- Calculate Current Ratio from the following information:
| Particulars | ₹ | Particulars | ₹ |
| Equity Share Capital Inventories Trade Receivables Advance Tax | 8,00,000 1,00,000 1,20,000 24,000 | Cash & Cash Equivalents Trade Payables Sort-term Borrowings (Bank Overdraft) 10% Investments | 56,000 60,000 40,000 80,000 |
Solution:- Current ratio= Current assets / Current liabilities
Current assets= trade receivable + inventories+ advance tax+ cash and cash equivalent
1,20,000+100,000+24000+56000=300,000
Current liabilities =trade payable+ short term borrowing
60,000+40,000=100,000
Current Ratio = 3 : 1.
2. Calculation current ratio from the following information:
| Particulars | ₹ | Particulars | ₹ |
| Total assets Fixed tangibles assets Shareholder’s funds | 20,00,000 10,00,000 12,80,000 | Non-current liabilities Non-current Investments | 5,20,000 6,00,000 |
Solution:-
Current assets = total assets – fixed tangible assets – noncurrent investment
=200000 – 100000 – 60000
= 40000
Calculation of current liabilities
Current liabilities = total assets – share holder’s fund – noncurrent liabilities
= 200000-1280000-520000
= 200000
Calculation of current ratio
Current ratio = Current assets / current liabilities
Current ratio = =2:1
3. A company had current Assets of 4,50,000 and current liabilities of 2,00,000. Afterwards it purchased goods for 30,000 on credit. Calculate current Ratio after the purchase.
Solution:
Calculation of Current Assets & Current Liabilities After Purchase
Current Assets After purchase = Current Assets + Stock
= 4,50,000 + 30,000
= 4,80,000
Current liabilities After purchase = Current liabilities + Creditors
= 2,00,000 + 30,000
= 2,30,000
Calculation of Current Ratio After purchase
= Current assets after purchase / Current Liabilities after purchase
= 4,80,000/2,30,000
= 2.09:1
4. Working capital 6,00,000, Total Debt 27,00,000, Non-Current Liabilities 24,00,000. Calculate Current Ratio.
Solution:
Calculation of Current Liabilities
Total Debt = Non-current liabilities + Current Liabilities
27,00,000 = 24,00,000 + Current Liabilities
Current Liabilities = 27,00,000 – 24,00,000
= 3,00,000
Calculate of current Assets
Working capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities
6,00,000 = Current Assets – 3,00,000
Current Assets = 6,00,000 + 3,00,000
= 9,00,000
Calculation of Current Ratio
Current ration = current assets / current liabilities
= 9,00,000 / 3,00,000
= 3:1
= 3:1
5. Current Ratio is 2.5, working capital is 1,50,000. Calculate the amount of current Assets and Current Liabilities.
Solution:
Current Ratio = 2.5
Current ration =
2.5 =
C.A. = 2.5 C.L ————————1
Working capital = Current Assets – current Liabilities
150000 = C.A – C.L.
C.A – C.L. = 1,50,000—————————-2
Putting Eq (1) into Eq (2)
1,50,000 = 2.5 C.L – C.L
1.5 C.L = 1,50,000
C.L =
Current liabilities = 1,00,000
Putting C.L value in Eq (1)
Current Assets = 2.5 x 1,00,000
= 2,50,000
6. Working capital is 18,00,000; trade payables 1,80,000; and other current liabilities are 4,200,000. Calculate Current Ratio.
Solution:
Calculation of current liabilities
Current liabilities = Trade payable + other current liabilities
= 1,80,000 + 4,20,000
= 6,00,000
Calculation of current Assets
Working capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities
1,80,000 = Current Assets – 6,00,000
Current Asses = 24,00,000
Calculation of Current Ratio
Current ration = current assets / current liabilities
= 24,00,000 /6,00,000
= 4:1
7. Working capital 9,00,000; total debts (Liabilities) 19,50,000; Long-term Debts 15,00,000. Calculate Current Ratio.
Solution:
Calculation of Current Liabilities
Total debts = Non-Current liabilities + Current liabilities
19,50,000 = 15,00,000 + Current liabilities
Current liabilities = 19,50,000 – 15,00,000
= 4,50,000
Calculation of Current Assets
Working capital = Current Assets – Current liabilities
9,00,000 = Current Assets – 4,50,000
Current assets = 9,00,000 + 4,50,000
= 13,50,000
Calculation of Current Ratio
Current ration = current assets / current liabilities
= 13,50,000 / 4,50,000
= 3:1
8. Current Assets 7,50,000 and working capital is 2,50,000. Calculate Current Ratio.
Solution:
Calculation of Current Liabilities
Working capital = Current Assets – Current liabilities
2,50,000 = 7,50,000 – Current liabilities
Current liabilities = 5,00,000
Calculation of Current Ratio
Current ration = current assets / current liabilities
= 7,50,000 / 5,00,000
= 1.5:1
9. Current liabilities of a company were 1,75,000 and its current Ratio was 2:1. It paid 30,000 to a creditor, calculate Ratio after payment.
Solution:
Calculation of current Assets before payment
Current liabilities = 1,75,000
Current Ratio = 2:1
Current ratio = current assets / current liabilities
2 = Current assets / 1,75,000
Current Assets = 1,75,000 x 2
= 3,50,000
Calculation of current Assets ofter payment
Current Assets = 3,50,000 – 30,000 = 3,20,000
Current liabilities = 1,75,000 – 30,000 = 1,45,000
New current Ratio = 3,20,000
After payment 1,45,000
2.21:1
10. Current Assets 20,00,000, inventories 10,00,000, working capital 12,00,000. Calculate current ratio.
Solution:
Calculation of current liabilities
Working capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities
12,00,000 = 20,00,000 – Current liabilities
Current liabilities = 20,00,000 – 12,00,000
= 80,00,000
Calculation of current Ratio
Current ration = current assets / current liabilities
= 20,00,000 / 80,000
= 2.5:1
11. Trade payables 50,000, Working capital 9,00,000, current liabilities 3,00,000. Calculate Current Ratio.
Solution:
Calculation of current Assets
Working capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities
9,00,000 = Current Assets – 3,00,000
Current Assests = 9,00,000 + 3,00,000
= 12,00,000
Calculation of Current Ratio
Current ration = current assets / current liabilities
= 12,00,000 / 3,00,000
= 4:1
12. Ratio of current (3,00,000) to current liabilities (2,00,00) is 1.5:1. The accountant of the firm is interested in maintaining a current Ratio of 2:1 by paying off a part of the current liabilities. Compute amount of the current liabilities that should be paid so that the current Ratio at the level of 2:1 may be maintained.
Solution:
Current Assets = 3,00,000
Current liabilities = 2,00,000
The accountant of the firm wants to maintain current ratio as 2:1
Let the current liabilities paid off be X
2 = 300000 – X
200000 – X
2(200000 – x) = 300000 – x
400000 – 2x = 300000 – x
X = 1,00,000
Thees, the liabilities to be paid off = 100000
13. Ratio of current assets (8,75,000) to current liabilities (3,50,000) is 2.5:1. The firm wants to maintain current Ratio of 2:1 by purchasing goods on credit. Compute amount of goods that should be purchased on credit.
Solution:
Current Assets = 8,75,000
Current liabilities = 3,50,000
The accountant of the firm wants to maintain current ratio as 2:1
Let the goods purchased on credit be X
It would increase stock & creditors at the same time
As per the question:
= 2 = 8,75,000+x / 3,50,000+x
2 (3,50,000 + x) = 8,75,000 + x
7,00,000 + 2x = 8,75,000 + x
X = 1,75,000
Thus good purchased on credit would be 1,75,000
14. A firm had current Assets of 5,00,000. It paid current liabilities of 1,00,000 and the current Ratio became 2:1. Determine current liabilities and working capital before and after the payment was made.
Solution:
Calculation of current Assets & Current liabilities before payment
Current Assets = 5,00,000
As per the question
Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
2 = 5,00,000 – 1,00,000 / C.L-1,00,000
2(C.L – 1,00,000) = 4,00,000
2 C.L – 2,00,000 = 4,00,000
= 2 C.L = 6,00,000
= Current liabilities = 3,00,000
Calculation of working capital before payment
= current Assets before payment = 5,00,000
= current liabilities before payment = 3,00,000
Working capital = current Assets – current liabilities
= 5,00,000 – 3,00,000
= 2,00,000
Calculation of working capital ofter payment
C.A after payment = 5,00,000 – 1,00,000 = 4,00,000
C.L offer payment = 3,00,000 – 1,00,000 = 2,00,000
Working capital after payment = 4,00,000 – 2,00,000
= 2,00,000
15. A firm had current liabilities of 5,40,000. It purchased stock of 60,000 on credit. After the purchase of stock. Current ratio was 2:1. Calculate current Assets and working capital after and before the stock was purchased.
Solution:
Current liabilities = 5,40,000
Stock purchased = 60,000
Current liabilities after = 5,40,000 + creditors of stock
= 5,40,000 + 60,000
= 6,00,000
Current ratio after stock Purchased = Current Assets + Stock / Current liabilities after stock purchase on credit
2 = Current Assets + 60,000 / 6,00,000
Current Assets before stock purchased = 12,00,000 – 600,000 = 11,40,000
Current Assets after stock = Current Assets before stock
Purchased purchased + stock
= 11,40,000 + 60,000 = 12,00,000
Working capital before purchase = current Assets – current liabilities
After purchased after purchased
= 12,00,000 – 6,00,000
= 6,00,000
16. State, giving reason, whether the current Ratio will improve of decline or will have no effect in each of the following transaction if current Ratio is 2:1:
- Cash paid to Trade payables.
- Bills payable discharged.
- Bills receivable endorsed to a creditor.
- Payment of final dividend already declared.
- Purchase of stock-in-Trade on credit.
- Bills receivable endorsed to a creditor dishonoured.
- Purchase of stock-in-Trade for cash.
- Sale of Fixed Assets (Book value of 50,000) for 45,000
- Sale of fixed assets (Book value of 50,000) for 60,000.
Solution-
- Improve;
- Improve;
- Improve;
- Improve;
- Decline;
- Decline;
- No Effect;
- Improve;
- Improve.
17. From the following information, calculate liquid Ratio:
| Particulars | ₹ | Particulars | ₹ |
| Current Assets Inventories Prepaid Expenses | 4,00,000 1,00,000 20,000 | Trade Receivables Current Liabilities | 2,00,000 1,40,000 |
Solution:
Liquid Assets = Current Assets – Inventories– Prepare Expenses
= 4,00,000 – 1,00,000 – 20,000
= 2,80,000
Current liabilities = 1,40,000
Liquid Ratio = Liquid Assets / Current Liabilities
= 2,80,000 / 1,40,000
= 2:1
18. From the following information, calculate Quick Ratio:
Total Debt 12,00,000
Total Assets 16,00,000
Property, plant and
Equipment (Fixed Assets) 6,00,000
Non-Current investments 1,00,000
Long- term Borrowings 4,00,000
Long-term provisions 4,00,000
Long-term Loans & Advances 1,00,000
Inventories 1 ,90,000
Prepaid Expenses 10,000
Solution:
Current Liabilities = Total Debt – Long-term Borrowings-long term provision
= 1,20,000 – 4,00,000 – 4,00,000
= 4,00,000
Current assets = Total Assets – Property, Plant & Equipment
– Non Current investment
– Long term Loans & advance
16,00,000 – 6,00,000 – 1,00,000 – 1,00,000
= 8,00,000
Quick Assets = Current Assets – prepaid Expenses – Inventories
= 8,00,000 – 10,000 – 1,90,000
= 6,00,000
Quick Ratio = 6,00,000 / 4,00,000
= 1.5:1
19. Current Assets 6,00,000; Inventories 1,20,000; working capital 5,04,000. Calculate Quick Ratio.
Solution:
Quick Assets = Current Assets – Inventories
= 6,00,000 – 1,20,000
= 4,80,000
Working Capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities
5,04,000 = 6,00,000 – Current Liabilities
Current liabilities = 96,000
Quick Ratio = 4,80,000 / 96,000
= 5:1
20. Quick Assets 3,00,000; Inventory (Stock) 80,000; prepaid Expenses 20,000; Working capital 2,40,000. Calculate Current Ratio.
