Private Sector Enterprises:-
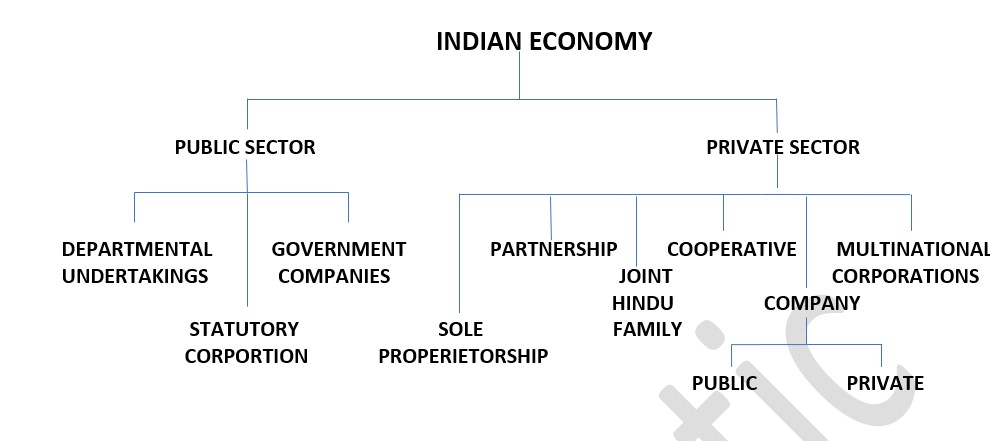
After independence, the emergence of public sector enterprises became a necessity for the all round development of the country. Moreover, India was committed to a socialistic pattern of economy. Therefore, it adopted a pattern of Mixed Economy, where both the public sector and the private sector are allotted their respective roles for the economic development of the country.
studynatic
Public Sector Enterprises:-
The public sector consists of various organizations owned and managed by central or state or by both governments. The government participates in economic activity of the country through these enterprises.
For example:- departmental under taking, public corporation and government company.
FORM OF PUBLIC ORGANISATION:-
A public enterprises may take any particular form of organization depending upon the nature of its operation and their relationship with the government. The suitability of a particular form of organization would depend upon its requirements. At the same time, in accordance with general principal, any organization in the public sector should ensure organization performance productivity and quality standards.
- DEPARTMENTAL UNDERTAKING
- STATUTORY CORPORATIONS
- GOVERNMENT COMPANY
The forms of organisation which a public enterprise may take are as follows:
studynatic
1.DEPARTMENTAL UNDERTAKING:-
This is the oldest and most traditional form of organising public enterprises. These enterprises are established as departments of the ministry and are considered part or an extension of the ministry itself. The Government functions through these departments and the activities performed by them are an integral part of the functioning of the government. Example railway, agriculture, commerce and industry.
studynatic
FEATURES:-
- Finance:- It is financed by annual budget allocation of the government and all its earning go to government treasury.
- Accounting & Audit:- The government rules relating to audit & accounting are applicable to it.
- Management:– It is managed and controlled by a government department and is subject to direct control of the ministry.
- Appointment of Employees:– As the undertaking does not have separate legal existence, its employees are Government employees and terms and conditions of their appointment, remuneration, promotion, etc., are determined by government.
- Accountability:– The employees of the enterprise are accountable to the concerned Minister, who is ultimately responsible to the parliament.
MERITS
- Complete government control:- It is completely owned, managed and controlled by a government ministry. It facilitates the parliament to exercise effective control over their operations.
- Answerable to Parliament:- All the departmental undertakings are accountable to parliament for their performances. So, they have to be careful about their progress and performance.
- Source of income:- The revenue earned by the enterprise is a source of income for the Government as it goes directly to the treasury.
IV. Suitable for national security:- This enterprise is most suitable when national security is concerned as it is under the direct control and supervision of the concerned Ministry.
Limitations:-
- Lack of Flexibility:- There is little scope for exercising initiative and making improvements. Due to lack of autonomy, it fails to provide flexibility in operations.
- Delay in Decision-Making:- The employees or heads of the departments have to take approval of the concerned ministry before taking any decision. This leads to delays in matters where prompt decisions are required.
