Thus, one of the most important functions of labels is to describe the product, its usage, caution in use, etc. and specify its contents.
- Identification of the Product or brand: The other important function performed by labels is to help in identifying the product or brand. For example, the brand name of any product, say Biscuits or Potato Chips imprinted on its package helps us to identify, from number of packages, which one is our favorite brand. Other common identification information provided by the labels include name and address of the manufacturer, net weight when packed, manufacturing date, maximum retail price and Batch number.
- Grading of Products: Another important function performed by labels is to help grading the products into different categories. Sometimes marketers assign different grades to indicate different features or quality of the product. For example, a popular brand of Hair Conditioners comes in different categories for different hair, say for ‘normal hair’ and for other categories. Different type of tea is sold by some brands under Yellow, red and Green Label categories.
- Helps in Promotion of Products: An important function of label is to aid in promotion of the products. A carefully designed label can attract attention and give reason to purchase. We see many product labels providing promotional messages for example, the pack of a popular Amla Hair Oil states, ‘Baalon Mein Dum, Life Mein Fun’. The label on the package of a brand of Detergent Powder says, ‘keep cloth look good and your machine in top condition’.
- Providing Information Required by Law: Another important function of labeling is to provide information required by law. For example, packaged food articles must have list of ingredients declaration regarding vegetarian or non-vegetarian food additives and date of manufacturing of packing on the label. Such information is required on processed foods, drugs and tobacco products. In case of hazardous or poisonous material, appropriate safety-warning need to be put on the label.
7. Discuss the role of intermediaries in the distribution of consumer non-durable products.
Ans. Intermediaries play an important role in the distribution of consumer non-durable. They facilitate the transfer of goods from the place of production to the place where they are consumed.
The following are the different function performed by the intermediaries in the case of non-durables.
- Arrangement:- An intermediary receives the supplyof goods from various sources. He then sorts these goods into homogeneous groups based on their characteristics such as size, quality, etc. For instance, an electronic goods seller receives a supply of different electronic goods (T.V., washing machine, etc.) and then sorts them based on their functions.
- Collection:- An intermediary maintains a large stock of the goods so as to ensure easy flow of supply. For instance, the electronic goods seller maintains a large stock of each type of electronic item.
- Allocation and Packing:- This function includes the larger stock into smaller units. For instance, each electronic item as well as its spare parts are packed separately.
- Building Variety:- An intermediary acquires various goods from different sources and assembles them in a single place. Thus, it maintains a variety of goods. He procures the products and them sells them in different combinations as desired by the consumers. For instance, a television and a video player are preferred together by most people. Thus, the retailer can sell a combination of both.
- Promotion of Product:- They assist in the promotion activities undertaken by the manufactures. For example, the manufacturers use advertising for the promotion of their products.
- Mediation:- Middlemen perform the function of setting a deal that can satisfy both the producers and the consumers. They negotiate the price, quality, quantity, etc. for efficient transfer of ownership so as to satisfy the need of both parties.
- Bearing Risk:- Intermediaries acquire goods from the producers and keep them in their possession till the final sale. In the process, they bear the risk of fluctuations in demand, price, spoilage, etc. for example, suppose a retailer acquires large quantities of air conditioners.
8. Define advertising? What are its main features? Explain.
Ans:
Advertising
We generally come across hundreds of advertising messages every day, which tell us about various products such as toilet soaps, detergent powder, soft drinks and services such as hotels, insurance policies, etc.
Advertising is perhaps the most commonly used tool of promotion. It is an impersonal form of communication, which is paid for by the marketers (sponsors) to promote some goods or service. The most common modes of advertising are ‘newspapers’, ‘magazines’, ‘television’, and ‘radio’. The important distinguishing features of advertising are as follows:
- Paid Form: Advertising is a paid form of communication. That is, the sponsor has to bear the cost of communicating with the prospects.
- Impersonality: There is no direct face-to face contact between the prospect and the advertiser. It is therefore, referred to as impersonal method of promotion. Advertising creates a monologue and not a dialogue.
- Identified Sponsor: Advertising is undertaken by some identified individual or company, who makes the advertising efforts and also bears the cost of it.
9. Discuss the role of ‘sales promotion’ as an element of promotion mix.
Ans:
Sales Promotion
Sales promotion refers to short-term incentives, which are designed to encourage the buyers to make immediate purchase of a product or service. These include all promotional efforts other than advertising, personal selling and publicity, used by a company to boost its sales. Sales promotion activities include offering cash discounts, sales contests, free gift offers, and free sample distribution. Sales promotion is usually undertaken to supplement other promotional efforts such as advertising and personal selling.
