Short Answers
- What are the objectives of preparing financial statements?
Ans. The following are the objectives of preparing financial statements:
- To ascertain profit earned or loss incurred by a business during an accounting period.
This is estimated by preparing Trading and Profit and Loss Account.
b. To ascertain the true financial position of a business.
This is reflected by the Balance Sheet.
c. To enable comparison of current year’s performance with that of the previous year’s, i.e., intra-firm comparisons.
Also, to compare own performance with that of the other firms in the same industry, i.e., inter-firm comparisions.
d. To assess the solvency and credit worthiness of the business
e. To provide various provisions and reserves to meet unforeseen future conditions and to toughen the financial position of the business
f. To provide vital information to facilitate various users of accounting information in decision-making process.
2. What is the purpose of preparing trading and profit and loss account?
Ans. The preparation of the trading account is done in order to record the gross profit or loss of the concerned business organization for a particular accounting period. The profit and loss account on the hand helps the business to calculate the net profit or net loss incurred by the business for a particular accounting period. This thus helps the business to compare their business performance and the necessary actions in this regard.
3. Explain the concept of cost of goods sold?
Ans. Cost of goods sold (COGS) is the cost of merchandise that is sold to the customers. It includes cost of raw materials purchased, direct expenses incurred, value of opening stock, i.e., the value of the last year’s unsold stock and excludes closing stock if any, i.e., the value of current year’s unsold stock. The formula to calculate COGS is:
Cost of Goods Sold = Opening Stock + Purchases + Direct Expenses – Closing Stock
4. What is a balance sheet. What are its characteristics?
Balance sheet is referred to as the statement which tells about the position of the assets and the liabilities and the owner’s equity on the given particular date.
Following are the characteristics of the balance sheet:
- Balance sheet is not prepared for an entire period and thus it depicts the situation of the business of a particular date.
- Balance sheet is prepared only after the completion of the profit and loss statement for the accounting period in order to tell about the financial position of the business.
- Balance comprises of two sides – Assets & Liabilities. The figure of both the sides should tally with each other in the balance sheet.
- Balance sheets establish the value of the position of the business on a particular date by discussing the position of the assets and liabilities of the business.
5. Distinguish between capital and revenue expenditure and state whether the following statements are items of capital or revenue expenditure:
- Expenditure incurred on repairs and whitewashing at the time of purchase of an old building in order to make it usable.
- Expenditure incurred to provide one more exit in a cinema hall in compliance with a government order.
- Registration fees paid at the time of purchase of a building.
- Expenditure incurred in the maintenance of a tea garden which will produce tea after four years.
- Depreciation charged on a plant.
- The expenditure incurred in erecting a platform on which a machine will be fixed.
- Advertising expenditure, the benefits of which will last for four years.
Ans.
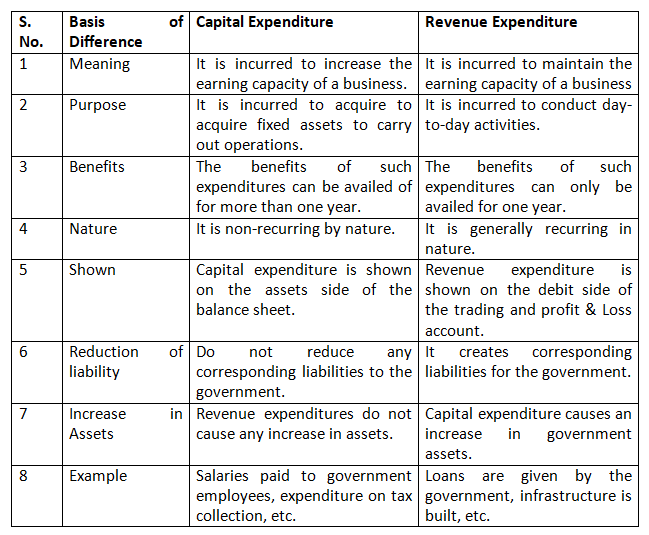
- Capital expenditure
- Revenue expenditure
- Capital expenditure
- Capital expenditure
- Revenue expenditure
- Capital expenditure
- Deferred expenditure
6. What is an operating profit?
Ans. The operating profit are considered to be the profit which is earned by the business from its core business operations. The calculation of the operating profit thus excludes interest and the taxes. The operating profit is thus determined by the following formula:
Operating profit = Gross profit – operating expenses – depreciation – amortization
Long Answers
- What are financial statements? What information do they provide?
Ans.
- The financial statements are considered to be the records which reflect the financial position and the condition of ay business activity.
- The financial statements are thus helpful in determining the financial standing of the company and the outcomes of the business process and the cash flows of the company.
- The information of the financial statements is used by the financial users of the business who determine the profitability of the business and determine their approach and the policies towards the business.