- Bureaucracy and Conservative Approach:- Departmental undertakings are unable to take benefits of business opportunities because they are not allowed to take risky ventures due to bureaucrat’s over-cautious and conservative approach.
- Red Tapism:- Even for routine matters and day-today operations, prior sanction of the relevant authority is necessary.
- Undue Government Interference:- There is a lot of political interference through the ministry.
- Indifferent to Consumers’ Needs:- These enterprises are somewhat insensitive to consumer needs and do not provide adequate services to them.
2.STATUTORY CORPORATIONS
Statutory corporations are public enterprises brought into existence by a Special Act of the Parliament. The Act defines its powers and functions, rules and regulations governing its employees and its relationship with government department.
This is a corporate body created by the legislature with defined powers and functions and is financially independent with a clear control over a specified area or a particular type of commercial activity.
FEATURES:-
- Formation:- It is established under a special Act of the parliament, that lays down the objects, powers and functions of the Corporation.
- Ownership:- It is wholly owned by the government. Government has the power to appropriate its profits and also has to bear the losses, if any.
- Corporate Existence:- A statutory corporation is a body corporate, which has a separate legal existence independent of the Government.
- Financial Autonomy:- This type of enterprise is usually independently financed. It obtains funds by borrowings from the government of through revenues derived from sale of goods and services to public.
- Accounting and audit procedures:- It is not subject to the government rules and regulations in the matter of accounting, budgeting and audit as applicable to departmental undertakings.
- Staffing and Terms of Service:- The employees of these enterprises are not government or civil servants and are not governed by government rules and regulations.
MERITS:-
- Operational Flexibility:- They enjoy independence in their functioning and there is sufficient scope for flexibility and initiative. They are free from undesirable government regulation and control.
- Freedom from interference:- AS funds of these organization do not come from the central budget, it is free from interference of the government in its day-to-day working, which ensures better and efficient working.
- Autonomous Set-up:- As these enterprises are autonomous organisations, they frame their own policies and procedures within the powers assigned to them by the Act. However, the Act may require prior approval of a particular ministry on certain issues.
- Facilitates Economic Growth:- Such enterprises contribute to the economic development as they have the power of the government along with the initiative of private enterprises.
Limitations:-
- Theoretical Autonomy:- The autonomy and flexibility of such enterprises exist on paper only. In reality, a statutory corporation is subject to many rules and regulations and does not enjoy as much operational flexibility in its working.
- Government Interference:- the working of public corporations is subject to interference from bureaucrats and politicians, especially in case of major decisions or where huge funds are involved.
- Undesirable Practices:- In statuary corporations, officials may misuse their autonomy and indulge in unfair practices (like corruption), that are against the objectives of such enterprises.
- Delay in Action:- Government often appoints advisors to the corporation Board. It adversely affects the freedom in entering into contracts and other decisions. In case of any disagreement, the matter is referred to government, which further delays action.
- Rigid Structure:- The objectives, powers and functions of statutory corporations are prescribed by the Act and these can be changed only by amending the Act, which is quite time consuming and complicated.
3.GOVERNMENT COMPANY:-
According to the section 2(45) of the Companies Act 2013, a government company means any company in which not less than 51 per cent of the paid up capital is held by the central government, or by any state government or partly by one or more State government and includes a company which is a subsidiary of a government company. Example- State trading corporation of India, Hindustan cooperative limited.
FEATURES:-
- Incorporation:- The government company is registered under the companies Act, 2013 or any previous company Low. It is formed by an executive rather than a legislative decision.
- Separate Legal Entity:- It has a separate legal existence independent of the government. The company can enter into a contract, acquire property on can file a suit in a court of law against any third party and be sued.
- Management:– It is managed by a board of directors nominated by the government. The management is regulated by the provisions of the Companies Act, like any other public limited company.
- Governed by Provisions of memorandum and Articles of Association:– The Memorandum and Articles of Association are the main documents of the company, containing the objects of the company and rules and regulation relating to appointment of employees of the company.