10. As the marketing manager of a big hotel located at an important tourist destination, what societal concerns would be faced by you and what steps would you plan to take care of these concerns? Discuss.
Ans. :- As a marketing manager of a hotel in a popular tourist city, I will have a certain societal concern
- Activities of the hotel should not harm the tourist place, should not affect locals, and should not cause any pollution.
- To maintain ethics and fair pricing of hotel rooms.
Steps: We will ensure that the activities of the hotel do not harm the environment and locality, we will have a proper process for waste management, sustainable use of natural resources like water electricity, etc. and will make guests also aware of it.
We will also ensure that our room prices are pieced appropriately and we should not take advantage of guests in peak season by pricing rooms inappropriately.
11. What information is generally placed on the package of a food product? Design a label for one of the food products of your choice.
Ans: A Label provides information about the product, in food products label provides the information about the manufacture, date of manufacturing, date of expiry, price of the product, net content, the process of making the product if it not ready and eat and ingredients of the products. It also provides information about the nutritional status of the product.
Below is the label for the well-known product Maggi
MRP: 12 Rs.
Date of manufacturing: 15 June 2019
Validity: 6 months from the date of manufacturing
Net weight: 70 Gram
Nutritional information (per 100 gram)
Energy: 427 Kcal
Protein: 8 Gram
Carbohydrate: 63 g
Fat: 15.7
Iron: 3.7
12. For buyers of consumer durable products, what ‘customer care services’ would you plan as a manager of a firm marketing new brand of motorcycle. Discuss.
Ans. :- As motorcycles are high-value items it is important to provide good post-sale services to the consumer. We also need to ensure that customer services are available near to the customer.
For which we need to have the following things
- Centralised customer care desk: at our head office we need to have a centralized customer care desk where customer can call in case of any difficulty and we can properly guide them about resolution
- Local office:- We need have local offices in all major cities and towns where customer can come and get their resolution. These services can also be outsourced to a third-party vendor like vehicle dealers.
Long Answer
- What is marketing concept? How does it help in the effective marketing of goods and services.
Ans. :-Marketing Concept:- Marketing concept of marketing management lays emphasis on customer satisfaction. It believes that customer satisfaction plays a vital role in the success of any organization. In the long run, any organization can survive and maximize profits only if it identifies customer needs and effectively works towards fulfilling them. This concept identifies the fact that people purchases a product for satisfaction of a specific need (such as functional need, social need, psychological need, etc.). Any organisation must aim towards identifying such need and satisfying them in an effective manner. That is, it must take all decisions based on the needs and requirements of the customers. An organization works and sells not according to what it has, but according to what the customer wants.
The marketing concept is based on the following points.
- The efforts of all marketing activities must be directed towards a particulars segment of the market or group of customers.
- The organisations must clearly identify the needs and requirements of the target customer.
- It should develop such products and services that satisfy the needs of the customers.
- It should not just independently work toward customer satisfaction, but should also aim at satisfying the customers better than its competitors.
- The crux of all efforts of marketing is profit.
Marketing concept helps in effective marketing of goods and services. If all marketing activities are directed towards customer satisfaction, marketing of goods and services would take place in an effective and smooth manner. If decisions of production, pricing, designing, etc. are based on the needs of the customers, selling would not be a problem. For example, if customers want dual sim mobile phones, high pixel cameras, GPS, etc. the company produces mobile phones with such features. Similarly, other decisions of the company such as pricing, branding, etc. are also based on the requirements of the customers.