- It comprises of the Income Statements and the Statement of Financial Position
- Income statements or the Trading Profit and Loss Account – It represents the direct and the indirect expenses made by the entity in order to generate the revenues it made in the any accounting period. The trading account is prepared in order to determine the gross profit or the gross loss of the business and the Profit and Loss Account helps the business to determine the net profit or the loss incurred by the business for the given accounting period.
- Statement of financial position or the Balance Sheet is helpful in determining the true financial position of the business by disclosing the book value of the assets and the liabilities of the business. This thus is helpful in determining the profitability of the business at any given particular date.
2. What are closing entries? Give four example of closing entries.
Ans. The balance of all nominal accounts are transferred to the Trading and Profit and Loss Account. The entries required for such transfers are termed as closing entries. The example of closing entries are given below.
The balance of all nominal accounts are transferred to the Trading and Profit and Loss Account. The entries required for such transfers are termed as closing entries. The example of closing entries are given below.
- Closing entries to transfer the following items to the debit side of trading account from Trial Balance:
Trading A/c Dr.
To Opening Stock A/c
To Purchases A/c
To Wages A/c
To Carriage A/c
To All Other Direct Expenses A/c
(Transferred debit balance to Trading Account)
II. Closing entries to transfer the following items to the credit side of trading account form Trial Balance:
Sales A/c Dr.
Closing Stock A/c Dr.
To Trading A/c
(Transferred credit balances to Trading Account)
III. Closing entries to transfer the following items to the debit side of Profit and Loss Account from Trial Balance:
Profit and Loss A/c Dr.
To Salaries
To Rent
To Bad Debts
To All in direct expenses
(transferred debit balances to Profit and Loss Account)
IV. Closing entries to transfer the following items to the credit side of Profit and Loss Account from Trial Balance:
Commission Received A/c Dr.
Interest Received A/c Dr.
All Other Indirect Income A/c Dr.
To Profit and Loss A/c
(Transferred credit balance to profit and loss Account)
3. Discuss the need of preparing a balance sheet.
Ans. The needs to prepare a Balance Sheet are given below:
- It helps in determining the nature and book value of various assets, such as fixed assets, investments, current assets, etc. at the end of an accounting period.
- It helps in ascertaining the nature and amount of various liabilities like long-term liabilities, current liabilities, provisions, etc., which a business owes.
- It discloses important information about capital invested in a business.
The additional capital invested during the accounting period, drawings of the owners and profit (or loss) added to (or deducted from) the capital of the business.
- It helps in assessing the solvency of a business.
- It discloses the true financial position of a business at a particular point of time.
- It lays down the basis for maintaining new books for next accounting period.
4. What is meant by Grouping and Marshalling of asset and liabilities. Explain the ways in which a balance sheet may be marshalled.
Ans. The rationale behind preparing financial statements is to present a summarized version of all financial activities in such a manner that all users can interpret and understand the information easily, appropriately and also take decisions accordingly.
Grouping of asset liabilities:- Grouping means showing similar assets and liabilities under a single head.
For example, all assets that can be used for more than a year are clubbed together under the heading ‘fixed assets’, for example, building, furniture, machinery, etc.
Marshalling of asset and liabilities: When assets and liabilities are shown in a particular order of liquidity or permanence, they are said to be marshaled.
In order of liquidity: liquidity means convertibility into cash. Assets that can be converted into cash in least possible time, i.e., more liquid assets are recorded first, followed by the lesser liquid assets. In a balance sheet, cash in hand is recorded at first and goodwill at last. In the same way, liabilities that are to be paid first, i.e., high priority liabilities are recorded first, followed by the lower priority ones. In a balance sheet, current liabilities are recorded first and then the long-term liabilities and capital at the last.
Balance Sheet of ……….., as on………….
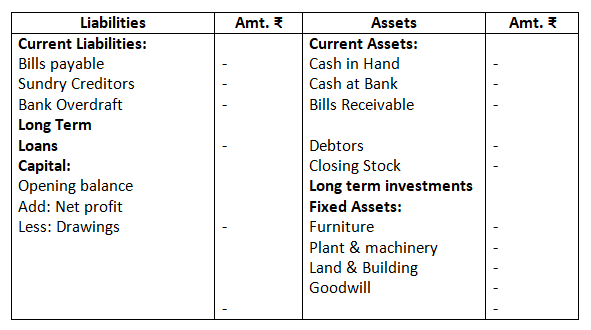
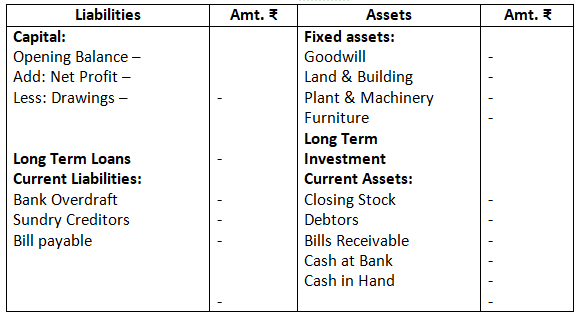
II. In order or permanence:- It is just the reverse of the above method. In this, assets and liabilities are arranged in their reducing level of permanence. The asset with higher degree of permanence are recorded first, followed by the assets with lower degree of permanence. For example, goodwill, land and building have the highest degree of permanence and hence are recorded at the top, whereas, cash at bank and cash in hand are recorded at the bottom. In the same way, liabilities are shown according to their life in the business. Liabilities with higher level of permanence like, capital is recorded at the top and other liabilities with lower permanence are recorded at the bottom.