Solution:
Quick Assets = C.A + Inventories + Prepaid Expenses
3,00,000 + 80,000 + 2,000
Current Assets = 4,00,000
Working Capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities
2,40,00 = 4,00,000 – Current Liabilities
Current Liabilities = 4,00,000 – 2,40,000
= 1,60,000
Current Ratio = 4,00,000 / 1,60,000
= 2.5:1
21. Current Liabilities of a company are 6,00,000. Its Current Ratio is 3:1 and Liquid Ratio is 1:1. Calculate value of Inventory.
Solution:
Calculation of Current Assets
Current Liabilities = 6,00,000
Current Ratio = 3:1
Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
3 = C.A / C.L
C.A = 3 C.L ————(1)
C.A = 3 x 6,00,000
= 18,00,000
Calculation of Inventors
Liquid Ratio = Quick Assets / Current liabilities
Liquid Ratio = Current Assets – Inventories / Current Liabilities
1 = Current Assets – Inventories / 6,00,000
C.A – Inventories = 6,00,000
18,00,000 – Inventories = 6,00,000
Inventories = 12,00,000
22. Umesh Ltd. has current Ratio of 4.5:1 and a Quick Ratio of 3:1. If its inventory is 36,000. find out its total Current Assets and total Current liabilities.
Current Ratio = Liquid Ratio = C.A /C.L
4.5 = C.A /C.L
4. 5 =C.A /C.L
4.5 C.L = C.A ———————–(1)
Quick Ratio = Quick Assets / Current Liabilities
= C.A – Inventories / Current Liabilities
3 = —————-(2)
From (1) & (2) Equation
3 C.L = 4.5 C.L – 36,000
1.5 C.L = 36,000
Current Liabilities = 36,000 / 1,5
= 24,000
Putting C.L value in (1) Equation
4.5 C.L = C.A
C.A = 4.5 x 24,000
C.A = 10,8000
quick Assets = C.A Inventories
= 10,800 – 36,000
= 7,200
23. Current Ratio 4; Liquid Ratio 2.5; Inventory 6,00,000. Calculate Liabilities, Current Assets and Liquid Assets.
Solution:
Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
4 = C.A / C.L
4 C.L = C.A ——-(1)
Quick Ratio = Quick Assets – Current Liabilities
2.5 = C.A – Inventories / C.L
2.5 = C.A – 6,00,000 / C.L
2.5 C.L = C.A – 6,00,000 —————(2)
From (1) & (2) Equation
2.5 C.L = 4 C.L – 6,00,000
Form (1) & (2) Equation
2.5 C.L = 4 C.L – 6,00,000
1.5 C.L = 6,00,000
C.L = 6,00,000 /1.5
Current Liabilities = 4,00,000
Putting C.L in Equatin —————(1)
4 C.L = C.A
C.A = 4 X 4,00,000
= 16,00,000
Quick Assets = C.A – Investment
= 16,00,000 – 6,00,000
= 10,00,000
24. Current Liabilities of a company are 1,50,000. Its Current Ratio is 3:1 and Acid Test Ratio (Liquid Ratio0 is 1:1. Calculate values of Current Assets, Liquid Assets and inventory.
Solution:
Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
3 = C.A / C.L
3 C.L = C.A——–(1)
C.A = 3 x 1,50,000
Current Assets = 4,50,000
Quick Ratio = Quick Assets / Current Liabilities
1 = Quick Assets / 1,50,000
Quick Assets = 1,50,000
Quick Assets = C.A – Inventories
1,50,000 = 4,50,000 – inventories
Inventories = 3,00,000
25. Xolo Ltd’s liquidity Ratio is 2.5; 1. Inventory is 6,00,000. Current Ratio is 4 : 1. Find out the current liabilities.
Solution:
Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
4 = C.A / C.L
C.A = 4 C.L ——-(1)
Quick Ratio = Quick Assets / Current Liabilities
2.5 = C.A – Inventories / C.L
2.5 = C.A – 6,00,000 / C.L
From (1) & (2) Equation
2.5 C.L = 4 C.L – 6,00,000
1.5 C.L = 6,00,000
C.L = 6,00,000 / 1.5
C.L = 4,00,000
26. Current Assets of a company are 5,00,000. Its Current Ratio is 2.5 : 1 and Quick Ratio is 1 : 1. Calculate values of Current Liabilities, Liquid Assets and inventory.
Solution:
Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
2.5 = C.A / C.L
2.5 C.L = C.A ——-(1)
C.L = 5,00,000 / 2.5
Current Liabilities = 2,00,000
Quick Ratio = Quick Assets / Current Liabilities
Quick Assets = 2,00,000
Quick Assets = Current Assets – Inventories
2,00,000 = 5,00,000 – Inventories
Inventories = 5,00,000 – 2,00,000
= 3,00,000
27. Working Capital of a company is 3,60,000; Total Debts 7,80,000; Long-term Debts 6,00,000; Inventories 1,80,000. Calculate Liquid Ratio.
Solution:
Working capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities
3,60,000 = C.A – C.L ————–(1)
Total Debts = Non Current Liabilities + Current Liabilities
7,80,000 = 6,00,000 + C.L
Current Liabilities = 1,80,000
Putting C.L value in Equation ——(1)
3,60,000 = C.A – 1,80,000
Current Assets = 5,40,000
Quick Assets = Current Assets – Inventories
= 5,40,000 – 1,80,000
Quick Assets = 3,60,000
Liquid Ratio = Quick Assets / Current Liabilities
= 3,60,000 / 1,80,000
= 2:1
28. Calculate Quick Ratio from the following:
Working Capital 4,00,000; Total Debts 18,00,000; Non-Current 16,00,000; Inventories 1,90,000; prepaid Expenses 10,000.
Solution:
Quick Ratio = Quick Assets / Current Liabilities
= 4,00,000 / 2,00,000
= 2:1
Working Note:
Total Debts = Non Current Liabilities + Current Liabilities
18,00,000 = 16,00,000 + Current Liabilities
Current Liabilities = 18,00,000 – 16,00,000
= 2,00,000
Working Capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities
4,00,000 = Current Assets – 2,00,000
Current Assets = 6,00,000
Quick Assets = Current Assets – Inventories – prepaid expenses
= 6,00,000 – 1,90,000 – 10,000
= 4,00,000
29. Quick Ratio of a company is 2 : 1. State, giving reasons, which of the following transactions would
- Improve
- Reduce
- Not change the Quick Ratio;
- Purchase of goods for cash
- Purchase of goods on credit
- Sale of goods (Costing 20,000) for 20,000;
- Sale of goods (costing 20,000) for 22,000;
- Cash received from Trade Receivables.
Solution-
- Reduce;
- Reduce;
- Improve;
- Improve;
- No Change
30. Quick Ratio of Z Ltd. is 1 : 1. state, with reason, which of the following transactions would
- Increase
- Decrease or
- Not change the ratio:
- included in the trade payables was bill payable of 3,000 which was met on maturity;
- Debentures of 50,000 were converted into equity shares.
Solution-
- No change
- Increase.
31. The Quick Ratio of a company is 0.8 : 1. State, with reason, whether the following transactions will increase, decrease or not change the Quick Ratio:
- purchase of loose tools for 2,000;
- Insurance premium paid in advance 500;
- sale of goods on credit 3,000;
- Honoured a bills payable of 5,000 on maturity.
Solution-
- Decrease;
- Decrease;
- Increase;
- Decrease.
32. Capital Employed 20,00,000; Fixed Assets 14,00,000; Current Liabilities 2,00,000. There are no Long-term Investments. Calculate Current Ratio.
Solution:
Total Assets = Capital Employed + Current Liabilities
= 20,00,000 + 2,00,000
= 22,00,000
Total Assets = fixed Assets + Current Assets
22,00,000 = 14,00,000 + Current Assets
Current Assets = 8,00,000
Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
= 8,00,000 / 2,00,000
= 4 : 1
33. Venus Ltd.’s Inventory is 3,00,000. Total Liquid Assets are 12,00,000 and Quick Ratio is 2 :1. Work out Current Ratio.
Solution:
Quick Ratio = Liquid Assets / Current Liabilities
2 = 12,00,000 / Current Liabilities
Current Liabilities = 6,00,000
Current Assets = Liquid Assets + Inventory
= 12,00,000 + 3,00,000
= 15,00,000
Current Ratio = C.A / C.L
= 15,00,000 / 6,00,000
= 2.5:1
34. Total Assets 11,00,000; Fixed Assets 5,00,000; Capital Employed 10,00,00. There were no Long-term Investments. Calculate Current Ratio.
Solution:
Total Assets = Non-Current Assets + non Current Investment + Current Assets
11,00,000 = 5,00,000 + 0 + Current Assets
Current Assets = 6,00,000
= Total Assets = Capital Employed + Current Liabilities
11,00,000 = 10,00,000 + Current Liabilities
= Current Liabilities = 1,00,000
Current Ratio = C.A / C.L
= 6,00,000 / 1,00,000
= 6:1
35. From the following calculate: (i) Current Ratio (ii) Quick Ratio:
Total Debt 12,00,000
Total Assets 16,00,000
property, plat and Equipment 6,00,000
Non-Current Investment 1,00,000
Long-term Loans and Advances 1,00,000
Long-term Borrowings 4,00,000
Long-term provisions 4,00,000
Inventories 1,90,000
Prepaid Expenses 10,000
Solution:
Total Debt = Long term Borrowings + Long Term provision + Current Liabilities
12,00,00 = 4,00,000 + 4,00,000 + Current Liabilities
Current Liabilities = 4,00,000
Total Assets = Fixed Assets + Non current investments + Long term loans & Advances + Current Assets
16,00,000 = 6,00,000 + 1,00,000 + 1,00,000 + Current Assets
Current Assets = 8,00,000
Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
= 8,00,000 / 4,00,000
= 2: 1
Quick Assets = Current Assets – Inventories – Prepaid expenses
= 8,00,000 – 1,90,000 – 10,000
= 6,00,000
Quick Ratio = Quick Assets / Current Liabilities
Quick Ratio = 6,00,000 / 4,00,000
= 1. 5 : 1
36. Following is the Balance Sheet of Crescent Chemical Works Limited as at 31st March, 2023:
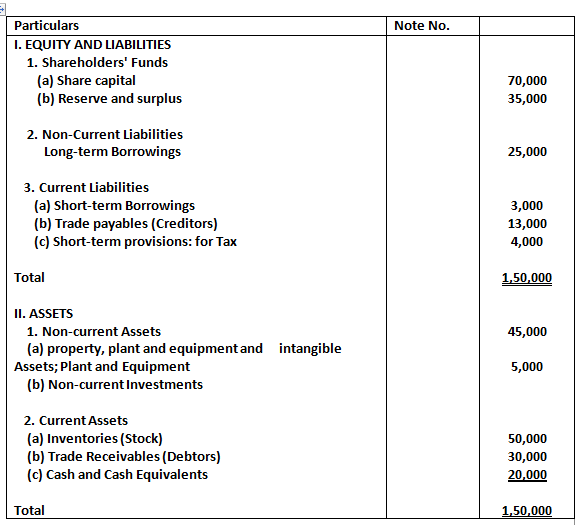
Current Assets = Inventories + Debtors + Cash & Cash Equivalents
= 50,000 + 30,000 + 20,000
= 1,00,000
Current Liabilities = Short term Borrowings + Trade payable + Short term provision
= 3000 + 13,000 + 4,000
= 20,000
Current Ratio = Current Assets / current Liabilities
= 1,00,000/20,000
= 5: 1
Liquid Assets = Current Assets – Inventories
= 1,00,000 – 50,000
= 50,000
Liquid Ratio = Liquid Assets / Current Liabilities
= 50,000 / 20,000
= 2.5: 1
DEBT TO EQUITY RATIO
37. Total Assets 2,60,000; Total Debts 1,80,000; Current Liabilities 20,000. Calculate Debt to equity Ratio.
Solution:
Total Debt = Long term Debts + Current Liabilities
1,80,000 = long term debts + 20,000
Long term debts = 1,60,000
Total Assets = Share holder’s funds + Total debts
2,60,000 = share holder’s funds + 1,80,000
Share holders funds (Equity) = 80,000
Debts to Equity Ratio = Debt / Equity
= 1,60,000 / 80,000
= 2 : 1
38. Calculate Debt to Equity Ratio: Equity share capital 5,00,000; General Reserve 90,000; Accumulated profits 50,000; 10% Debentures 1,30,000; Current Liabilities 1,00,000.