2. What is marketing mix? What are its main elements? Explain.
Ans:
Marketing Mix:- Marketing mix refers to the set of marketing tools that are used to achieve the various objectives of marketing. In the process of marketing, market offering plays an important role. That is, for effective marketing, an organization must decide the various feature of a product such as its size, quality, location of sale of etc. Such decisions are affected by a large number of factors. Some of them are controllable by the firm. For example, decisions regarding packing, branding, pricing, advertising, etc. are within the control of the firm. However, there are certain non-controllable factors as well that affect the decision-making of a firm. For example, government policies, credit policies of the banks are beyond the control of the firm. A firm continuously alters the various controllable factors to achieve the objective of marketing. Such factors form the pillars of marketing and are know as marketing tools. From the various alternative marketing tools, a firm chooses the best combination to develop a market offering. Such a set of marketing tools used by the firm to achieve the desired objectives of marketing is known as the marketing mix. The marketing mix consists of various elements, which have been classified into four categories, popularly known as four Ps of marketing. These are: (i) Product, (ii) Price, (iii) Place, and (iv) Promotion. These are briefly discussed as follows:
- Product: Product means goods or services or ‘anything of value’, which is offered to the market for sale. For example, Hindustan lever offers number of consumer products like toiletries (Close-Up toothpaste, Lifebuoy soap, etc.), detergent powder (Surf, Wheel), food products (Refined Vegetable Oil); Tata offers Tata Steel, Trucks, Salt and a large number of other products; LG electronics offers televisions, refrigerators, colour monitors for computers, etc; Amul offers a number of food products (Amul milk, ghee, butter, cheese, chocolates, etc.).
- Price: Price is the amount of money customers have to pay to obtain the product. In case of most of the products, level of price affects the level of their demand. The marketers have not only to decide about the objectives of price setting but to analyse the factors determining the price and fix a price for the firm’s products. Decisions have also to be taken in respect of discounts to customers, traders and credit terms, etc., so that customers perceive the price to be in line with the value of the produt.
- Place: Place or Physical Distribution include activities that make firm’s products available to the target customers. Important decision areas in this respect include selection of dealers or intermediaries to reach the customers, providing support to the intermediaries (by way of discounts, promotional campaigns, etc.). The intermediaries in turn keep inventory of the firm’s products, demonstrate them to potential buyers, negotiate price with buyers, close sales and also service the products after the sale.
- Promotion: Promotion of products and services include activities that communicate availability, features, merits, etc., of the products to the target customers and persuade them to buy it. Most marketing organisations, undertake various promotional activities and spend substantial amount of money on the promotion of their goods through using number of tools such as advertising, personal selling and sales promotion techniques (like price discounts, free samples, etc.).
3. How does branding help in creating product differentiation? Does it help in marketing of goods and services? Explain.
Ans. :- Branding implies giving a unique name, sing, symbol, or term for the identification of a product. Branding is one of the most important decisions for a marketer. Through branding, the firms differentiate their products from that other similar products. If instead of branding the firm opt for a generic name for their product, they would not be able to distinguish their product form that of competitors. This is because a generic name would represent the whole class of the product. For example, all shampoos are use for cleansing hair. However, one shampoo differs from that of other based on their brand name, symbol, or sign used by different shampoo manufacturing firms.
Branding not only helps in product differentiation, rather also helps in the marketing of goods and services. The following points highlight the importance of branding in the marketing of goods and services.
Ans. :- Branding implies giving a unique name, sing, symbol, or term for the identification of a product. Branding is one of the most important decisions for a marketer. Through branding, the firms differentiate their products from that other similar products. If instead of branding the firm opt for a generic name for their product, they would not be able to distinguish their product form that of competitors. This is because a generic name would represent the whole class of the product. For example, all shampoos are use for cleansing hair. However, one shampoo differs from that of other based on their brand name, symbol, or sign used by different shampoo manufacturing firms.
Branding not only helps in product differentiation, rather also helps in the marketing of goods and services. The following points highlight the importance of branding in the marketing of goods and services.
- Helps in Advertisement:- Branding helps a firm to advertise their product. Unless branding is not done a product connot be advertised. Advertisement for a generic product can only create awareness about the category of the product as a whole. It cannot attract customers towards a specific product. On the other hand, an advertisement for a branded product helps in highlighting the specific qualities and features of the product.
- Enables Differential Pricing:- Good branding helps in creating a loyalty of the consumers towards the product. The firm can benefit from this loyalty and charge a different price for their product from that of their competitors. For example, if consumers become habitual of using a particular product they would not mind paying a slightly higher price for it.
- Facilitates Introduction of New Products:- Good branding helps in establishing a base for the introduction of a new product. If a new product is launched under an established and reputed brand then, it gets an initial boost and benefits from the brand name. Nowadays, many companies such as Samsung, Cadbury, etc. have multiple products under a single brand name.
4. What are the factors affecting determination of the price of a product or service? Explain.
Ans:
Factors affecting Price Determination
There are number of factors which affect the fixation of the price of a product. Some of the important factors in this regard are discussed as below:
- Product cost: One of the most important factor affecting price of a product or service is its cost. This includes the cost of producing, distributing and selling the product. The cost sets the minimum level or the floor price at which the product may be sold. Generally all marketing firms strive to cover all their costs, at least in the long run.