- Accounting and Audit Procedures:– It is free from budgetary, accounting and audit controls applied to departmental undertakings. However, an Annual Report is to be presented in the parliament or the state legislature by the auditor appointed by the Central Government.
- Finance:– At least 51% of the capital of the company is contributed by the state or the central government while the rest can be raised from the capital market.
MERITS:-
- Easy Formation:- There is no need for separate legislation of the parliament for its formation. It can be established by fulfilling the requirements of the Indian Companies Act.
- Operational Autonomy:- It enjoys autonomy in all management decisions and takes actions according to business prudence.
- Independent Status:- It has a separate legal entity, apart from the Government. So, it carries on business activities like any other private company.
- Prevents Unhealthy Business Practices:- These companies provide good quality products at reasonable prices. It helps to control the market and reduce unhealthy business practices.
Limitations:-
- Freedom only in name:- As Government is the majority shareholder, it exercises control over affairs of the company & provisions of the Companies Act does not have much relevance.
- Lack of Accountability:- As it is financed by the government, it should be accountable to the government. However, it is not answerable directly to the Parliament due to ineffective government control.
- Defeat of main Purpose:- Being a major shareholder, the government controls the whole management and administration of the company. It defeats the main purpose of registering it under the companies Act.
GLOBAL ENTERPRISES:-
Multinational company or global enterprises may be defined of a company that has business operations in several countries by having its factories, branches or offices in those countries. But is has its headquarter in one country in which it is incorporated.
Example:- PHILIPS, COCA COLA ,SAMSUNG etc.
FEATURES:-
- Huge capital resources:- These enterprises are characterized by possessing huge financial resources and the ability to raise funds from different sources. They are able to tap funds from various sources. They may issue equity shares, debentures or bonds to the public. They are also in a position to borrow from financial institution and international bank.
- Foreign Collaboration:- Global enterprises usually enter into agreements with Indian companies pertaining to the sale of technology, production of goods, use of brand names for the final products, etc. These MNCs may collaborate with companies in the public and private sector. There are usually various restrictive clauses in the agreement relating to transfer of technology, pricing, dividend payments, tight control by foreign technicians, etc.
- Advanced Technology:- These enterprises possess technological superiorities in their methods of production. They are able to conform to international standards and quality specification. they lead to industrial progress of country in which such corporation operate since they are able to optimally exploit local resources and raw material.
- Product Innovation:- These enterprises are characterized by having highly sophisticated research and development departments engaged in the task of developing new products and superior designs of existing products. Qualitative research requires huge investment which only global enterprises can afford.
- Marketing Strategies:- The marketing strategies of global companies are far more effective than other companies. They use aggressive marketing strategies in order to increase their sales in a short period. They posses a more reliable and up-to-date market information system.
- Expansion of Market Territory:- Their operation and activities extend beyond the physical boundaries of their own countries. Their international image also builds up and their market territory expends enabling them to become international brands.
- Centralized Control:- They have their headquarters in their home country and exercise control over all branches and subsidiaries. However, this control is limited to the broad policy framework of the parent company. There is no interference in day-to-day operations
Merits:-
- Employment Opportunities:- Multinationals create numerous employment opportunities in host countries because they carry on business on large scale.
- Advanced Technology:- Multinational companies act as a source of advanced technology because they have their own Research and Development (R & D) department, where they develop new techniques.
- Inflow of Foreign Capital:- Multinationals command huge financial resources. They make foreign direct investment (FDI), which leads to economic development of host countries.
- Improves standard of living:- by providing superior products and services, MNCs help to improve standard of living.
- Growth of Domestic firms:- The multinational companies also help in the growth of the domestic firms.
- Healthy Competition:- MNCs compel the local firms to improve their efficiency in order to face competition form them.
- World Economy:- Multinationals promote the concept of global economy. They help to integrate national economies into a world economy.
Demerits:-
- Disregard of National Priorities:- MNCs invest their capital only in the profitable projects without any regard to national priorities of the host county.
- Creation of Monopoly:- Multinationals give rise to concentration of economic power and monopoly in the host country.
- Depletion of natural resources:- MNCs exploit the resources of the host country to maximize their global profits.
