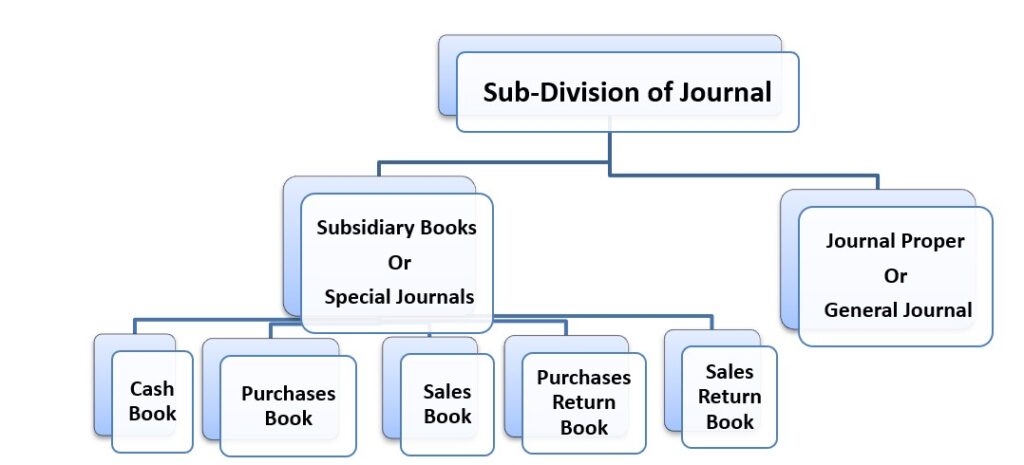
Purchases Book or Purchases Journal:-
Purchases Book is a subsidiary book in which credit purchases of goods, i.e., Goods in which the firm deals or uses for manufacturing goods are recorded. Thus, cash purchases of goods and purchases of non-goods like fixed assets are not recorded in Purchases Book. The entries in the purchases Book are recorded on the basis of Invoices received from the suppliers with the amount net of trade discount, i.e., List price or catalogue Price less Trade Discount.
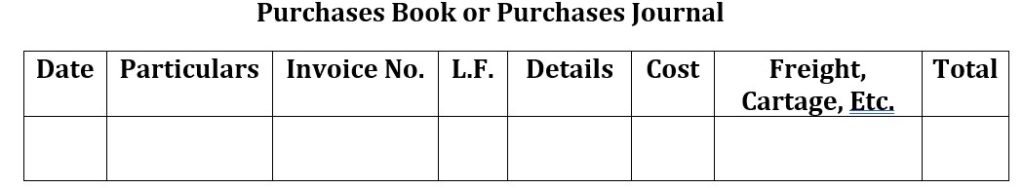
Sales Book or Sales Journal:-
Sales Book or Sales Journal is a subsidiary Book or Special Journal in which credit sales of goods dealt in by the firm are recorded. Cash sales are recorded in the Cash Book and not in the Sales Book. Also, credit sales of items other than goods dealt in by the firm (e.g., sale of assets) are not recorded in the Sales Book; they are recorded in Journal Proper. Entries in the Sales Book are on the basis of invoices issued to the customers with the net amount after allowing trade discount.
sales book or sales return book
Purchases Return Book or Returns Outward Book:-
Purchases Return Book or Returns Outward Book is a subsidiary book maintained to record the goods or materials returned to the sellers of goods that were purchased on credit. Neither the return of goods purchased on cash nor the returns of any asset are recorded in this book. Goods may be returned because of any of the following reasons:
- Goods are not as per sample.
- Goods are defective.
- Goods are not as per order.
- Goods have been delivered late and the customer has refused to accept them.

Sales Return Book or Returns Inward Book:-
A Book to record returns of goods sold on credit. Sales Returns Book or Returns Inward Book is a subsidiary book maintained to record the goods or materials returned by the purchaser that had been sold on credit. This book is maintained if the return of goods is frequent otherwise it can be recorded in the Journal.