Solution:
Share holders funds = equity share capital + general reserve + Accumulated profits
= 5,00,000 + 90,000 + 50,000
= 6,40,000
Debt = 10% Debentures
1,30,000
Debt to Equity ratio = Debt / Equity
= 1,30,000 / 6,40,000
Debt to Equity Ratio = 0.203
39. From the following information, calculate debt to equity ratio:
20,000 Equity shares of 10 each fully paid 2,00,000
10,000, 9% preference shares of 10 each fully paid 1,00,000
General Reserve 90,000
Surplus, i.e., Balance in Statement of profit & Loss 40,000
10% Debentures 1,50,000
Current Liabilities 1,00,000
Solution:
Share holder’s Funds = Equity share + preference share + General reserve + surplus, i.e. Balance in statement of profit & loss
= 2,00,000 + 1,00,000 + 90,000 + 40,000
Share holder’s funds = 4,30,000
Debts = 1,50,000
= 1,50,000
Debt to Equity Ratio = 1,50,000 / 4,30,000
= 0.348
= 0.35
40. Calculate Debt to Equity Ratio from the following information:
Property, plant and equipment (Gross) 8,40,000
Accumulated Depreciation 1,40,000
Non-current investment 14,000
Long-term Loss and Advances 56,000
Current Assets 3,50,000
Current Liabilities 2,80,000
10% Long-term Borrowings 4,20,000
Long-term Provisions 1,40,000
Solution:
Debt = Long-term Borrowings + Long term provisions
= 4,20,000 + 1,40,000
= 5,60,000
Equity = Total Assets – Total Outside Liabilities
Total Assets = (Fixed Assets – Acc. Depreciation) + Non-current Investment + Long-term loans and Advances + Current Assets
= (8,40,000 – 1,40,000) + 14,000 + 56,000 + 3,50,000
= 11,20,000
Total outside liabilities = Non-current liabilities + current Liabilities
= 5,60,000 + 2,80,000 = 8,40,000
Equity = Total Assets – Total outside liabilities
= 11,20,000 – 8,40,000
= 2,80,000
Debt to Equity ratio = Debt / Equity
= 5,60,000 /2,80,000
= 2:1
41. From the following information, calculate Debt to equity share ratio: Total Debts 6,00,000; current liabilities 2,00,000 and capital employed 6,00,000.
Solution:
Total Debts = Non-Current liabilities + Current liabilities
6,00,000 = Non-current liabilities + 2,00,000
Non-current liabilities (debt) = 4,00,000
capital employed = equity + non-current liabilities
6,00,000 = equity + 4,00,000
Equity = 2,00,000
Debt to Equity ratio = Debt / Equity
= 4,00,000 / 2,00,000
= 2:1
42. Calculate Debt to Equity Ratio: Total Assets 14,00,000; Total debt 12,00,000; capital employed 10,00,000.
Solution:
Equity = Total Assets – Total Debts
= 14,00,000 – 12,00,000
= 2,00,000
Capital Employed = Equity + Debt (Non-Current liabilities)
10,00,000 = 2,00,000 + Debt (Non-current liabilities)
Debt (Non-current liabilities) = 8,00,000
Debt to Equity ratio = Debt / Equity
= 8,00,000 / 2,00,000
= 4:1
43. Capital Employed 8,00,000; shareholder’s funds 2,00,000. Calculate Debt to Equity Ratio.
Solution:
Debt = Capital Employed – Share holders funds
= 8,00,000 – 2,00,000
= 6,00,000
Share holders funds (Equity) = 2,00,000
Debt to Equity ratio = Debt / Equity
= 6,00,000 / 2,00,000
= 3:1
44. King Ltd has current ratio of 2.5:1. Its working capital is 1,20,000. Total Assets are of 3,80,000 and Total Debt of 2,80,000. Calculate Debt to equity ratio.
Solution:
Current Ratio = 2.5:1
Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
2.5 = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
2.5 C.L = C.A ———-(1)
Working capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities
1,20,00 = C.A – C,L ——(2)
putting equation (1) value in equation (2)
1,20,000 = 2.5 C.L – C.L
C.L = 1,20,000 / 1.5
Current liabilities = 80,000
Debt (Non-current liabilities) = Total Debt – Current liabilities
= 2,80,000 – 80,000
= 2,00,000
Equity (Share holder’s funds) = Total Assets – Total Debts
= 3,80,000 – 2,80,000
= 1,00,000
Debt to Equity ratio = Debt / Equity
= 2,00,000 / 1,00,000
= 2:1
45. Monica Ltd. has Quick Ratio of 1.5 : 1. Its working capital is 1,20,000 and its inventions are of 80,000. Total Assets of 3,80,000 and total debts of 2,80,000. Calculate Debt to equity Ratio.
Solution:
Quick Ratio = Quick Assets / Current liabilities
= Current Assets – Inventories / Current Liabilities
1.5 = Current Assets – 80,000 / Current Liabilities
1.5 C.L = C.A – 80,000
C.A = 1.5 C.L + 80,000 ———(1)
Working capital = Current Assets – Current liabilities
1,20,000 = C.A -C.L ————-(2)
Putting C.A Value from Eq (1) into Eq (2)
1,20,000 = 1.5 C.L + 80,000 – C.L
5. C.L = 40,000
Current Liabilities = 40,000 /5
= 80,000
Debt (Non-current liabilities) = Total Debt – Current liabilities
= 2,80,000 – 80,000
= 2,00,000
Equity (share holder’s funds) = Total Assets – Total Debt
= 3,80,000 – 2,80,000
= 1,00,000
Debt to Equity ratio = Debt / Equity
= 2,00,000 / 1,00,000
= 2:1
46. When Debt to Equity Ratio is 2, State, giving reason, whether this ratio will increase, decrease or will have no change in each of the following cases;
- Sale of land (Book value 4,00,0000 for 5,00,000;
- issue of equity share for the purchase of plant and machinery worth 10,00,000;
- issue of preference shares for redemption of 13% Debentures, worth 10,00,000.
Solution-
- Decrease;
- Decrease;
- Decrease.
47. Debt to equity ratio of a company is 0.5 : 1. Which of the following would increase, decrease or not change it:
- Issue of Equity shares;
- Cash received form debtors;
- Redemption of debentures
- Purchased good on credit?
Solution-
- Decrease;
- No change;
- No change;
- No change.
48. Balance Sheet had the following amounts as at 31st March, 2025;
10% preference share capital 5,00,000
Equity share capital 15,00,000
Security premium reserve 1,00,000
Reserve and surplus 4,00,000
long-term loan from IDBI @ 9% 30,00,000
Current Assets 12,00,000
Current Liabilities 8,00,000
Investment (in other companies) 2,00,000
Property, plant and Equipment – cost 60,00,000
Depreciation written off 14,00,000
Calculate rations indicating the Long-term and the short-term financial position of the company
solution:
Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
= 1,20,000 / 8,00,000
Current Ratio = 1.5:1
Equity = preference share = Equity share + Reserve & Surplus
= 5,00,000 + 15,00,000 + 4,00,000
= 24,00,000
Debt = Long term loan form IDBI @ 9%
= 30,00,000
Debt to Equity ratio = Debt / Equity
= 30,00,000 / 24,00,000
= 1.25:1
49. Assuming that the debt to Equity ratio is 2 : 1, state, giving reasons, which of the following transactions would (i) Increase (ii) Decrease (iii) Not alter Debt to equity Ratio.
- Issue of new share for cash.
- Conversion of debentures into equity shares.
- Sale of fixed assets at profit.
- Purchase of a fixed asset on long-term deferred payment basis.
- Payment to Creditors.
Solution-
- Decrease;
- Decrease;
- Decrease;
- Increase;
- No change.
50. From the following Balance Sheet to ABC Ltd. as at 31st March, 2023, Calculate Debt to Equity Ratio.
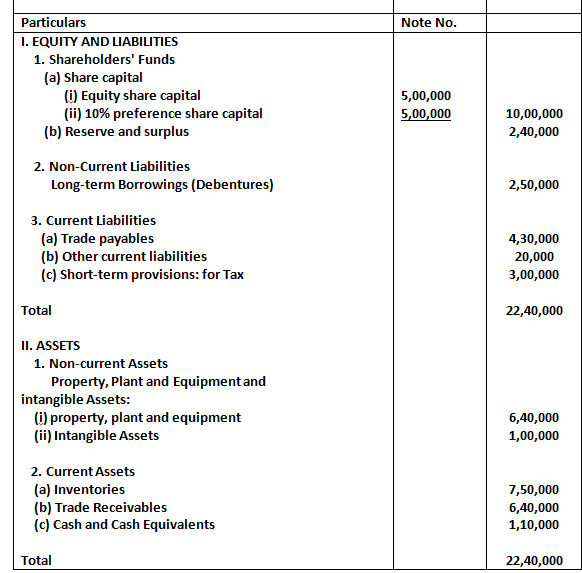
Solution:
Debt = Long term Borrowings
= 2,50,000
Equity = Equity share Capital + 10% preference share capital reserve & Surplus
= 5,00,000 + 5,00,000 + 2,40,000
= 12,40,000
Debt to equity ratio = Debt / Equity
= 2,50,000 / 12,40,000
= 0.2016:1
= 0.2:1
TOTA ASSETS TO DEBT RATIO
51. Calculate total Assets to Debt ratio from the following information:
Long-term Debts 4,00,000; Total Assets 7,70,000.
Solution:
Total Assets = 7,70,000
Long-term Debts (Debts) = 4,00,000
Total Assets to Debt Ratio = Total Assets / Debt
= 7,70,000 / 4,00,000
= 1.925 : 1
52. Total Debt 15,00,000; Current liabilities 5,00,000; Capital Employed 15,00,000. Calculate Total Assets to Debt Ratio.
Solution:
Total Assets = Capital Employed + Current Liabilities
= 15,00,000 + 5,00,000
= 20,00,000
Total Debt = Non-Current Liabilities + Current Liabilities
15,00,000 = Non-Current Liabilities + 5,00,000
Non-Current Liabilities = 10,00,000
Total Assets to Debt Ratio = Total Assets / Debt
= 20,00,000 / 10,00,000
= 2 : 1
53. Shareholder’s Funds 1,60,000; Total Debts 3,60,000; current Liabilities 40,000.
Calculate Total Assets to Debt Ratio.
Solution:
Total Assets = Share holder’s Funds + Total Debts
= 1,60,000 + 3,60,000
= 5,20,000
Total Debts = Non-current liabilities + current liabilities
3,60,000 = Non-current liabilities + 40,000
Non-current liabilities (Debt) = 3,20,000
Total Assets to Debt Ratio = Total Assets / Debt
= 5,20,000 / 3,20,000
= 1.625 : 1
54. Total Debt 60,00,000; Shareholder’s funds 10,00,000; Reserve and surplus 2,50,000; Current Assets 25,00,000; Working Capital 5,00,000. Calculate Total Assets to Debt Ratio.
Solution:
Total Assets = Total Debt + Share holder’s Funds
= 60,00,000 + 10,00,000
= 70,00,000
Working Capital = Current Assets – Current liabilities
5,00,000 = 25,00,000 – Current Liabilities
Current Liabilities = 20,00,000
Total Debt = Non-Current Liabilities + Current Liabilities
60,00,000 = Non-Current Liabilities + 20,00,000
Non-Current Liabilities = 40,00,000
Total Assets to Debt Ratio = Total Asset / Debt
= 70,00,000 / 40,00,000
= 1.75 : 1
55. Total Debt 12,00,000; Shareholders funds 2,00,000; Reserve and surplus 50,000; Current Assets 5,00,000; Working capital 1,00,000. Calculate Total Assets to Debt Ratio.