Balance Sheet of ……….., as on………….
Numerical Questions
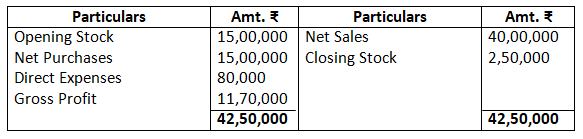
- From the following balances taken from the books of Simmi and Vimmi Ltd. For the year ending March 31, 2017, calculate the gross profit.
Closing stock 2,50,000
Net sales during the year 40,00,000
Net purchases during the year 15,00,000
Opening stock 15,00,000
Direct expenses 80,000
Solution:-
Dr. Trading Account as on March, 31, 2017 Cr.
2. Form the following balances extracted from the books of M/s Ahuja and Nanda. Calculate the amount of:
- Cost of goods available for sale
- Cost of goods sold during the year
- Gross Profit
Opening stock Rs.25,000
Credit purchases Rs.7,50,000
Cash purchases Rs.3,00,000
Credit sales Rs.12,00,000
Cash sales Rs.4,00,000
Wages Rs.1,00,000
Salaries Rs.1,40,000
Closing stock Rs.30,000
Sales return Rs.50,000
Purchases return Rs.10,000
Solution:-
- Cost of Goods Sold Available for Sales = Opening Stock + Net Purchases + Wages
= 25,000 + 10,40,000 + 1,00,000
= Rs.11,65,000
b. Cost of Goods Sold = Opening Stock + Net Purchases + Wages – Closing Stock
= 25,000 + 10,40,000 + 1,00,000 – 30,000
= Rs.11,35,000
c. Dr. Trading Account Cr.
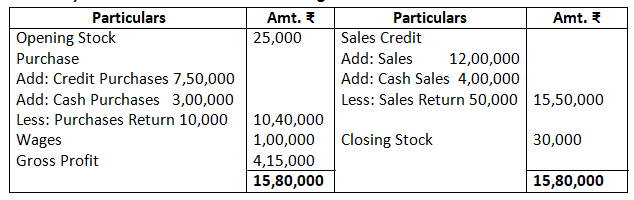
Gross Profit Rs.4,15,000.
3. Calculate the amount of gross profit and operating profit on the basis of the following balances extracted from the books of M/s Rajiv & Sons for the year ended March 31, 2017.
Opening stock Rs.50,000
Net sales Rs.11,00,000
Net purchases Rs.6,00,000
Direct expenses Rs.60,000
Administration expenses Rs.45,000
Selling and distribution exp. Rs.65,000
Loss due to fire Rs.20,000
Closing stock Rs.70,000
Solution:-
Dr. Trading Account as of March, 31, 2017 Cr.
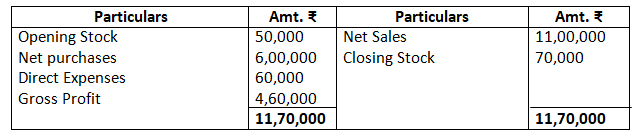
Operating Profit = Net profit + Non operating expenses – Non operating incomes
Operating Profit = Sales – (Opening Stock + Net Purchases + direct Expenses + Administration Expenses + Selling and Distribution Expenses) + Closing Stock
= 11,00,000 – (50,000 + 6,00,000 + 60,000 + 45,000 + 65,000) + 70,000
= 11,00,00 – 8,20,000 + 70,000
= Rs.3,50,000
4. Operating profit earned by M/s Arora & Sachdeva in 2016 – 17 was Rs.17,00,000. Its non-operating incomes were Rs.1,50,000 and non-operating expenses were Rs.3,75,000. Calculate the amount of net profit earned by the firm.
Solution:-
Net Profit = Operating Profit + Non-operating Income – Non-operating Expenses
= 17,00,000 + 1,50,000 – 3,75,000
= 14,75,000
Net profit earned by M/S Arora and Sachdeva in 2016 – 17 is Rs.14,75,000.
5. The following are the extracts from the trial balance of M/s Bhola & Sons as on March 31, 2017
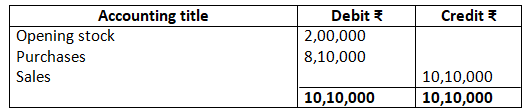
(only relevant items)
Closing Stock as on date was valued at Rs.3,00,000.
You are required to record the necessary journal entries and show how the above items will appear in the trading and profit and loss account and balance sheet of M/s Bhola & Sons.