- Obsolete technology:- The technology by MNCs in host countries is usually obsolete or outdated.
- Threat to National Sovereignty:- MNCs enjoy considerable political influence due to their huge operations.
JOINT VENTURES:-
When two or more firms join together for a common purpose and mutual benefit, it is known as joint venture. For Example- joint venture of Maruti with Suzuki.
- The firms may be private, government- owned or a foreign company.
- Joint ventures are very useful to strengthen long-term relationship or to collaborate on short-term projects.
- Firms enter into joint venture for business expansions, development of new products or moving into new markets, particularly in another county.
- Joint venture involves pooling of resources and expertise by two or more businesses in order to achieve a particular goal.
- A joint venture may also arise between firms of different countries. However, in such case, firms will have to comply with the provisions provided by the governments of the two countries.
Formation of joint Venture
- Transfer of business to new company:- Two parties incorporate a new company and business of one party is transferred to a new company in consideration of issue of shares to such party.
- New Joint Venture Company:- Both the parties subscribe to the shares of the joint venture company in cash in agreed ratio and start a new business.
- Collaborations of existing Indian company with other party:- When promoter shareholder of an existing Indian company collaborates with other party (resident or non-resident), to jointly carry on the business of that company.
TYPE OF JOINT VENTURES TYPES:-
Contractual Joint Venture (CJV):- In a contractual joint venture, a new jointly-owned entity is not created. There is only an agreement to work together. The parties do not share ownership of the business but exercise some elements of control in the joint venture. A typical example of a contractual joint venture is a franchisee relationship. Exp PNB Metlife , uber and volvo In such a relationship the key elements are:
- Two or more parties have a common intention- of running a business venture;
- Each party brings some inputs;
- Both parties exercise some control on the business venture
- The relationship is not a transaction-to-transaction relationship but has a character of relatively longer duration.
Equity-based Joint Venture (EJV) :- An equity joint venture agreement is one in which a separate business entity, jointly owned by two or more parties, is formed in accordance with the agreement of the parties. The key operative factor in such case is joint ownership by two or more parties. The form of business entity may company, partnership firm, trusts, limited liability partnership firms, venture capital funds exp. Air Asia India
- There is an agreement to either create a new entity or for one of the parties to join into ownership of an existing entity;
- Shared ownership by the parties involved;
- Shared management of the jointly owned entity;
- Shared responsibilities regarding capital investment and other financing arrangements;
- Shared profits and losses according to the agreement.
A joint venture must be based on memorandum of understanding signed by both parties ,highlighted the bases of joint venture agreement. the term should be discussed and negotiated to avoid any legal complications at the later stage.
BENEFITS:-
Business can achieve unexpected gains through joint ventures with a partner. Joint Ventures can prove to be extremely beneficial for both parties involved. One party may have strong potential for growth and innovative ideas, but is still likely to benefit from entering into a joint venture because it enhances its capacity, resources and technical expertise. The major benefits of joint ventures are as follows;
- Increased resources and capacity:- Joining hands with another or teaming up adds to existing resources and capacity enabling the joint venture company to grow and expand more quickly and efficiently. The new business pools in financial and human resources and is able to face market challenges and take advantage of new opportunities.
- Access to new markets and distribution networks:- When a business enters into a joint venture with a partner from another country, it opens up a vast growing market. For example, when foreign companies form joint venture companies in India they gain access to the vast Indian Market.
- Access to Technology:- Technology is a major factor for most businesses to enter into joint ventures. Advanced techniques of production leading to superior quality products saves a lot of time, energy and investment as they do not have to develop their own technology.
- Innovation:- The markets are increasingly becoming more demanding in terms of new and innovative products. Joint ventures allow business to come up with something new and creative for the same market. Specially foreign partners can come up with innovative products because of new ideas and technology.
- Low cost of production:- When international corporations invest in India, they benefit immensely due to the lower cost of production. They are able to get quality products for their global requirements. India is becoming an important global source and extremely competitive in many products.