Solution:
Total Assets = Shareholder’s + Total Debt
= 2,00,000 + 12,00,000
= 14,00,000
Working capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities
1,00,000 = 5,00,000 – Current liabilities
Current Liabilities = 4,00,000
Total Debt = Non-Current Liabilities + Current Liabilities
12,00,000 = N.C.L (Debt) + 4,00,000
Non-Current liabilities (Debt) = 8,00,000
Total Assets to Debt Ratio = Total Assets / Debt
= 14,00,000 / 8,00,000
= 1.75 : 1
56. From the following information, Calculate ‘Total Assets to Debt Ratio:
| Particulars | ₹ | Particulars | ₹ |
| Current assets Current Liabilities 10% Debentures | 8,00,000 5,00,000 4,00,000 | 9% Long-term Bank Loan Shareholders’ Funds | 1,00,000 15,00,000 |
Solution-
Total assets= share holder fund+ long term bank loan + debenture+ current liability
= 15,00,000+100,000+400,000+500,000
= 2500,000
Debt = 10% debenture+9% long term bank loan
= 4,00,000+100,000
= 5,00,000
Total assets to debt ratio = Total Asset / Debt
= 25,00,000 / 5,00,000
Debts Ratio = 5:1.
57. Calculate ‘Total Assets to Debt Ratio’ From the following information:
Equity share capital 4,00,000
Long-term Borrowing 1,80,000
Surplus, i.e., Balance of P & L 1,00,000
General Reserve 70,000
Current Liabilities 30,000
Long-term provisions 1,20,000
Solution:
Debt = Long term borrowings + Long term provisions
= 1,80,000 + 1,20,000
= 3,00,000
Share holder’s funds = Equity share capital + Surplus profit & Loss + General Reserve
= 4,00,000 + 1,00,000 + 70,000
= 5,70,000
Total Assets = Share holder’s funds + Non-Current liabilities (Debt) + Current Liabilities
= 5,70,000 + 3,00,000 + 30,000
= 9,00,000
Total Assets = Share holder’s funds + Non-Current liabilities (Debt) + Current Liabilities
= 5,70,000 + 3,00,000 + 30,000
= 9,00,000
Total Assets to Debt Ratio = Total Asset / Debt
= 9,00,000 / 3,00,000
= 3 : 1
58. From the following information, calculate Total Assets to debt Ratio:
Property, plant and Equipment (Gross) 6,00,000
Non-Current Investment 10,000
Current Assets 2,50,000
Long term Borrowings 3,00,000
Accumulated Depreciation 1,00,000
Long-term Loans and Advances 40,000
Current Liabilities 2,00,000
Long-term provisions 1,00,000
Solution:
Total Assets = [Fixed Assets (Gross) – Acc. Depreciation] + Non Current investment + Long term loans & advances + Current Assets
= (6,00,000 – 1,00,000) + 10,000 + 40,000 + 2,50,000
= 5,00,000 + 10,000 + 40,000 + 2,50,000
= 8,00,000
Debt = Long term Borrowings + Long term provisions
= 3,00,000 + 1,00,000
= 4,00,000
Total Assets to Debt Ratio = Total Asset / Debt
= 8,00,000 / 4,00,000
= 4 : 1
PROPERIETARY RATIO
59. From the following information, calculate proprietary Ratio:
Share capital 3,00,000
Non-Current Assets 13,20,000
Reserve and Surplus 1,80,000
Current Assets 6,00,000
Solution:
Total Assets = Non-Current Assets + Current Assets
= 13,20,000 + 6,00,000
= 19,20,000
Share holder’s funds = Share capital + Reserve & Surplus
= 3,00,000 – 1,80,000
Share holder’s funds = 4,80,000
Property Ratio = Shareholders’ Funds / Total Assets
= 4,80,000 / 19,20,000
= 0.25: 1
60. Calculate proprietary ratio form the following:
Equity share capital 4,50,000
10% preference share capital 3,20,000
Reserve and surplus 65,000
Creditors 1,10,000
9% Debentures 3,00,000
Property, plant and equipment 7,00,000
Trade investment 2,45,000
Current Assets 3,00,000
Solution:
Shareholder’s funds = equity share capital + 10% preference share
Capital + reserve & surplus
450,000+3,20,000+65000=8,35,000
Total assets= property plant and equipment + trade investment + current assets
= 7,00,000 + 2,45,000 + 3,00,000
= 12,45,000
Proprietary Ratio = Shareholders’ Funds / Total Assets
= 8,35,000 / 12,45,000
= 0.67:1
61. From the following information, calculation proprietary Ratio:
Equity share capital 3,00,00
Preference share capital 1,50,000
Reserves and surplus 75,000
Debentures 1,80,000
Trade payables 45,000
7,50,000
Property, plant and equipment 3,75,000
Short-term investments 2,25,000
Other current Assets 1,50,000
7,50,000
Solution:
Total Assets = fixed Assets + Short terms investments + others Current
Assets
= 3,75,000 + 2,25,000 + 1,50,000
= 7,50,000
Shareholder’s funds = equity share capital + preference share
Capital + reserves & surplus
= 3,00,000 + 1,50,000 + 75,000
= 5,25,000
Proprietary Ratio = Shareholders’ Funds / Total Assets
= 5,25,000/7,50,000
= 0.70:1
62. Calculate proprietary ratio, if total assets to debt ratio is 2:1. Debt is 5,00,000. Equity shares capital is 0.5 times of debt. Preference share capital is 25% of equity share capital. Net profit before tax is 10,00,000 and rate of tax is 40%.
Solution:
Total Assets to Debt Ratio = 2:1
Debt = 5,00,000
Total Assets to Debt ratio = Total Assets / Debt
2 = total assets / 5,00,000
Total Assets = 10,00,000
Equity share capital = 0.5 x 5,00,000
= 2,50,000
Preference share capital = 25% of equity share capital
= x 2,50,000
= 62,500
Net profit before tax = 10,00,000
Tax ratio = 40%
Profit after tax = 10,00,000 – 40/100 x 10,00,000
= 10,00,000 – 4,00,000
= 6,00,000
Share holder’s funds = equity share capital + preference share Capital + profit
= 2,50,000 + 62,500 + 6,00,000
= 9,12,500
Property Ratio = Shareholders’ Funds / Total Assets
= 9,12,500 / 10,00,000
= 0.9125:1
63. State, with reasons, whether the proprietary ratio will improve, decline or will not change because of the following transactions if proprietary ratio is 0.8:1:
- Obtained a loan of 5,00,000 from state bank of India payable after five years.
- Purchased machinery of 2,00,000 by cheque.
- Redeemed 7% Redeemable preference shares 3,00,000.
- Issued equity shares to the vendor of building purchased for 7,00,000.
- Redeemed 10% redeemable debentures of 6,00,000.
Solution-
- Decline;
- No change;
- Decline;
- Improve;
- Improve.
Calculate of Debt to Equity Ratio, Proprietary Ratio, and Total Assets to Debt Ratio
64. Form the following information, calculate:
- Proprietay ratio:
- Debt to Equity Ratio; and
- Total Assets to Debt Ratio.
Current Assets 40,00,000
Long-term borrowings 15,00,000
Non-current Assets 40,00,000
Current Liabilities 20,00,000
Long-term provisions 25,0,000
Solutions:
Total Assets = Non-current Assets + Current Assets
= 40,00,000 + 4,00,000
= 80,00,000
Debt = long term borrowings + Long term provisions
= 15,00,000 + 25,00,000
= 40,00,000
Total Assets = Equity + Non-Current liabilities + Current Liabilities
8,00,000 = Equity + 40,00,000 + 20,00,000
Equity = 20,00,000
1. Property Ratio = Shareholders’ Funds / Total Assets
= 20,00,000 /80,00,000
= 0.25:1
2. Debt to equity Ratio = Debt /Equity
= 40,00,000 / 20,00,000
= 2:1
3. Total Assets to Debt Ratio = Debt / Equity
= 80,00,000 / 40,00,000
= 2:1
65. From the following information, calculate:
- Proprietary Ratio:
2. Debt to Equity Ratio; and
3. Total Assets to Debt Ratio.
Total Debt 18,00,000
Capital Employed 15,00,000
Current Assets 7,50,000
Working capital 1,50,000
Solution:
Working capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities
15,000 = 7,50,000 – Current Liabilities
Current Liabilities = 6,00,000
Total Debt = Non-Current Liabilities (Debt) + Current Liabilities
18,00,000 = Non-Current Liabilities (Debt) + 6,00,000
Non-Current Liabilities (Debt) = 12,00,000
Shareholder’s funds = capital Employed – non- Current Liabilities
= 15,00,000 – 12,00,000
= 3,00,000
Total Assets = Capital Employed + Current Liabilities
= 15,00,000 +6,00,000
= 21,00,000
Property Ratio = Shareholders’ Funds / total assets x 100
= 3,00,000 / 21,00,000x 100
= 14.29%
Debt to equity Ratio = Debt / Equity
= 12,00,000 / 3,00,000
= 4:1
Total Assets to Debt Ratio = Debt / Equity
= 12,00,000/3,00,000
= 4:1
Total Assets to Debt Ratio = Total Assets / Debt
= 21,00,000 / 12,00,000
= 1. 75 : 1
INTEREST COVERAGE RATIO
66. If net profit before interest and tax is 10,00,000 and interest on long-term funds is 2,00,000, find interest coverage Ratio.
Solution:
Interest charge Ratio = profit before interest & tax / Interest on long term loans
= 10,00,000 /2,00,000
= 5 times
67. From the following information, calculate interest coverage Ratio: Net profit after Tax 4,25,000; tax 75,000; interest on long-term funds 1,25,000.
Solution:
Net profit before interest and tax = Net profit After tax + tax +Interest
= 4,25,000 + 75,000 + 1,25,000
= 6,25,000
Interest charge Ratio = profit before interest & tax / Interest on long term loans
= 6,25,000 / 1,25,000
= 5 times
68. From the following details, calculate interest coverage Ratio:
Net profit after tax 7,00,000
6% Debentures 20,00,000
Tax rate 30%
Solution:
Let the profit before tax be ₹ x
Net profit after tax = Net profit before tax – tax
7,00,000 = x – – x
70x/100 = 7,00,000
X = 70 x 100 / 70
Net profit before tax = 10,00,000
Interest on debentures = 6% of Debentures
= 1,20,000
Profit before interest and tax = profit before tax + interest
= 10,00,000 + 1,20,000
= 11,20,000
Interest charge Ratio = profit before interest & tax / Interest on long term loans
= 11,20,000 / 1,20,000
= 9.33 times
69. From the following information, calculate interest coverage ratio:
Net profit after interest and tax 1,20,000; rate of income tax; 40%; 15% debentures 1,00,000 12% mortgage loan 1,00,000.