Solution:-
Books of M/s Bhola and Sons
Journal
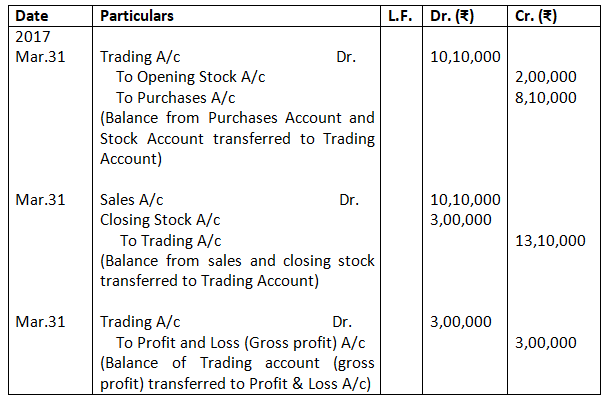
Dr. Trading Account as on March 31, 2017 Cr.
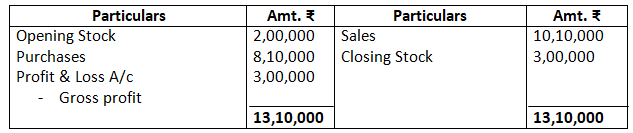
Balance Sheet as on March 31, 2017

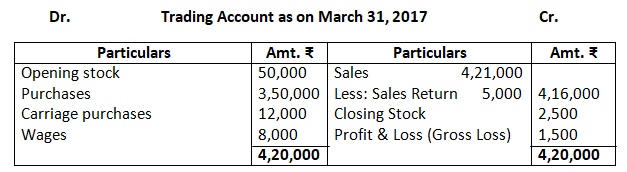
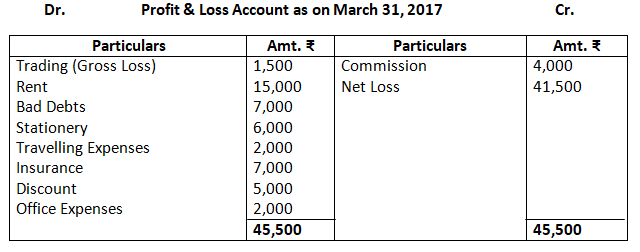
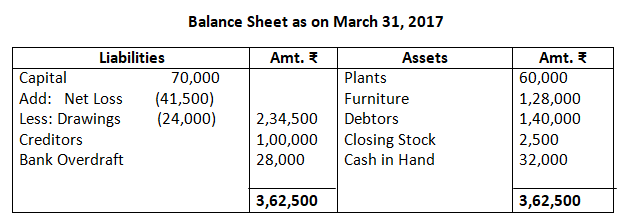
6. Prepare trading and profit and loss account and balance sheet as on March 31, 2017:
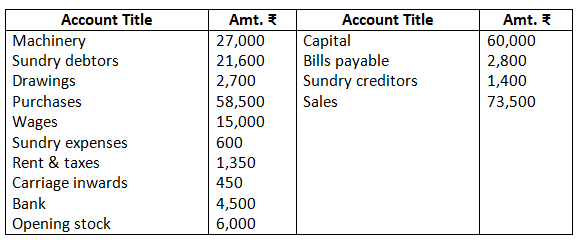
Closing stock as on March 31, 20178 Rs.22,400.
Solution:-
Dr. Trading Account as on March 31, 2017 Cr.
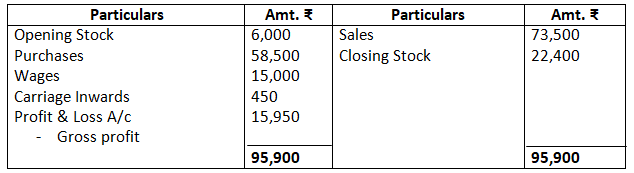
Dr. Profit & Loss Account as on March 31, 2017 Cr.
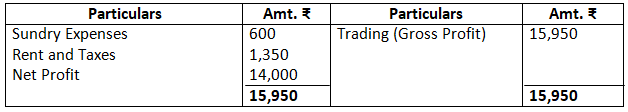
Balance Sheet as on March 31, 2017
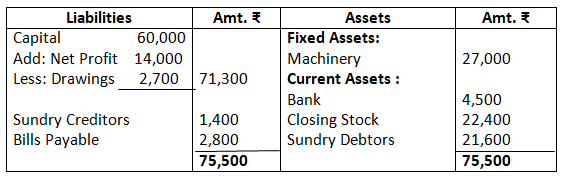
7. The following trial balance is extracted from the books of M/s Ram on March 31, 2017. You are required to prepare trading and profit and loss account and the balance sheet on date:
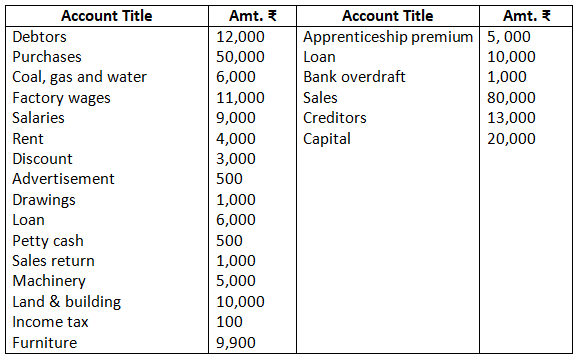
Solution:-
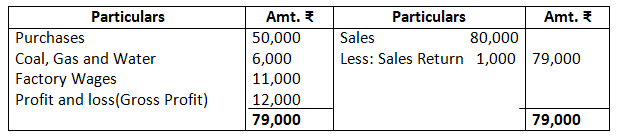
Dr. Trading Account as on March 31, 2017 Cr.