- Established brand name:- When two businesses enter into a joint venture, one of the parties benefits from the other’s goodwill which has already been established in the market. If the joint venture is in India and with an Indian company, the Indian company does not have to spend time or money is developing a brand name for the product or even a distribution system
Disadvantages:-
- Conflict of Interest:- The dual ownership may lead to conflicts between the partners over control of business.
- Risk of Loss of Trade Secrets:- There is a risk of disclosure of technology and trade secrets.
- Lack of Coordination:- there can be lack of coordination among the partners, which may affect the efficient functioning of the Joint Venture.
PUBLIC PRIVATE PARTNERSHIP (PPP):-
The Public Private Partnership model allocates tasks, obligations and risks among the public and private partners in an optimal manner. The public partners in PPP are Government entities, ministries, government departments, municipalities or state owned enterprises. The private partners can be local or foreign (international) and include businesses or investors with technical or financial expertise relevant to the project. PPP also includes NGOs and/or community. Example of PPP redevelopment of railway stations ,international cricket stadium project.
Public Private Partnership Model
- Features:- The main features are:
- There is a contract with the private party to design and build public facility.
- The facility is financed and owned by the public sector.
- The key driver is the transfer of design and construction risk.
II. Application:- PPP is suitable in the following cases:
- It is suitable to capital projects with small operating requirement.
- It is also suitable to capital projects where the public sector wishes to retain the operating responsibility.
III. Strengths or Benefits:-
- Sharing of project Risks: The Structuring of a PPP project allocates the risks to the agency best-suited to handle the same.
- Increased Efficiency: Involvement of private sector brings efficiency in implementation of projects and cut down time and cost.
- Innovation: PPP helps in bringing innovation design and construction practices.
- Better Viability: Involvement of experienced and creditworthy sponsors and commercial lenders enhances viability of the project.
Short Answer Questions
1.Explain the concept of public sector and private sector.
Ans-
Public sector organisations are owned, controlled and managed by the government or other state-run bodies. Private sector organisations are owned, controlled and managed by individuals, groups or business entities.
2.State the various types of organizations in the private sector.
Ans –
- Sole proprietorship
- Joint Hindu Family business
- Partnership
- Cooperative societies
- Joint Stock Company
3.What are the different kinds of organizations that come under the public sector?
studynatic
Ans-
- DEPARTMENTAL UNDERTAKING
- STATUTORY CORPORATIONS
- GOVERNMENT COMPANY
4.List the names of some enterprises under the public sector and classify them.
- Indian railway-departmental undertaking
- Tamil Nadu police
- department- departmental undertaking
- Food cooperation of India-public cooperation
- Tourism cooperation in India -public cooperation
- Coal India ltd-government company
- Steel authority of India- government company
5.Why is the government company form of organization preferred to other types in the public sector?
Ans- Government company form of organization preferred to other types in the public sector because it has management and financial autonomy. the government company come directly under the concern ministry.
6.How does the government maintain a regional balance in the country?
ANS-The government maintain regional balance in the country by paying particular attention to those regions which were lagging behind and public sector industries were deliberately set up. This helps in creating employment opportunities and facilitate the economic development and growth of rural and backward areas.
7.State the meaning of public private partnership.
The Public Private Partnership model allocates tasks, obligations and risks among the public and private partners in an optimal manner. The public partners in PPP are Government entities, ministries, government departments, municipalities or state owned enterprises. The private partners can be local or foreign (international) and include businesses or investors with technical or financial expertise relevant to the project. PPP also includes NGOs and/or community.
studynatic
.
Long Answer Questions
1.Describe the industrial policy 1991, towards the public sector.
Ans-
The Industrial Policy of 1991 in India introduced significant reforms aimed at liberalizing the economy and reducing the role of the public sector in industry. The key features of the policy toward the public sector include:
1. Reduction in Reserved Areas: The number of industries reserved exclusively for the public sector was reduced from 17 to 8. This meant that several sectors previously monopolized by the government were opened up to private investment.
2. Disinvestment: The policy introduced a program of disinvestment in public sector enterprises (PSEs). This involved selling shares of PSEs to the public and private sector to reduce the fiscal burden on the government and improve efficiency.