Solution:
Let profit before tax be x
Profit after tax = profit before tax – interest
1,20,000 = x – 40/100 x
60x/100 = 1,20,000
X = 1,20,000 x 100 /60
profit before tax = 2,00,000
interest = 15% debentures + 12% mortgage loan
= x 1,00,000 + x 1,00,000
=15,000 +12,000
= 27,000
Profit before interest and tax = profit before tax + interest
= 2,00,000 + 27,000
= 22,7,000
Interest charge Ratio = profit before interest & tax / Interest on long term loans
= 2,00,000 / 27,000
= 8.41 times
70. From the following information, calculate interest coverage ratio:
10,000 equity shares of 10 each 1,00,000
8% preference shares 70,000
10% debentures 50,000
Long-term loans from bank 50,000
Interest on long-term loans from bank 5,000
Net profit after tax 75,000
Tax 9,000
Solution:
Net profit before tax = net profit after tax + tax
= 5,000 + 5,000
Interest = 10,000
Net profit before tax and interest=net profit after tax+ interest on long term loan term bank + interest on debentures
= 75000+9000+5000+50,000×10%
= 94000
Interest coverage ratio = profit before interest & tax / Interest on long term loans
= 94,000 / 10,000
= 9.4 times
DEBT TO CAPITAL EMPLOYED RATIO
71. From the following information, calculate Debt to capital employed ratio:
Shareholder’s funds 24,00,000
Long-term borrowings (9% debentures) 12,00,000
Current liabilities 2,00,000
Non-current Assets 28,00,000
Current Assets 10,00,000
Solution:
Long term Debt = long term borrowings (9% debentures)
= 12,00,000
Capital employed = share holder’s funds + long term borrowings
(9% debentures)
= 24,00,000 + 12,00,000
= 36,00,000
Debt to capital employed ratio = long term debt / capital employed
= 12,00,000 /36,00,000
= 0.33:1
72. From the following, calculate ‘Debt to capital Employed Ratio’:
9% Debentures 2,00,000
8% public Deposits 5,00,000
Long-term provisions 2,00,000
Equity share capital 8,00,000
Reserve and surplus 5,00,000
Solution:
Long-term Debts = 9% Debentures + long term Provisions 8% Public deposits
= 2,00,000 + 2,00,000 + 5,00,000
= 9,00,000
Capital employed = equity share capital + reserve and surplus + 9% Debentures + long-term provisions + 8% public Deposit
= 8,00,000 + 5,00,000 + 2,00,000 + 2,00,000 + 5,00,000
= 22,00,000
Debt to capital employed ratio = long term debt / capital employed
= 9,00,000 / 22,00,000
= 0.409:1
= 0.41:1
73. From the following, calculation Debt to capital employed Ratio:
Capital employed 87,00,000
Investments 4,80,000
Machinery 14,00,000
Trade receivables 8,00,000
Cash and cash equivalents 7,20,000
Equity share capital 45,00,000
8% Debentures 36,00,000
Capital reserve 6,80,000
Solution:
Long term Debts = 8% Debentures
= 36,00,000
Capital employed = 87,00,000
Debt to capital employed ratio = long term debt / capital employed
= 36,00,000 / 87,00,000
= 0.41:1
74. Calculate debt to capital employed ratio from the following information:
Shareholder’s funds 50,00,000
Non-current liabilities;
Long-term borrowings 20,00,000
Long-term provisions 17,50,000 37,50,000
Non-current Assets:
Property, plant and equipment
And intangible Assets 90,00,000
Non-current investment 12,50,000 1,02,50,000
Current Assets 23,75,000
Solution:
Long term Debts = Long term Borrowings + long term provisions
= 20,00,000 + 17,50,000
= 37,50,000
Capital employed = share holder’s funds + long term borrowings +Long terms provisions
= 50,00,000 + 20,00,000 + 17,50,000
= 87,50,000
Debt to capital employed ratio = long term debt / capital employed
= 37,00,000 / 87,50,000
= 0.4285
= 0.43:1
75. Calculation debt to capital employed ratio from the following information:
Total debts 60,00,000; current Assets 25,00,000; non-current Assets 95,00,000; working capital 5,00,000.
Solution;
Working capital = current Assets – current liabilities
5,00,000 = 25,00,000 – current liabilities
Current liabilities = 20,00,000
Long term debts = total debts – current liabilities
= 60,00,000 – 20,00,000
= 40,00,000
Capital employed = current Assets + non-current Assets – Current liabilities
= 25,00,000 + 95,00,000 – 20,00,000
= 100,00,000
Debt to capital employed ratio = long term debt / capital employed
= 40,00,000 / 100,00,000
= 0.40:1
76. From the following calculate debt to capital employed Ratio:
10% preference share capital 5,00,000; Equity share capital 15,00,000; securities premium 1,00,000; reserve and surplus 2,00,000; 9% loan from IDBI 30,00,000.
Solution;
Long term Debt = 9% loan form IDBI
= 30,00,000
Capital employed = 10% preference share capital + Equity share
Capital + reserves & surplus + 9% loan from IDBI
= 5,00,000 + 15,00,000 + 2,00,000 + 30,00,000
= 52,00,000
Debt to capital employed ratio = long term debt / capital employed
= 30,00,000 / 52,00,000
= 0.58:1
77. Calculate Debt to Capital Employed Ratio form the following information:
Debt to Equity Ratio 2:1; Long term Borrowing Rs.18,00,000; Long term Provision Rs.6,00,000; Reserves and Surplus Rs.2,00,000.
debt= long term borrowing + long term provision
18,00,000+600,000
2400,000
Equity=total debt
Ans. 0.67 : 1.
78. Debt to capital employed ratio of a company is 0.4:1. State giving reasons, which of the following will improve, reduce not change the ratio?
- Sale of machinery at a loss of 50,000.
- Purchase of stock-in-trade on credit of two months for 80,000.
- Conversion of debentures into equity shares of 5,00,000.
- Purchase of fixed assets for 4,00,000 on a long-term deferred payment basis.
Solution:-
- Improve;
- Not Change,
- Reduce,
- Improve.
INVENTORY TURNOVER RATIO
79. From the following details, calculate inventory turnover ratio:
Cost of revenue from operations (cost of Goods sold) 9,00,000
Inventory in the beginning of the year 3,50,000
Inventory at the close of the year 2,50,000
Solution:
Cost of goods sold = 9,00,000
Average inventory = Opening inventory + closing inventory / 2
= 2,50,000 + 3,50,000 /2
= 3,00,000
Inventory turnover ratio = Cost of goods sold / average inventory
= 9,00,000 / 3,00,000
= 3 times
80. Cost of revenue from operations (cost of goods sold) 5,00,000: purchases 5,50,000; opening inventory 1,00,000.
Calculate inventory turnover ratio.
Solution:
Cost of goods sold = opening inventory + purchase – purchased return – closing inventory
5,00,000 = 1,00,000 + 5,50,000 – 0 – closing inventory
Closing inventory = 1,50,000
Cost of goods sold = 5,00,000
Avg. inventory = Opening inventory + closing inventory / 2
= 1,00,000 + 1,50,000 / 2
= 1,25,000
Inventory turnover ratio = Cost of goods sold / average inventory
= 5,00,000 / 1,25,000
= 4 times
81. Calculation inventory turnover ratio form the following information:
Opening inventory is 50,000; purchase 3,90,000; revenue form operations, I.e., net sales 6,00,000; gross profit ratio 30%.
Solution:
Gross profit ratio = 30% of net sales
= x 6,00,000
= 1,80,00,000
Cost profit = net sales – cost of goods sold
1,80,000 = 6,00,000 – cost of goods sold
Cost of goods sold = 4,20,000
Cost of goods sold = opening inventory + purchases – purchase return+ direct expenses – closing inventory
4,20,000 = 50,000 + 3,90,000 – 0 + 0 – closing inventory
Closing inventory = 20,000
Avg. inventory = Opening inventory + closing inventory / 2
= 50,000 + 20,000 / 2
= 35,000
Inventory turnover ratio = Cost of goods sold / average inventory
= 4,20,000 / 35,000
= 12 times
82. Form the following information, calculate inventory turnover ratio:
Opening inventory 2,00,000
Purchase 4,60,000
Carriage inwards 20,000
Closing inventory 60,000
Wages 30,000
Freight outwards 37,500
Solution:
Cost of goods sold = opening inventory + purchases + carriage inwards+ wages – closing inventory
= 2,00,000 + 4,60,000 +20,000 + 30,000 – 60,000
= 6,50,000
Avg. inventory = Opening inventory + closing inventory / 2
= 2,00,000 + 60,000 / 2
= 1,30,000
Inventory turnover ratio = Cost of goods sold / average inventory
= 6,50,000 / 1,30,000
= 5 times
83. Calculate inventory turnover ratio from the following:
Opening inventory 58,000
Closing inventory 62,000
Revenue from operation, i.e., net sales 6,40,000
Gross profit ratio 25%.
Solution:
Gross profit = 25% of net sales
= 25/100 x 6,40,000
= 1,60,000
Gross profit = net sales – cost of goods sold
1,60,000 = 6,40,000 – cost of goods sold
Cost of goods sold = 4,80,000
Avg. inventory = Opening inventory + closing inventory / 2
= 58,000 + 62,000 / 2
= 60,000
Inventory turnover ratio = Cost of goods sold / average inventory
= 4,80,000 / 60,000
= 8 times
84. From the following information, calculate inventory turnover Ratio:
Revenue form operations 16,00,000
Average inventory 2,20,000
Gross loss Ratio 5%.
Solution:
Gross loss = 5% of revenue from operation
= 25 / 100 x 16,00,000
= 80,000
Gross loss = cost of goods sold – revenue from operation
80,000 = cost of goods sold – 16,00,000
Cost of goods sold = 16,80,000
Inventory turnover ratio = Cost of goods sold / average inventory
= 16,80,000 / 2,20,000
= 7.64 times
85. Revenue from operations 4,00,000; gross 1,00,000; closing inventory 1,20,000; excess of closing inventory over opening inventory 40,000. Calculate inventory turnover Ratio.
Solution;
Revenue from operation = 4,00,000
Opening inventory = 1,20,000 – 40,000
= 80,000
Gross profit = revenue from operation – cost of goods sold
1,00,000 = 4,00,000 – cost of goods sold
Cost of goods sold = 3,00,000
Avg. inventory = Opening inventory + closing inventory / 2
= 80,000 + 1,20,000 / 2
= 1,00,000
Inventory turnover ratio = Cost of goods sold / average inventory
= 3,00,000 / 1,00,000
= 3 times
86. From the following data, calculate turnover Ratio:
Total sales 1,00,000; sales return 1,00,000; gross profit 1,80,000; closing inventory 2,00,000; excess of closing inventory over opening inventory 40,000.
Solution:
Net sales(revenue from operation ) = gross sales – sales return
= 10,00,000 – 1,00,000
= 9,00,000
Revenue from operation =9,00,000
Opening inventory = 2,00,000 – 40,000
= 1,60,000
Gross profit = revenue from operation – cost of goods sold
1,80,000 = 9,00,000 – cost of goods sold
Cost of goods sold = 7,20,000
Avg. inventory = Opening inventory + closing inventory / 2
= 1,60,000 + 2,00,000 / 2
= 1,80,000
Inventory turnover ratio = Cost of goods sold / average inventory
= 7,20,000 / 1,80,000
= 4 times
87. ₹ 2,00,000 is the cost of revenue from operations (cost of good sold), during the year. If inventory turnover Ratio is 8 times, calculate inventories at the end of the year. Inventory at the end is 1.5 times that of in the beginning.
Solution:
Inventory turnover ratio = Cost of goods sold / average inventory
= 2,00,000 x 2 / opening inventory + Closing inventory
8 = 2,00,000 x 2/ x + 1.5x
8 *2.5x = 4,00,000
X = 4,00,000 / 2.5 x 8
X = 20,000
Opening inventory = 20,000 x 1.5
Closing inventory = 20,000 x1.5
= 30,000
88. From the following information obtained from the books of kundan Ltd. calculate the inventory turnover Ratio for the years 2015-16 and 2016-17:
| Particular | 2015-16 ₹ | 2016-17 ₹ |
| Inventory on 31st March Revenue from operations (gross profit is 25% on cost of revenue from operation) | 7,00,000 50,00,000 | 17,00,000 75,00,000 |
In the year 2015-16, inventory by 2,00,000.
Solution:
2015-16
Opening inventory = 5,00,000
Closing inventory = 7,00,000
Assume cost of goods sold=X
Gross profit = revenue from operation – cost of goods sold
25/ 100X = 50,00,000 – X
25x + x /100 = 50,00,000
25X+125X =50,00,000
100
Logs = 50,00,000 x 100 / 125
cost of goods sold = 40,00,000
Avg. inventory = Opening inventory + closing inventory / 2
= 5,00,000 + 7,00,000 / 2
= 6,00,000
Inventory turnover ratio = Cost of goods sold / average inventory
= 40,00,000 / 6,00,000
= 6.666
= 6.67 times
2016-17
Opening inventory = 7,00,000
Closing inventory = 17,00,000
Average inventory = Opening inventory + closing inventory / 2
= 7,00,000 + 17,00,000 / 2
= 12,00,000
Gross profit = revenue form operation – cost of goods
Sold
logs = 75,00,000 – logs
logs = 75,00,000
Logs = 75,00,000 x
cost of goods sold = 60,00,000
Inventory turnover ratio = Cost of goods sold / average inventory
= 60,00,000 / 12,00,000
= 5 times
89. Calculate inventory turnover ratio from following information:
Opening inventory 40,000; purchases 3,20,000; and closing inventory 1,20,000 state, giving reason, which of the following transactions would (i) increase, (ii) decrease, (iii) neither increase nor decrease the inventory turnover Ratio:
- Sale of goods for 40,000 (cost 32,000).