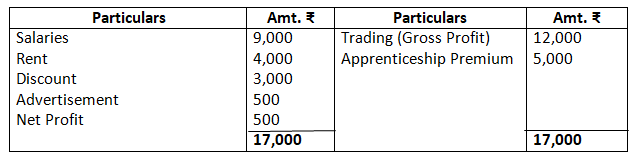
Dr. Profit & Loss Account as on March 31, 2017 Cr.
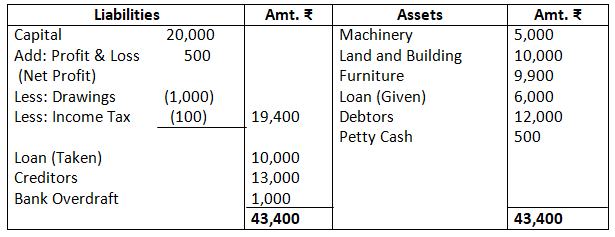
Balance Sheet as on March 31, 2017
8. The following is the trial balance of Manju Chawla on March 31, 2017. You are required to prepare trading and profit and loss account and a balance sheet as on date:
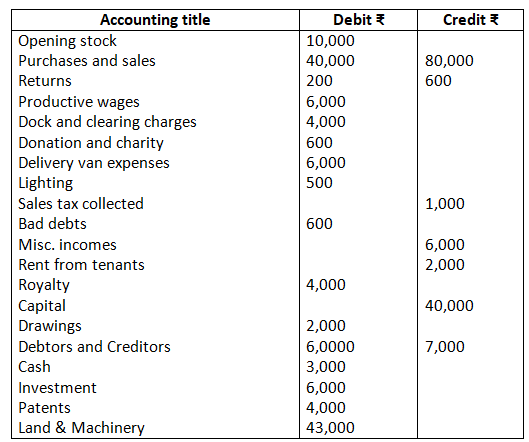
Closing stock Rs.2,000.
Solution:-
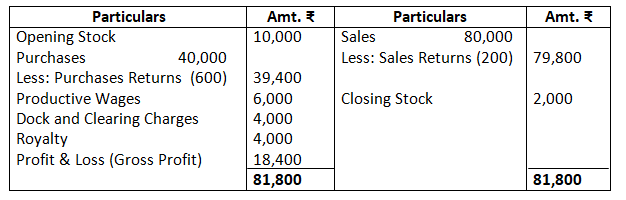
Dr. Trading Account as on March 31, 2017 Cr.
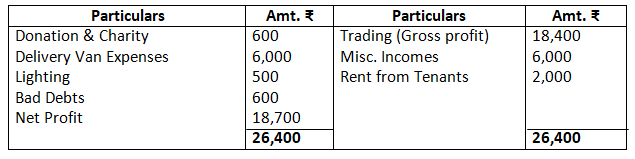
Dr. Profit & Loss Account as on March 31, 2017 Cr.
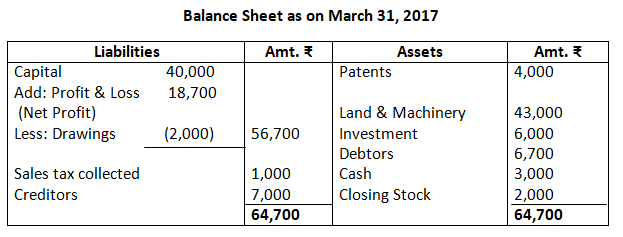
Note:
As per the solution, net profit is R.18,700; however, according to the answer given in the book, it is Rs.18,400. There is a misprint the trial balance given in the questions. In order to match the trial balance, debtors have been taken as Rs.6,700; however, the debtors given in the trial balance is Rs.60,000.