3. Performance Improvement: Emphasis was placed on improving the performance of public sector enterprises through measures like greater autonomy, accountability, and professional management. The goal was to make PSEs more competitive and self-sustaining.
4. Sick Public Sector Units: The policy proposed measures to address the issue of loss-making and inefficient public sector units. This included restructuring, closing down unviable units, and divestment.
5. Greater Private Sector Participation: The policy encouraged greater participation of the private sector in areas previously dominated by the public sector, thereby fostering competition and efficiency.
6. Focus on Core Areas: The public sector was to focus on strategic, high-tech, and essential infrastructure areas where private sector participation was inadequate or not feasible.
Overall, the Industrial Policy of 1991 marked a shift from a heavily regulated and state-controlled industrial framework to a more liberalized, market-driven economy with a reduced but more strategic role for the public sector.
2.What was the role of the public sector before 1991?
Ans-
Before 1991, the public sector in India played a dominant role in the economy, reflecting the country’s socialist-inspired economic policies. Key aspects of the public sector’s role included:
1. Economic Development: The public sector was considered the primary engine for economic development. The government established public sector enterprises (PSEs) to build infrastructure, promote industrialization, and ensure equitable distribution of resources.
studynatic
2. Control of Key Industries: The public sector controlled and operated core and strategic industries such as steel, coal, heavy machinery, railways, telecommunications, and defense production. This was done to prevent monopolies and ensure that critical industries were aligned with national priorities.
3. Employment Generation: Public sector enterprises were significant employers, providing jobs to a large number of people, thus playing a crucial role in reducing unemployment and promoting social welfare.
4. Self-Reliance: The government aimed to achieve self-reliance in key sectors, reducing dependence on foreign technology and capital. This was part of the broader strategy to establish economic sovereignty.
5. Balanced Regional Development: The public sector was used as a tool to promote balanced regional development by setting up enterprises in underdeveloped and remote areas to stimulate economic activity and reduce regional disparities.
6. Revenue Generation: Public sector enterprises contributed significantly to government revenues through dividends, taxes, and other financial contributions.
7. Control of the Commanding Heights: The government maintained control over the “commanding heights” of the economy, a concept articulated by the first Prime Minister, Jawaharlal Nehru. This meant that the state would control critical sectors to ensure that they were run in the public interest and not just for private profit.
8. Social Equity: The public sector aimed to promote social equity by ensuring that essential goods and services were available to all sections of society at reasonable prices, often subsidized.
Overall, the role of the public sector before 1991 was to lead and regulate the economy, ensuring that development was broad-based, equitable, and aligned with national goals. However, this approach also led to inefficiencies, bureaucratic red tape, and financial losses in many public sector enterprises, which eventually prompted economic reforms and liberalization starting in 1991.
3.Can the public sector companies compete with the private sector in terms of profits and efficiency? Give reasons for your answer.
Ans-public sector companies not compete with the private sector in terms of profits and efficiency due to these reasons:
(i)Objective: Private sector firms operate with the objective of profit maximisation while public sector companies have social welfare as the prime objective and private sectors cannot be completely profit oriented.
(ii)Ownership: The government is the major shareholder in public sector companies. The management and administration of these companies, therefore, rest in the hands of the government which may not make economically sound policies due to political considerations.
(iii) Management: Public sector companies are managed by government officials who may not be professionally trained while private sector companies are run and managed by professional managers. This leads to higher efficiency in the private sector
(iv)Area of Operation: Private sector operates in all areas with an adequate return on investment while the public sector operates mainly in basic and public utility sectors where returns are not very high.
(v)Motive. The motive of public sector is social service whereas the motive of private sector is earning profit.
(vi)Autonomy. The working of public sector enterprise is subject to interference of government whereas private sector enjoys complete freedom of operation.
4.Why are global enterprises considered superior to other business organization?
Ans-Global enterprises may be defined of a company that has business operations in several countries by having its factories, branches or offices in those countries. But is has its headquarter in one country in which it is incorporated. Example:- PHILIPS, COCA COLA ,SAMSUNG etc.