- The Utility and Demand: While the product costs set the lower limits of the price, the utility provided by the product and the intensity of demand of the buyer sets the upper limit of price, which a buyer would be prepared to pay. In fact the price must reflect the interest of both the parties to the transaction- the buyer and the seller. The buyer may be ready to pay up to the point where the utility from the product is at least equal to the sacrifice made in term of the price paid. The seller would , however, try to at least cover the costs. According to the law of demand, consumers usually purchase more unit at a low price than at a high price.
- Extent of Competition in the Market: Between the lower limit and the upper limit where would the price settle down? This is affected by the nature and the degree of competition. The price will tend to reach the upper limit in case there is lesser degree of competition while under conditions of free competition, the price will tend to be set at the lowest level.
- Government and Legal Regulations: In order to protect the interest of public against unfair practices in the field of price fixing, Government can intervene and regulate the price of commodities. Government can declare a product as essential product and regulate its price. For example, the cost of a drug manufactured by a company having monopoly in the production of the same come to 20 per strip of ten and the buyer is prepared to pay any amount for it, say 200.
- Pricing Objectives: Pricing objectives are another important factor affecting the fixation of the price of a product or a service. Generally the objective is stated to be maximize the profits. But there is a difference in maximizing profit in the short run and in the long run. If the firm decides to maximize profits in the short run, it would tend to charge maximum price for its products. But if it is to maximize it total profit in the long run, it would opt for a lower per unit price so that it can capture larger share of the market and earn greater profits through increased sales.
- Marketing Methods Used: Price fixation process is also affected by other elements of marketing such as distribution system, quality of salesmen employed, quality and amount of advertising, sales promotion efforts, the type of packaging, product differentiation, credit facility and customer services provided. For example, if a company provided free home delivery, it has some of flexibility in fixing prices. Similarly, uniqueness of any of the elements mentioned above gives the company a competitive freedom in fixing prices of its products.
5. Explain the major activities involved in the physical distribution of products.
Ans. : The physical handling and movement of goods from place of production to the place of distribution, is called physical distribution. It covers all the activities required to physically move the goods from the manufacturing to the customers.
The major activities involved in the physical distribution of products are:
- Order processing: A good physical distribution system should provide for an accurate and speedy processing of orders. In the absence of this, goods would reach the customers in wrong quality or quantity, resulting in dissatisfaction of customers.
- Transportation: It means carrying raw materials and finished goods from one place to another. It helps in creating ‘place utility’, by making available the goods where they are required.
- Warehousing: It refers to the act of storing and assorting products in order to create ‘time utility’. It helps in proper placement of goods and providing facilities to store them, so that they can be made available as and when demanded by the market.
- Inventory control: An important decision in physical distribution is deciding about the level of inventory. Higher the level of inventory, higher will be level of service and cost of carrying the inventory and vice-versa. Various factors which are considered for determining inventory levels are:
i. Firms’ policy regarding level of customer service.
ii. Degree of accuracy of sales forecast.
iii. Responsiveness of distribution system.
iv. Cost of holding inventory.
A good inventory decision aims at timely fulfillment of demand at minimum cost.
6. ‘Expenditure on advertising is a social waste.’ Do you agree? Discuss.
Ans. :- Advertising expenditure is considered as a social waste due to multiple factors, such as-it adds to cost of the production of the company, and also increases customer requirements for more such products. Following points will help in determining whether advertising is a social waste or not
1. Advertising is high cost intensive: the businesses thus pass on this cost to the consumers at the time of determining the price of the product. But the positive point that can be seen is that advertisement can help in reducing cost of production by increasing customer demand for the product.
2. The major point which impacts advertising is that weakens the social values and promotes the sense of materialism in the society. Customers want to acquire any new product to fulfil their desires. But this process will run forever as long as any new product is prepared.
3. Advertisements are said to create confusion among customers as so many different varieties of same product will be available in the market. Customers get confused as to which brand to buy.
4. Advertisement is done for both good and bad quality products. Again, good and bad quality concept will vary from customer to customer.
5. Advertisements are said to erode social values by using content, images, action, gestures or language, which is not acceptable by all sections of society. Again, the same rule will apply that what is perceived as bad by someone may be seen as good by the other.