9. The following is the trial balance of Mr.Deepak as on March 31, 2017. You are required to prepare trading account, profit and loss account and a balance sheet as on date:
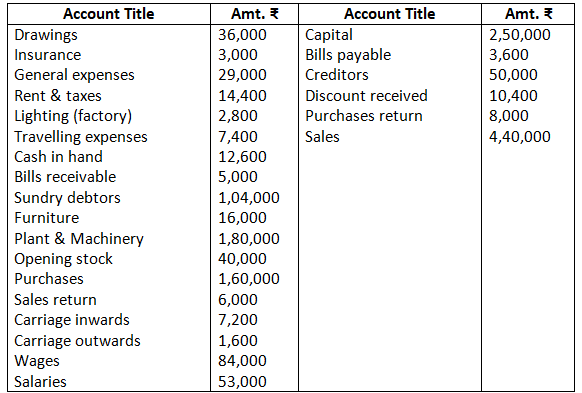
Closing stock Rs.35,000
Solution:-
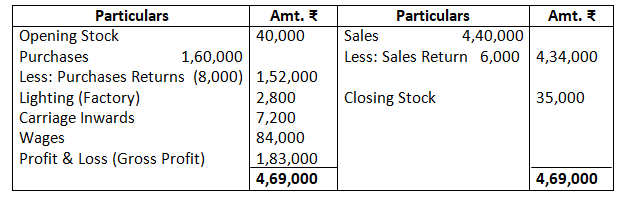
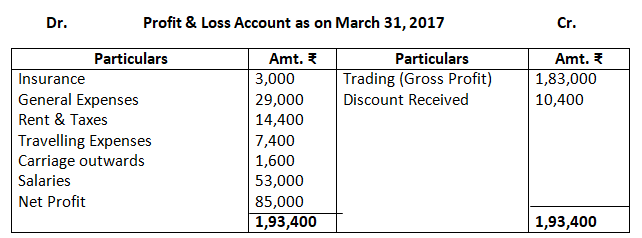
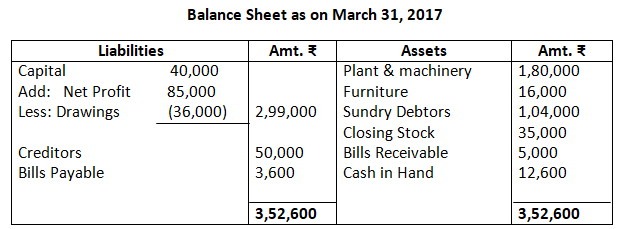
Dr. Trading Account as on March 31, 2017 Cr.
10. Prepare trading and profit and loss account and balance sheet from the following particulars as on March 31, 2017.
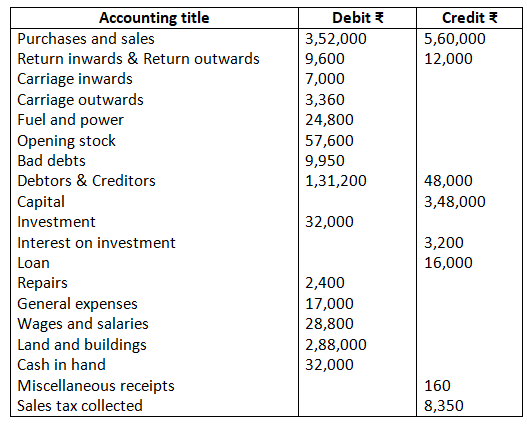
Closing stock Rs.30,000.
Solution:-
Dr. Trading Account as on March 31, 2017 Cr.
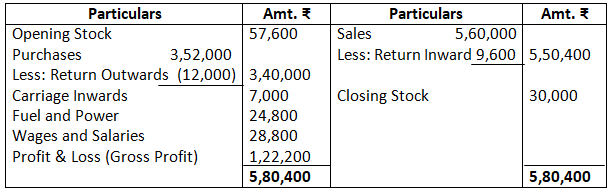
Dr. Profit & Loss Account as on March 31, 2017 Cr.
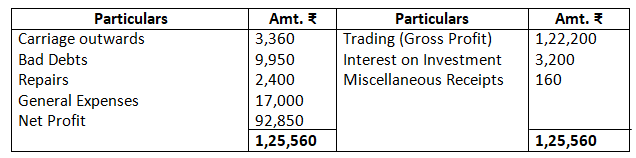
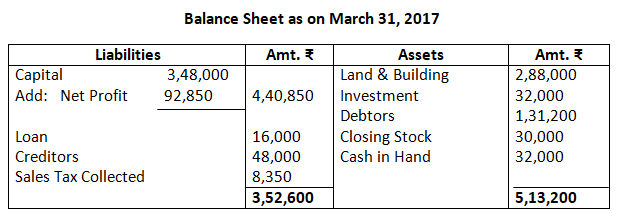
11. From the following trial balance of Mr. A. Lal, prepare trading, profit and loss account and balance sheet as on March, 31, 2017.
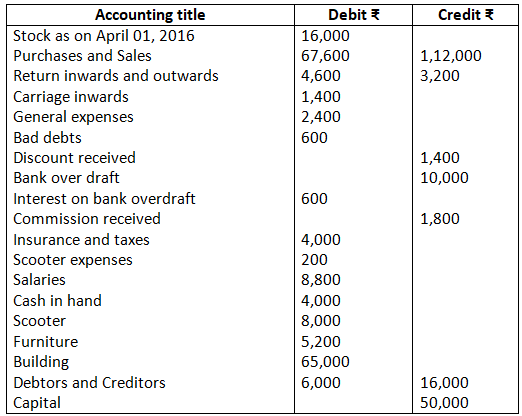
Closing stock Rs.15,000.