- Increase in the value of closing inventory by 40,000.
- Goods purchased for 80,000.
- Purchase return 20,000.
- Goods costing 10,000 withdrawn for personal use.
- Goods costing 20,000 distributed as free samples.
Solution- Inventory Turnover Ratio = 3 Times.
- Increase ;
- Decrease;
- Decrease;
- Increase;
- Increase;
- Increase.
90. From the following information, calculate inventory turnover Ratio:
Credit revenue from operations 6,00,000; cash revenue from operations 2,00,000 gross profit 25% of cost, closing was 3 times the opening inventory. Opening inventory was 10% of cost of revenue from operations.
Solution:
Net revenue from operation = credit revenue from operation +Cash revenue from operation
= 6,00,000 + 2,00,000
= 8,00,000
Let the cost of goods sold be x
Gross profit = net revenue from operations – cost of goods sold
25 / 100x = net revenue from operation – x
(1 + 25/100) x = 8,00,000
x = 8,00,000 x 100/125
cost of revenue from operations = 6,40,000
opening inventory = 10% of cost of revenue from operations
= 10/100x 6,40,000
= 64,000
Closing inventory = 3 x 64,000 = 1,92,000
Avg. inventory = Opening inventory + closing inventory / 2
= 64,000 + 1,92,000 / 2
= 1,28,000
Inventory turnover ratio = Cost of goods sold / average inventory
= 6,40,000 / 1,28,000
= 5 times
91. Following figures have been extracted form shivalika mills Ltd.
Inventory in the beginning of the year 60,000.
Inventory at the end of the year 1,00,000.
Inventory turnover Ratio 8 times.
Selling price 25% above cost.
Compute amount of Gross Profit and Revenue from operations (Net sales).
Solution:
Avg. inventory = Opening inventory + closing inventory / 2
= 60,000 + 1,00,000 / 2
= 80,000
Inventory turnover ratio = Cost of goods sold / average inventory
8 = Cost of good sold / 80,000 cost of goods sold = 6,40,000
Selling price = 25% above cost
Revenue from operation = 6,40,000 +25%/100 x 6,40,000
= 6,40,000 + 1,60,000
= 8,00,000
Gross profit = revenue from operation – cost of goods sold
= 8,00,000 – 6,40,000
= 1,60,000
Calculation of Opening and Closing Inventory
92. From the following information, calculation value of opening inventory:
Closing inventory 68,000
Total sales 4,80,000 (including cash sales 1,20,000)
Total purchases 3,60,000 (including credit purchases 2,39,200)
Goods are sold at a profit of 25% on cost.
Solution:
Gross profit = revenue from operation – cost of goods sold
25/100x = 4,80,000 – x
25x + x / 100 = 4,80,000
Cost of goods sold = 4,80,000 x 100/ 25
= 3,84,000
Cost of goods sold = opening inventory + purchase – closing inventory
3,84,000 = opening inventory + 3,60,000 – 68,000
Opening inventory = 3,84,000 – 3,60,000 + 68,000
= 92,000
93. From the following information, determine opening and closing inventories:
Inventory turnover Ratio 5 times, total sales 2,00,000, gross profit Ratio 25%. Closing inventory is more y 4,000 than the opening inventory.
Solution:
Gross profit = 25% of sales
= 25/100 x 2,00,000
= 50,000
Gross profit = revenue from operation – cost of goods sold
50,000 = 2,00,000 – cost of goods sold
Cost of goods sold = 1,50,000
Let the opening inventory be x
Closing inventory = x + 4,000
Inventory turnover Ratio = Cost of goods sold / average inventory
= 1,50,000 / x + x + 4,000 / 2
5 (2x + 4,000) = 1,50,000 x 2
10 x + 20,000 = 3,00,000
X = 3,00,000 – 20,000 / 10
Opening inventory = 28,000
Closing inventory = 28,000 + 4,000
= 32,000
94. Inventory turnover Ratio 5 times; cost of Revenue from operations (cost of goods sold) 18,90,000. Calculate opening inventory and closing inventory if inventory at the end is 2.5 times more than that in the beginning.
Solution:
Let the opening inventory be x
Closing inventory = x + 2.5 x = 3.5 x
Inventory turnover Ratio = Cost of goods sold / average inventory
5 = 1,50,000 / x+x+2.5 / 2
5 (4.5 x) = 18,90,000 x 2
X = 18,90,000 – 2x / 5x 4.5
Opening inventory = 16,80,000
Closing inventory = 16,80,000 x 3.5
= 5,88,000
Calculate of Revenue from Operations
95. Average inventory of AB Ltd. Is Rs.1,00,000 and the inventory turnover ratio is 6 times. Calculate the amount of Revenue from Operation if goods are sold at a profit of 25% on Revenue from Operations:
Inventory turnover ratio=cost of revenue from operation
Average inventory
6 = cost of revenue from operation
100,000
= 600,000
Goods sold at a profit of 25% on revenue from operation which means
Cost of revenue from operation=75% revenue from operation
Lets assume revenue from operation x
Cost of revenue from operation=revenue from operation
600,000 =75x
100
X=800,000
Revenue from Operation = Rs.8,00,000.
TRADE RECEIVABLES TURNOVER RATIO
96. Credit revenue from operations, i.e., Net credit sale for the year
Debtors 12,00,000
Bills Receivable 1,20,000
Calculate Trade receivables turnover Ratio 80,000
Calculate Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio.
Solution:
Avg. trade receivables = 1,20,000 + 80,000
Trade receivable turnover Ratio = Credit revenue from operation / Average trade receivable
= 12,00,000 / 2,00,000
= 6 times
97. Calculate trade receivables turnover Ratio from the following information:
Opening Balance closing Balance
Sundry debtors 28,000 25,000
Bills Receivables 7,000 15,000
Provision for doubtful debts 1,500 4,500
Total sales 1,00,000; sales return 1,5000; cash sales 23,5000.
Solution:
Avg. Trade Receivable = Opening debtors + closing debtors / 2 + Op. T/R + Cl. T/R / 2
= 28,000 + 25,000/2+ 7,000 + 15,000/2
= 26,500 + 11,000
= 37,500
Net credit sales = 1,00,000 – 1500 – 23,500
= 75,000
Trade receivable turnover Ratio = Credit Revenue from operation / Average Trade Receivable
= 75,000 / 37,000
= 2 times
98. Closing Trade receivables 90,000 revenue from operation 7,20,000, cash revenue from operations 1,80,000. Provision for doubtful debts 8,000. Calculate Trade receivables turnover Ratio.
Solution:
Avg. Trade Receivable = 90,000
Credit revenue from operations = 7,20,000 – 1,80,000
= 5,40,000
Inventory turnover Ratio = Cost of goods sold / average inventory
= 5,40,000 / 90,000
= 6 times
99. Closing Trade Receivables 1,00,000; cash sales being 25% of credit sales; Excess of closing Trade Receivables over opening Trade Receivables 40,000; revenue from operations, i.e., net sales 6,00,000. Calculate trade receivable turnover Ratio.
Solution:
Closing Trade receivable = 1,00,000
Opening Trade receivable = 60,000
Net sales = cash sales + credit sales
6,00,000 = 25/100x + x
25x / 100 = 6,00,000
Credit sales = 6,00,000 x 100 / 125
Credit + sales = 4,80,000
Inventory receivable turnover Ratio = Net credit + Sales / Average trade receivable
5 = 4,80,000 / 60,000 + 1,00,000/2
= 4,80,000 x 2 / 1,60,000
= 6 times
100. compute Trade receivables turnover Ratio from the following:
31st March, 31st March,
2024 2025
Revenue from operations (Net sales) 8,00,000 7,00,000
Debtors in the beginning of year 83,000 1,17,000
Debtors at the end of year 1,17,000 83,000
Sales Return 1,00,000 50,000
solution:
2021
Avg. Trade Receivable = Opening debtors + closing debtors / 2
= 83,000 + 1,17,000 /2
= 1,00,000
Trade Receivable Turnover Ratio = Credit Revenue from operation / Average Trade Receivable
= 8,00,000 / 1,00,000
= 8 Times
2022
Avg. Trade Receivable = Opening debtors + closing debtors / 2
= 1,17,000 + 83,000 /2
= 1,00,000
Trade Receivable Turnover Ratio = Credit Revenue from operation / Average Trade Receivable
= 7,00,000 / 1,00,000
= 7 Times
101. Closing Trade Receivables 1,20,000, Revenue from operations 14,40,000. provision for Doubtful Debt 20,000. Calculate trade receivables Ratio.
solution:
Trade Receivable Turnover Ratio = Credit Revenue from operation / Average Trade Receivable
= 14,40,000 / 1,20,000
= 12 Times
102. Closing Trade Receivables 4,00,000; Cash sales being 25% of credit sales; Excess of closing Trade Receivables over opening Trade Receivables 2,00,000; Revenue from operations, i.e., Net sales 15,00,000. Calculate Trade Receivables Turn over Ratio.
Solution:
Closing Trade Receivable = 4,00,000
Opening Trade Receivable = 4,00,000 – 2,00,000
= 2,00,000
Net Revenue from operation = Cash sales + Credit + Sales
15,00,000 = 25x /100 + x
Closing Trade Receivable = 4,00,000
Opening Trade Receivable = 4,00,000 – 2,00,000
= 2,00,000
Net sales = Cash sales + Credit + Sales
15,00,000 = 25x /100 + x
x = 15,00,000 x 100 / 125
credit sales = 12,00,000
Trade Receivable Turnover Ratio = Credit Revenue from operation / Average Trade Receivable
= 12,00,000/2,00,000+4,00,000/2
= 12,00,000 x 2 / 6,00,000
= 4 Times
103. A form normally has Trade Receivables equal to two months credit sales. During the coming year it expects credit sales of 7,20,000 spread evenly over the year (12 months). What is estimated amount of Trade Receivables at the end of the year?
Solution:
Closing Trade Receivable = Two months credit sales
= x 2
= 1,20,000
104. Mercury Ltd. made credit sales of 4,00,000 during the financial period. If the collection period is 36 days and year is assumed to be 360 days, calculate:
- Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio;
- Average Trade Receivables;
- Trade Receivables at the end when Receivables at the end are more than in the beginning by 6,000.
Solution:
Debt Collection period = Number of Days / Trade receivable turnover ratio
36 = 360 / Trade receivable turnover ratio
Trade Receivable Turnover Ratio = Net Credit Sales / Average Trade Receivable
10 = 4,00,000 / Average Trade Receivable
Avg. Trade Receivables = 40,000
Let the opening trade receivable be x
closing Trade receivable = x + 6,000
Avg. Trade Receivable = Op. T / R + Cl. T / R /2
40,000 = x + x + 6,000 / 2
2 x + 6,000 = 80,000
Opening trade r = 37,000
Closing Inventory = 43,000
105. Calculate Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio in each of the following alternative cases:
Case 1: Net credit sales 4,00,000; Average Trade receivables 1,00,000.
Case 2: Revenue from operations (Net sales) 30,00,000; Cash revenue from operations, i.e., Cash sales 6,00,000; opening trade receivables 2,00,000; closing trade receivables 6,00,000.
Case 3: Cost of revenue from operations or cost of goods gold 3,00,000; Gross profit on cost 25% cash sales 20% of Total sales; opening trade receivables 50,000; closing trade receivables 1,00,000.
Case 4: Cost of Revenue from operations or cost of goods sold 4,50,000; Gross profit on sales 20% cash sales 25% of net credit sales, opening trade receivables 90,000; closing trade receivables 60,000.