6. Distinguish between advertising and personal selling.
Ans:
Advertising
We generally come across hundreds of advertising messages every day, which tell us about various products such as toilet soaps, detergent powder, soft drinks and services such as hotels, insurance policies, etc.
Advertising is perhaps the most commonly used tool of promotion. It is an impersonal form of communication, which is paid for by the marketers (sponsors) to promote some goods or service. The most common modes of advertising are ‘newspapers’, ‘magazines’, ‘television’, and ‘radio’.
The important distinguishing features of advertising are as follows:
- Paid Form: Advertising is a paid form of communication. That is, the sponsor has to bear the cost of communicating with the prospects.
- Impersonality: There is no direct face-to face contact between the prospect and the advertiser. It is therefore, referred to as impersonal method of promotion. Advertising creates a monologue and not a dialogue.
- Identified Sponsor: Advertising is undertaken by some identified individual or company, who makes the advertising efforts and also bears the cost of it.
Merits of advertising
Advertising, as a medium of communication, has the following merits:
- Mass Reach: Advertising is a medium through which a large number of people can be reached over a vast geographical area. For example, an advertisement message placed in a national daily reaches lakhs of its subscribers.
- Enhancing Customer Satisfaction and Confidence: Advertising creates confidence amongst prospective buyers as they feel more comfortable and assured about the product quality and hence feel more satisfied.
- Expressiveness: With the developments in art, computer designs, and graphics, advertising has developed into one of the most forceful medium of communication. With the special effects that can be created, even simple products and messages can look very attractive.
- Economy: Advertising is a very economical mode of communication if large number of people are to be reached. Because of its wide reach, the overall cost of advertising gets spread over numerous communication links established. As a result the per-unit cost of reach come low.
Personal Selling
Personal selling involves oral presentation of message in the form of conversation with one or more prospective customers for the purpose of making sales. It is a personal form of communication. Companies appoint salespersons to contact prospective buyers and create awareness about the product and develop product preferences with the aim of making sale.
Features of Personal selling
- Personal Form: In personal selling a direct face-to-face dialogue takes place that involves an interactive relationship between the seller and the buyer.
- Development of Relationship: Personal selling allows a salesperson to develop personal relationships with the prospective customers, which may become important in making sale.
Merits of Personal selling
- Flexibility: There is lot of flexibility in personal selling. The sales presentation can be adjusted to fit the specific needs of the individual customers.
- Direct Feedback: As there is direct face-to-face communication in personal selling, it is possible to take a direct feed back from the customer and to adapt the presentation according to the needs of the prospects.
- Minimum Wastage: The wastage of efforts in personal selling can be minimized as company can decide the target customers before making any contact with them.
8. Explain the factors determining the choice of channel of distribution.
Ans. :- One of the important decisions of marketing involves the choice regarding which channel of distribution to opt for. The following factors determine the choice of channels:
- Product Type: The choice of channel of distribution is based on the type of the product that is produced. It is important to check whether the product is perishable or non-perishable, whether it is an industrial or a consumer product, whether its unit value is high or low and also, the degree of complexity of the product. For instance, if a good is perishable then short channels should be used rather than the long ones. Similarly, if a product has a low unit value then longer channel are preferred. In a similar manner, consumer products are distributed through long channels while industrial products are distributed through short channels.
- Characteristics of the Company: The two important characteristics of a company that affect the choice of channel are its financial strength and the degree of control that the company wishes to hold on the intermediaries. Shorter channels require greater funds than longer channels and also offer greater control over the members of the channel (intermediaries). Thus, companies that are financially strong or wish to command greater control over the channel of distribution opt for shorter channels of distribution.
- Competitive Factors: The degree of competition and the channels opted by other competitors affect the choice of distribution channel. Depending on its policies a company can adopt a similar channel as adopted by its competitors or opt for a different channel. For example, if competitors of a company opt for sale through retail store, it may also do the same or it can opt a different channel such as direct selling.
- Environmental Factors: Environmental factors such as economic constraints and legal policies play an important role in the choice of channel of distribution. For example, requirement of complex legal formalities at each step of distribution induces the companies to opt for shorter channels.
- Market Factors: Various other factors such as size of the market, geographical concentration of buyers, quantity demanded, etc. also affect the choice between the channels. For instance, if potential buyers are concentrated in a small geographical area then, shorter channels are used. As against this, if the buyers are dispersed in a larger area then longer channels of distribution may be used.