Solution:-
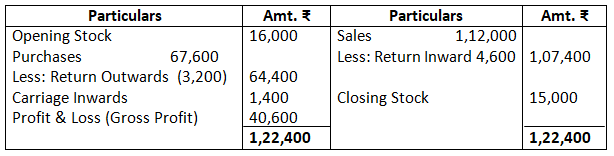
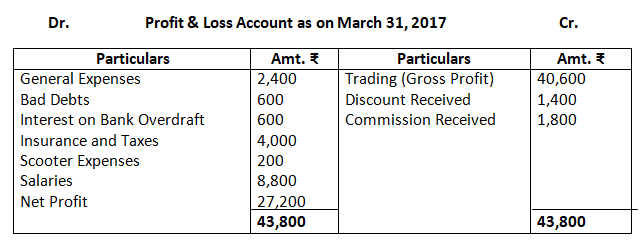
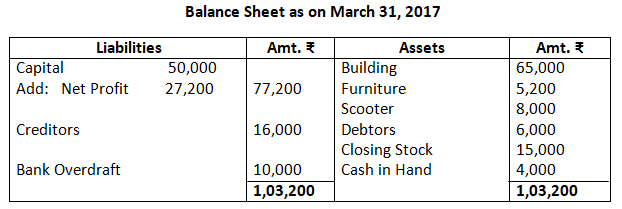
Dr. Trading Account as on March 31, 2017 Cr.
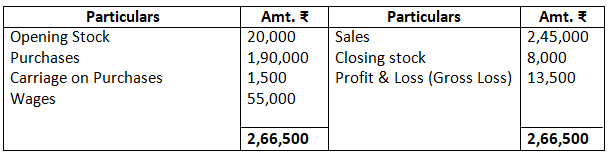
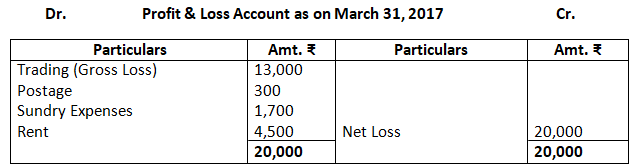
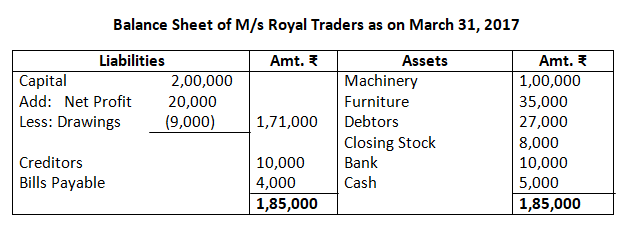
12. Prepare trading and profit and loss account and balance sheet of M/s Royal Traders from the following balance as on March 31, 2017.
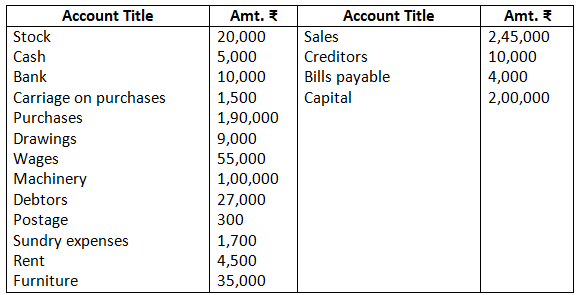
Closing stock Rs.8,000
Solution:-
Dr. Trading Account as on March 31, 2017 Cr.
13. Prepare trading and profit and loss account from the following particulars of M/s Neema Traders as on March 31, 2017.
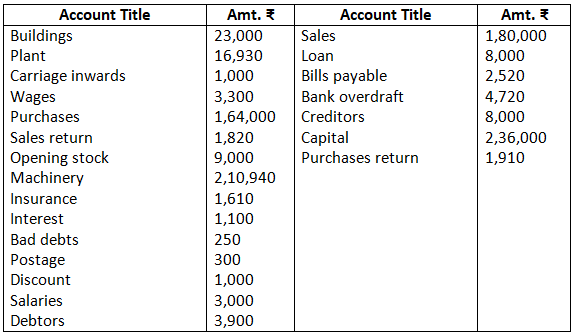
Stock on March 31, 2017 Rs.16,000.
Solution:-
Dr. Trading Account as on March 31, 2017 Cr.