Case 1:
Trade Receivable Turnover Ratio = Net Credit Sales + Revenue from Operation /Ave. Trade Receivable
= 4,00,000 / 1,00,000 = 4 times
Case 2: Net credit revenue from operation = Net sales – cash sales
= 30,00,000 – 6,00,000
= 24,00,000
Avg. Trade Receivable = Op. T/R + Cl. T/R /2
= 2,00,000 + 6,00,000 / 2
Average Trade Receivable = 4,00,000
Trade Receivable Turnover Ratio = Net Credit Sales / Ave. Trade Receivable
= 24,00,000 / 4,00,000 = 6 times
Case 3:
Gross profit = 25 /100 of cost goods sold
= 25/ 100 x 3,00,000
= 75,000
Gross profit = Revenue from operation – cost of goods sold
75,000 = Revenue form operation – 3,00,000
Revenue from operation (Net sales) = 3,75,000
Net sales = Cash Sales + Credit sales
3,75,000 = 25/100 x 3,75,000 + Credit sales
credit sales = 3,75,000 – 75,000
= 3,00,000
Inventory Turnover Ratio = Net Credit Revenue from operation / Average Trade Receivable
= 3,00,000/50,000 + 1,00,000 / 2
= 3,00,000 x 2 / 1,50,000
= 4 times
Case 4:
Gross profit = Net Return from operation – cost of goods sold
25/100x = x – 4,50,000
80x / 100 = 4,50,000
Net revenue from operations = 4,50,000 x 100 / 80
= 5,62,500
Net sales = cash sales + credit sales
5,62,500 = 25/100x + x
Net credit revenue from operations = 5,62,500 x 100 / 125
= 4,50,000
Avg. Trade Receivable = Op. T/R + Cl. T/R / 2
= 90,000 + 60,000 / 2
= 75,000
Inventory Turnover Ratio = Net Credit Revenue from operation / Average Trade Receivable
= 4,50,000 / 75,000
= 6 times
106. From the information given below calculate Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio:
Credit Revenue from operations, i.e., Credit sales 8,00,000; opening Trade Receivables 1,20,000; and closing Trade Receivables 2,00,000.
State, giving reason, which of the following would increase, decrease or not change Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio:
- Collection From Trade Receivables 40,000.
- Credit Revenue from operations, i.e., credit sales 80,000
- Sales Return 20,000
- Credit Purchase 1,60,000.
Solution:- Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio = 5 Times.
- Increase,
- Decrease;
- Increase,
- No Change.
CALCULATION OF OPENING AND CLOSING TRADE RECEIVABLES
107. 1,75,000 is the Credit revenue from operations, i.e., Net credit of an enterprise. If Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio is 8 times, calculate Trade Receivables in the beginning and at the end of the year. Trade Receivables at the end is 7,000 more than in the beginning.
Solution:
Credit revenue from operation = 1,75,000
Let the Trade receivable in the begening be = x
Closing Trade Receivable = x + 7,000
Trade Receivable Turnover Ratio = Net Credit Revenue from operation / Average Trade Receivable
8 = 1,75,000/ x + x + 7,000 / 2
8 = 1,75,000 / 2x + 7,000
8(2x + 7,000) = 1,75,000 x 2
2x + 7,000 = 1,75,000 x 2 / 8
2x = 43,750 – 7,000
Opening Trade Receivable (x) = 36,750 / 2
= 18,375
Closing Trade Receivable = 18,375 + 7,000
= 25,375
108. From the following information, calculation opening and closing Trade Receivables, if Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio is 3 Times.
- Cash Revenue from operations is 1/3rd of credit Revenue from operations .
- Cost of Revenue from operations is 3,00,000.
- Gross profit is 25% of the Revenue from operations.
- Trade Receivables at the end are 3 times more than that of the beginning.
Solution:
Gross profit = Net sales – Cost of Goods sold
= 25/100 x = x – 3,00,000
x – 25 /100 = 3,00,000
= 75/100 x = 3,00,000
x = 3,00,000 x 100 /75
Net revenue from operations = 4,00,000
let cash sales be x
Net revenue from operations = cash sales + credit sales
4,00,000 = 1/3 x + x
= 4x/3 = 4,00,000
x = 4,00,000 x 3 / 4
Net credit revenue from operation = 3,00,000
Let the opening trade receivable be x
closing trade receivables = x + 3x
Trade Receivable Turnover Ratio = Net Credit Revenue from operation / Average Trade Receivable
3 = 3,00,000 / x + 4x / 2
3 (x + 4x) = 3,00,000 x 2
x = 3,00,000 x 2 / 3 x 5
Opening Trade Receivable = 40,000
Closing Trade Receivable = 40,000 x 4
= 1,60,000
109. Cash revenue from operations (cash sales) 2,00,000, cost of Revenue from operations or cost of goods sold 3,50,000; Gross profit 1,50,000; Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio 3 times. Calculate opening and closing Trade Receivables in each of the following alternative cases:
Case 1: If closing Trade Receivables were 1,00,000 in excess of Opening Trade Receivables.
Case 2: If Trade Receivables at the end were 3 times than in the beginning.
Case 3: If Trade Receivables at the end were 3 times more than that of in the beginning.
Solution:
Gross profit = Net sales – Cost of goods sold
1,50,000 = Net sale – 3,50,000
Net sales = 5,00,000
Net sales = Cash sales + Credit sales
5,00,000 = 2,00,000 + Credit sales
Net credit revenue from operation = 3,00,000
(Net credit sales)
Case : 1
Opening Trade Receivable = x
Closing Trade Receivable = x + 1,00,000
Trade Receivable Turnover Ratio =
3 =
2x + 1,00,000 = 3,00,000 x 2
3
2x = 2,00,000 – 1,00,000
x =
Opening Trade Receivable = 50,000
Closing Trade Receivable = 50,000 + 1,00,000
= 1,50,000
Case : 2
Opening Trade Receivable = x
Closing Trade Receivable = 3x
Trade Receivable Turnover Ratio = Net Credit Revenue from operation / Average Trade Receivable
3 = 3,00,000 / x + (x + 1,00,000) / 2
3(x + 3x) = 3,00,000 x 2
3 x 4
Opening Trade Receivable = 50,000
Closing Trade Receivable = 50,000 x 3
= 1,50,000
Case : 3
Opening Trade Receivable = x
Closing Trade Receivable = x + 3x = 4x
Trade Receivable Turnover Ratio = Net Credit Revenue from operation / Average Trade Receivable
3 = 3,00,000 / x + 3x / 2
3(x + 4x) = 3,00,000 x 2
3 x 5
Opening Trade Receivable = 40,000
Closing Trade Receivable = 40,000 x 4
= 1,60,000
TRADE PAYABLES TURNOVER RATIO
110. Calculate Trade payable turnover ratio from the following information:
Opening Creditors 1,25,000; opening bills payable 10,000; closing creditors 90,000 closing bills payable 5,000 purchase 9,50,000 cash purchase 1,00,000 purchase return 45,000.
Solution:
Net credit purchase = Total purchase – cash purchase – purchase Return
= 9,50,000 – 1,00,000 – 45,000
= 8,05,000
Avg. Creditors = Op. Creditors + Cl. Creditors / 2
= 1,25,000 +90,000 / 2
= 1,07,500
Avg. Trade payable = Op. B/P + Cl. B/P /2
= 10,000 + 5,000 / 2
= 7,500
Avg. Trade payable = Avg. creditors + Avg. Bills payable
= 1,07,500 + 7,500
= 1,15,000
Trade Payable Turnover Ratio = Net Credit Purchase / Avg. Trade Receivable
= 8,05,0000 / 1,15,000
= 7 times
111. Calculate Trade payable turnover ratio and Average Debt payment period from the following111. information:
1st April, 2022 31st March, 2023
Sundry Creditors 1,50,000 4,50,000
Bills payable 50,000 1,50,000
Total purchases 21,00,000; purchases Return 1,00,000; cash purchases 4,00,000.
Solution:
Total purchase = Cash purchase + purchase return
21,00,000 = 4,00,000 + Credit purchase
Credit purchase = 17,00,000
Net credit purchase = Credit purchase – purchase Return
= 17,00,000 – 1,00,000
Avg. Trade payables = Op. Creditors + Cl. Creditors / 2 + Op. B /p + Cl. B /p /2
= 1,50,000 + 4,50,000 / 2 + 50,000 + 1,50,000 / 2
= 3,00,000 + 1,00,000
= 4,00,000
Trade Payable Turnover Ratio = Net Credit purchase / Avg. Trade Receivable
= 16,00,000 / 4,00,000
= 4 times
Avg. Debt Payment Ratio = Months in a year / Trade payable Turnover Ratio
= 12 / 4
= 3 months
112. Closing Trade Payables Rs.5,40,000, Net Purchases Rs.43,20,000. Cash Purchases Rs.10,80,000. Calculate Trade Payable Turnover Ratio.
Solution- Credit Purchase = Net Profit – Cash Purchase
= 43,20,000 – 10,80,000
= 32,40,000
Trade Payable Turnover Ratio = Credit Purchase/average trade payable
= 32,40,000 = 6 times
540,000
113. Calculate trade payables turnover ratio for the year 2022-23 in each of the alternative cases:
Case 1: Closing Trade payables 454,000 net purchase 3,60,000 purchases return 60,000 cash purchase 90,000
Case 2: Opening Trade payables 15,000 closing Trade payables 45,000 net purchases 3,60,000
Case 3: Closing trade payables 45,000 net purchases 3,60,000
Case 4: Closing trade payables (including 25,000 due to a supplier of machinery) 55,000 net credit purchases 3,60,000.
Case -1
Net credit purchase = Net purchase – cash purchase
= 3,60,000 – 90,000
= 2,70,000
Average trade payable = closing trade payable
= 45,000
Trade Payable Turnover Ratio = Net Credit purchase / Avg. Trade receivable
= 2,70,000 / 45,000
= 6 times
Case – 2
Net credit purchase = Net purchase
= 3,60,000
Average Trade payable = Op. T /P + Cl. T/ P / 2
= 15,000 + 45,000 / 2
= 30,000
Trade Payable Turnover Ratio = Net Credit Purchase / Avg. Trade Payable
= 3,60,000 / 30,000
= 12 times
Case – 3
Avg. trade payables = closing trade payable
= 45,000
Net credit purchase = Net purchases = 3,60,000
Trade Payable Turnover Ratio = Net Credit Purchase / Avg. Trade Payable
= 3,60,000 / 45,000
= 8 times
Case – 4
Avg. trade payable = closing trade payable – due to supplier of machinery
= 55,000 – 25,000
= 30,000
Net credit purchase = 3,60,000
Trade Payable Turnover Ratio = Net Credit Purchase / Avg. Trade Payable
= 3,60,000 / 30,000
= 12 times
Calculation of Opening and Closing Trade Payable
114. From the following information, calculate Opening and closing trade payables:
Cash Purchases 25% of Total Purchases; Revenue from Operations Rs.3,00,000; Gross profit 25% on Revenue form Operations; Opening Inventory Rs.75,000; Closing Inventory Rs.1,50,000; Trade Payables Turnover ratio 3 Times; Closing Trade Payables were Rs.75,000 in excess of Opening Trade Payable.