Features
- Huge capital resources:- These enterprises are characterized by possessing huge financial resources and the ability to raise funds from different sources. They are able to tap funds from various sources. They may issue equity shares, debentures or bonds to the public. They are also in a position to borrow from financial institution and international bank.
- Foreign Collaboration:- Global enterprises usually enter into agreements with Indian companies pertaining to the sale of technology, production of goods, use of brand names for the final products, etc. These MNCs may collaborate with companies in the public and private sector. There are usually various restrictive clauses in the agreement relating to transfer of technology, pricing, dividend payments, tight control by foreign technicians, etc.
- Advanced Technology:- These enterprises possess technological superiorities in their methods of production. They are able to conform to international standards and quality specification. they lead to industrial progress of country in which such corporation operate since they are able to optimally exploit local resources and raw material.
- Product Innovation:- These enterprises are characterized by having highly sophisticated research and development departments engaged in the task of developing new products and superior designs of existing products. Qualitative research requires huge investment which only global enterprises can afford.
- Marketing Strategies:- The marketing strategies of global companies are far more effective than other companies. They use aggressive marketing strategies in order to increase their sales in a short period. They posses a more reliable and up-to-date market information system.
- Expansion of Market Territory:- Their operation and activities extend beyond the physical boundaries of their own countries. Their international image also builds up and their market territory expends enabling them to become international brands.
- Centralized Control:- They have their headquarters in their home country and exercise control over all branches and subsidiaries. However, this control is limited to the broad policy framework of the parent company. There is no interference in day-to-day operation
5.What are the benefits of entering into joint ventures and public private partnership?
Ans-When two or more independent firms together establish a new enterprise by pooling their capital, technology and expertise, it is known as a joint venture.
Example:- Hero cycle of india and Honda Motors Company of Japan jointly established Hero Honda. Similarily, Suzuki Motors of Japan and Maruti of Government of india come together to from Maruti suzuki.
BENEFITS:-
Business can achieve unexpected gains through joint ventures with a partner. Joint Ventures can prove to be extremely beneficial for both parties involved. One party may have strong potential for growth and innovative ideas, but is still likely to benefit from entering into a joint venture because it enhances its capacity, resources and technical expertise. The major benefits of joint ventures are as follows;
- Increased resources and capacity:- Joining hands with another or teaming up adds to existing resources and capacity enabling the joint venture company to grow and expand more quickly and efficiently. The new business pools in financial and human resources and is able to face market challenges and take advantage of new opportunities.
- Access to new markets and distribution networks:- When a business enters into a joint venture with a partner from another country, it opens up a vast growing market. For example, when foreign companies form joint venture companies in India they gain access to the vast Indian Market.
- Access to Technology:- Technology is a major factor for most businesses to enter into joint ventures. Advanced techniques of production leading to superior quality products saves a lot of time, energy and investment as they do not have to develop their own technology.
- Innovation:- The markets are increasingly becoming more demanding in terms of new and innovative products. Joint ventures allow business to come up with something new and creative for the same market. Specially foreign partners can come up with innovative products because of new ideas and technology.
- Low cost of production:- When international corporations invest in India, they benefit immensely due to the lower cost of production. They are able to get quality products for their global requirements. India is becoming an important global source and extremely competitive in many products.
- Established brand name:- When two businesses enter into a joint venture, one of the parties benefits from the other’s goodwill which has already been established in the market. If the joint venture is in India and with an Indian company, the Indian company does not have to spend time or money is developing a brand name for the product or even a distribution system
The Public Private Partnership model allocates tasks, obligations and risks among the public and private partners in an optimal manner. The public partners in PPP are Government entities, ministries, government departments, municipalities or state owned enterprises. The private partners can be local or foreign (international) and include businesses or investors with technical or financial expertise relevant to the project. PPP also includes NGOs and/or community. Example of ppp redevelopment of railway stations ,internation cricket stadium project.
FEATURES:-
- Facilitates partnership between public sector and private sector.
- Pertaining high priority project.
- Suitable for big project (capital intensive and heavy industries).
- Public welfare example Delhi Metro Railway Corporation.
- Sharing revenue – Revenue is shared between government and private enterprises in the agreed Ratio.