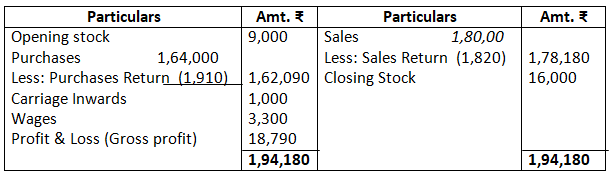
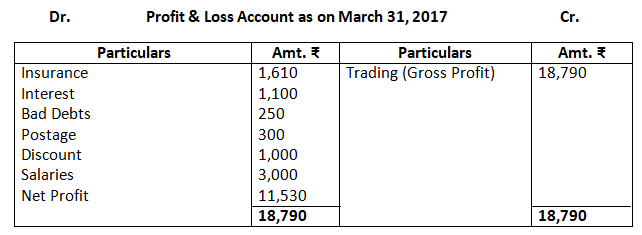
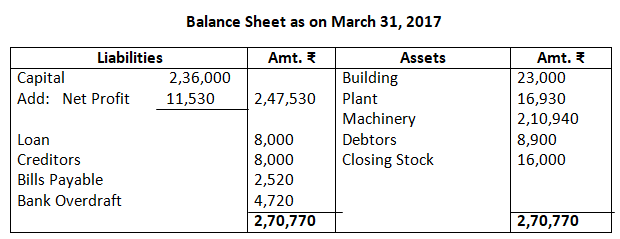
14. From the following balances of M/s Nilu Sarees as on March 31, 2017. Prepare trading and profit and loss account and balance sheet as on date.
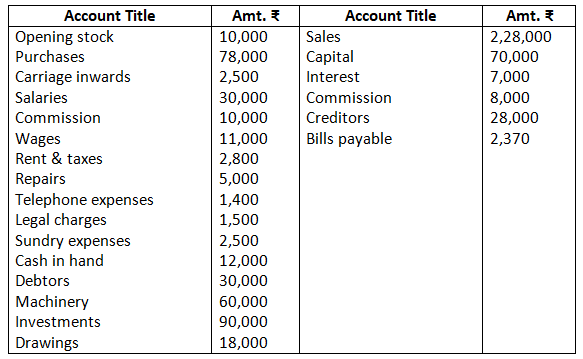
Closing stock as on March 31, 2017 Rs.22,000.
Solution:-
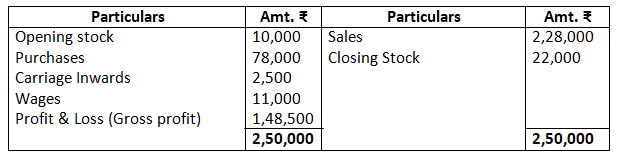
Dr. Trading Account as on March 31, 2017 Cr.
Note:
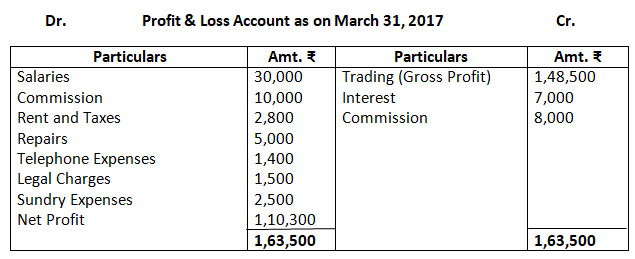
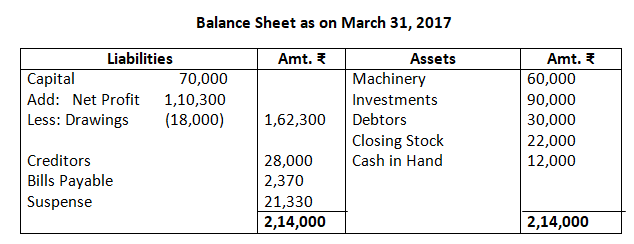
As per solution, the Gross profit is Rs.1,48,500; however, the answer given in the book is Rs.1,56,500. The trial balance given in the questions has an error, as the balance of the debit exceeds the credit side by an amount of Rs.21,330. Therefore, in order to match the two sides of the balance sheet, suspense has been opened with an amount equal to the difference amount, i.e. by Rs.21,230.
15. Prepare trading and profit and loss account of M/s Sports Equipments for the year ended March 31, 2017 and balance sheet as on that date:
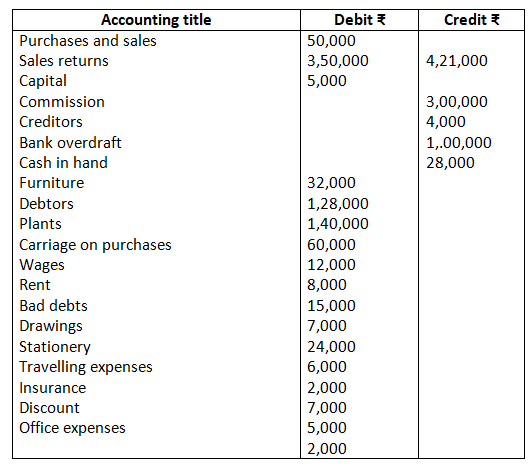
Closing stock as on March 31, 2017 Rs.2,500.
Solution:-