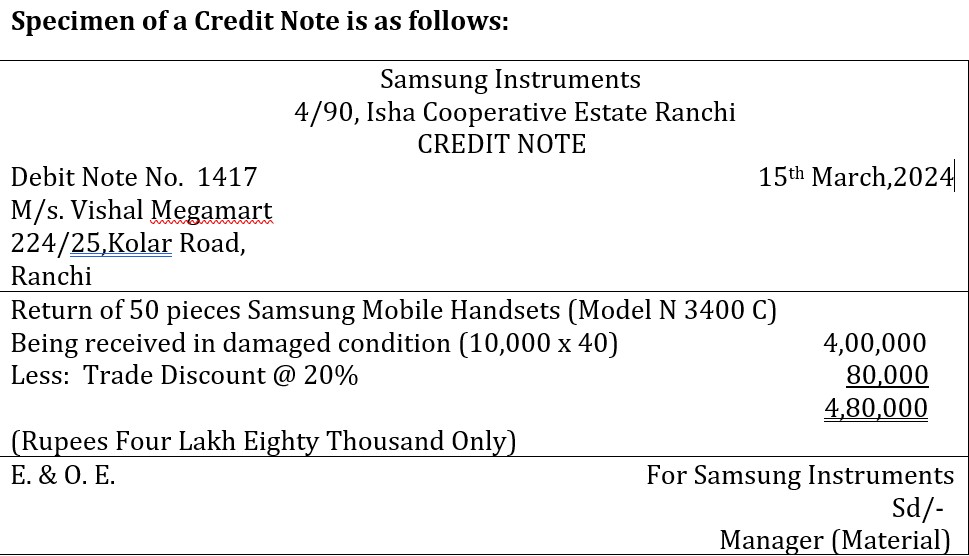
A credit Note is Prepared when goods are returned by the purchaser and on its basis entry is recorded in the Sales Return Book. Credit Note is a document evidencing that a credit entry has been recorded to the account of the debtor.
Journal Proper or General Journal:-
Journal Proper is used for recording those transactions which cannot be recorded in any of the other subsidiary books. The role of the Journal Proper is, thus, usually restricted to the Following Types of entries:
- Opening Entry – Opening entry is recorded in the beginning of a financial year to open the books by debiting assets and crediting liabilities and the capital appearing in the Balance Sheet of the previous year.
Entry: Sundry Assets A/c ….Dr
To Sundry Liabilities A/c
To Capital A/c
- Closing Entries – Closing entries are passed at the end of the year to close the accounts relating to expenses and revenues (or Nominal Accounts) by transferring them to the Trading Account and Profit and Loss Account. For example, the Salary Account is closed by transferring its balance to the Profit and Loss Account, the Purchases Account is closed by transferring its balance to the Trading Account and so on.
The entries passed are:
For Closing Purchases Account:
Trading A/c …Dr
To Purchases A/c
For Closing Sales Account:
Sales A/c ….Dr
To Trading A/c
For Closing Salaries Account:
Profit and Loss A/c ….Dr
To Salaries A/c
- Rectification Entries – Entries to rectify the errors in the books of original entries or of a Ledger are recorded in the Journal Proper.
- Transfer Entries – If an amount is to be transferred from one account to another, such a transfer is also made through a Journal entry.
- Adjustment Entries – At the end of the year, the amount of expenses or incomes may have to be adjusted for amounts paid or received in advance or for amounts yet to be paid. Such an adjustment is also made through Journal entries. Usually the adjustment entries are for the following:
- Outstanding expenses, i.e., expenses incurred but not yet paid;
- Prepaid expenses, i.e., expenses already paid in advance for some period in the future;
- Accrued Incomes, i.e., income earned but not yet received;
- Income Received in Advance, i.e., income that has not been earned but received in advance;
- Interest on capital, i.e., the interest which the proprietor thinks proper to allow on his investment;
- Depreciation, i.e., fall in the value of the assets used on account of wear and tear over a period. Miscellaneous Entries – Besides the above, the following entries also require journalising:
- Credit purchase of goods other than goods dealt in or materials required for production of goods, e.g., credit purchase of furniture or machinery will be journalised.
- Discount allowed and Discount Received.
- An allowance to be given to customers or a charge to be made to them after the issue of the invoice.
- On an amount becoming irrecoverable, say, because of the customer becoming insolvent.
- Effects of accidents such as loss of property by fire.
- Capital brought in kind by the proprietor.