Solution- Gross Profit = Revenue from operation – Cost of Revenue from operation
25% of 3,00,000 = 3,00,000 – Cost of Revenue from operation
Cost of Revenue from operation = 3,00,000 – 75,000
= Rs.2,25,000
Cost of Revenue from = Op. Inventory + Total Purchase – CI. Inventory operation
2,25,000 = 75,000 = Total Purchase – 1,50,000
Total Purchase = Rs.3,00,000
Net Credit + Purchase = Total Purchase – Cash Purchases
= Rs.3,00,000 – Rs.75,000
= Rs.2,25,000
Opening Trade Payable = X
Closing Trade Payable = X + 75,000
Net Credit + Purchase
Trade Payable Turnover Ratio =
Aug T/P
3 = 2,25,000 / X + X + 75,000 / 2
3 = 2,25,000 X 2 / 2x + 75,000
3 (2x + 75,000) = 2,25,000 X 2
6x + 75,000 X 3 = Rs.4,50,000
X = 4,50,000 – 2,25,000 / 6
Opening Trade Payable = Rs.37,500
Closing Trade Payable = Rs.37,500 + Rs.75,000
= Rs.1, 12,500
WORKING CAPITAL TURNOVER RATIO
115. Calculate working capital turnover ratio from the following information:
Revenue from operations 12,00,000
Current Assets 5,00,000
Current Liabilities 2,00,000
Solution:
Working capital = current Assets – current liabilities
= 5,00,000 – 2,00,000
= 3,00,000
Revenue from operation = 12,00,000
Working capital Turnover Ratio = Net Revenue from operation / Working capital
= 12,00,000 / 3,00,000
= 4 times
116. From the following information, calculate working capital turnover Ratio:
Cost of revenue from operations (cost of goods sold) 10,00,000
Current Assets 5,00,000
Current Liabilities 3,00,000
Solution:
Net revenue from operation = cost of revenue from operations
= 10,00,000
Working capital = current Assets – current liabilities
= 5,00,000 – 3,00,000
= 2,00,000
Working capital Turnover Ratio = Net Revenue from operation / Working capital
= 10,00,000 / 2,00,000
= 5 times
117. Revenue from operations: cash sales 5,00,000; credit sales 6,00,000; sales return 1,00,000 current Assets 3,00,000; current liabilities 1,00,000. Calculate working capital turnover Ratio.
Solution:
Net revenue from operation = cash sales + credit sales – sales return
= 5,00,000 + 6,00,000 – 1,00,000
= 10,00,000
Working capital = current Assets – Current liabilities
= 3,00,000 – 1,00,000
= 2,00,000
Working capital Turnover Ratio = Net Revenue from operation / Working capital
= 10,00,000 / 2,00,000
= 5 times
118. Equity share capital 15,00,000; Gross profit on Revenue from operations, i.e., sales Cost of revenue from operations or cost of goods sold 20,00,000; Current Assets 10,00,000; Current liabilities 2,50,000. Calculate working capital turnover Ratio.
Solution;
Gross profit = revenue from operation – cost of revenue from op.
33 of x = x – 20,00,000
X – 1/3x = 20,00,000
X = 20,00,000 x 3 / 2
Revenue from operation = 30,00,000
Working capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities
= 10,00,000 – 2,50,000
= 7,50,000
Working capital Turnover Ratio = Net Revenue from operation / Working capital
= 30,00,000 / 7,50,000
= 4 times
119. Capital employed 12,00,000 net fixed Assets 8,00,000 cost of goods sold or cost or revenue form operations 40,00,000 gross profit is 20% on cost. Calculate working capital turnover Ratio.
Solution:
Gross profit = Revenue from operation – cost of revenue from operation
20% of 40,00,000 = Revenue from operation – 40,00,000
Revenue from operation = 40,00,000 + 8,00,000
= 48,00,000
Working capital=Capital employed -net fixed assets
=1200,000-800,000
working capital = 4,00,000
Working capital Turnover Ratio = Net Revenue from operation / Working capital
= 48,00,000 / 4,00,000
= 12 times
120. Calculate working capital turnover ratio from the following information:
Revenue from operations 15,00,000; current Assets 6,25,000; Total Assets 10,00,000; Non-current liabilities 5,00,000, shareholders funds 2,50,000.
Solution:
Shareholder’s funds + Non-current + Current = Total Assets
Liabilities Liabilities
= 2,50,000 + 5,00,000 + current liabilities = 10,00,000
= Current liabilities = 10,00,000 – 7,50,000
= 2,50,000
Working capital = Current Assets – Current liabilities
= 6,25,000 – 2,50,000
= 3,75,000
Revenue from operations = 15,00,000
Working capital Turnover Ratio = Net Revenue from operation / Working capital
= 15,00,000 / 3,75,000
= 4 times
121. Gross profit at 25% on cost: Gross profit 5,00,000 equity share capital 10,00,000 reserve and surplus 2,00,000 long-term loan 3,00,000; fixed Assets (Net) 10,00,000. Calculate working capital Turnover Ratio.
Solution:
Gross profit = 25% on cost of goods sold
5,00,000 = x cost of goods sold
Cost of goods sold = 5,00,000 x 100 / 25
= 20,00,000
Cost of goods sold=revenue from operation-gross profit
revenue from operation = cost of goods sold + gross profit
= 20,00,000 + 5,00,000
= 25,00,000
Total long term fund i.e. Equity share capital + reserves & surplus+long term loan
10,00,000 + 2,00,000 + 3,00,000 =15,00,000
Fixed assets (given)10,00,000
Total fund =fixed assets+ working capital
1500,000 =10,00,000+working capital
Working capital =1500,000-10,00,000
=500,000
Working capital = 5,00,000
Working capital Turnover Ratio = Net Revenue from operation / Working capital
= 25,00,000 / 5,00,000
= 5 times
122. A company earns Gross profit of 25% on cost. for the year ended 31st March, 2017 its Gross profit was 5,00,000; Equity share capital of the company was 10,00,000; Reserves and surplus 2,00,000; long-term loan 3,00,000 and Non-current Assets were 10,00,000.
Compute the ‘working capital Turnover Ratio’ of the company
Solution:
Gross profit = 25% on cost of goods sold
5,00,000 = x cost of goods sold
Cost of goods sold = 5,00,000 x 100 / 25
= 20,00,000
Net revenue from operation = cost of goods sold + Gross profit
= 20,00,000 + 5,00,000
= 25,00,000
Equity share capital + reserve & surplus = Non-current Assets + long-term loans
current Assets
10,00,000 + 2,00,000 + 3,00,000 + current liabilities = 10,00,000 + Current Assets
Current liabilities – current Assets = 10,00,000 + 2,00,000 + 3,00,000 – 10,00,000
working capital = 5,00,000
Working capital Turnover Ratio = Net Revenue from operation / Working capital
= 25,00,000 / 5,00,000
= 5 times
FIXED ASSETS TURNOVER RATIO
123. Net fixed Assets 5,00,000, Revenue from operations 25,00,000. Calculate fixed Assets turnover ratio.
Solution:
Revenue from operation = 25,00,000
Net Fixed Assets = 5,00,000
Fixed Assets Turnover Ratio = Net Revenue from operation / Net Fixed Assets
= 25,00,000 / 5,00,000
= 5 times
124. Fixed Assets (at cost) 7,00,000, Accumulated Depreciation 1,00,000, Credit Revenue from operations 17,00,000 cash revenuer from operations 1,00,000. Calculated Fixed Assets Turnover Ratio.
Solution:
Revenue from operations = Credit revenue from operations + cash revenue from operation
= 17,00,000 + 1,00,000
= 18,00,000
Fixe Assets = 6,00,000
Fixed Assets Turnover Ratio = Net Revenue from operation / Net Fixed Assets
= 18,00,000 / 6,00,000
= 3 times
125. Capital Employed 2,50,000, working capital 50,000, cost of Revenue from operations 8,00,000, Gross profit 2,00,000. Calculate fixed Assets Turnover Ratio.
Solution:
Cost of revenue from operation = revenue from operation -gross profit
800,000 = revenue from operation-200,000
Revenue from operation = 800,000+200,000
= 10,00,000
Revenue from operation = 10,00,000
Fixed assets = Capital Employed – working capital
= 2,50,000 – 50,000
= 2,00,000
Fixed Assets turnover ratio = Net Revenue from operation / Net Fixed Assets
= 10,00,000 / 2,00,000
= 5 times
126. Capital employed 30,00,000; working capital 5,00,000; cost of revenue from operations 40,00,000; Gross profit 25% of cost. Calculate Fixed Assets Turnover Ratio.
Solution:
Net fixed Assets = Capital employed – working capital
= 30,00,000 – 5,00,000
= 25,00,000
Gross profit = Revenue from operation – cost of revenue from operation
x 40,00,000 = Revenue from operation – 40,00,000
Revenue from operation = 40,00,000 + 10,00,000
= 50,00,000
Fixed Assets turnover ratio = Net revenue from operation / Net fixed Assets
= 50,00,000 / 25,00,000
= 2 times
127. Following information is of Raja Ltd. for 2 years, calculate fixed Assets Turnover Ratio:
2023-24 2024-25
Fixed Assets at written down value 3,00,000 6,00,000
Cost of Revenue form operations 12,00,000 18,00,000
Solution:
2021-22
Net fixed Assets = 3,00,000
Revenue from operations = cost of revenue from operations
= 12,00,000
Fixed Assets turnover ratio = Net revenue from operation / Net fixed Assets
= 12,00,000 / 3,00,000
= 4 times
Note: In the absence of any further data, revenue from operation is equal to cost of revenue from operation
2022-23
Net fixed Assets = 6,00,000
Revenue from operations = cost of revenue from operations
= 18,00,000
Fixed Assets turnover ratio = Net revenue from operation / Net fixed Assets
= 18,00,000 / 6,00,000
= 3 times
Note: In the absence of any further data, revenue from operation is equal to cost of revenue from operation
NET ASSETS TURNOVER RATIO
128. Based on the following information, calculate net Assets or capital employed turnover ratio:
Share holder’s funds 20,00,000 Equity share capital 10,00,000 Reserves and surplus 10,00,000 8% debentures 10,00,000 and revenue from operations 75,00,000.
Solution:
Capital employed = shareholders’ funds + 8% Debentures
= 20,00,000 + 10,00,000
= 30,00,000
Revenue form operation = 75,00,000
Net Assets Turnover Ratio = Revenue from operation / Capital Employed
= 75,00,000 / 30,00,000
= 2.5 times
129. From the following information calculate Net Assets Turnover Ratio:
Equity Share Capital Rs.15,00,000; Long-term Borrowing Rs.30,00,000; Reserve and Surplus Rs.5,00,000; Non-current Assets Rs.32,00,000; Revenue from Operations Rs.1,00,00,000.
Solution-
- Compute Net Assets(capital employed)
(Net Assets) = (Equity Share Capital) + (Reserves & Surplus) + (Long term Borrowings) – (Not-current Assets)
= (15,00,000 + 5,00,000 + 30,00,000 ) – 32,00,000
= 50,00,000 – 32,00,000
= 18,00,000
Turnover Ratio = 1,00,00,000 / 18,00,000
= 2 times
130. Property, plant and equipment and intangible Assets (at cost) 30,00,000; Accumulated depreciation 5,00,000; Trade investment 2,50,000; Current Assets 11,00,000; Current liabilities 8,50,000; Cash Revenue from operations 10,00,000; Credit revenue from operations 40,00,000
Calculate Net Assets Turnover Ratio.
Solution:
Net Assets = property plant and equipment and intangible Assets (at cost – Acc. depreciation + Trade investment + current Assets – Current liabilities
= 30,00,000 – 5,00,000 + 2,50,000 + 11,00,000 – 8,50,000
= 30,00,000
Revenue from operation = cash revenue from operation + credit revenue from operation
= 10,00,000 + 40,00,000
= 50,00,000
Net Assets Turnover Ratio = evenue from operation / Capital Employed
= 50,00,000 / 30,00,000
= 1.67 times
131. Property, Plant and Equipment and intangible Assets Rs.10,00,000; Working Capital Rs.5,00,000; cost of Revenue from Operations Rs.50,00,000; Gross profit 20% of Cost.
Solution-
- Calculate Revenue from Operations
Revenue from Operations = cost of Revenue + Gross profit X Revenue from Operations
= 50,00,000 – 20% X 50,00,000
= 50,00,000 + 10,00,000
= 60,00,000
2. Calculate Capital Employed
Capital Employed = Property, Plant & Equipment & Intangible Assets) + Working Capital
= 10,00,000 + 5,00,000
= 15,00,000
3. Calculate Net Assets
Turnover Ratio
Net Asset Turnover Ratio = Revenue from Operations / Capital Employed
= 60,00,000 / 15,00,000
= 4 times
Final Answer = 4 times
132. Shareholder’s funds 10,00,000; Long-term Debts 20,00,000; Gross profit at 20% on cost was 20,00,000. Calculate Net Assets or capital employed turnover Ratio.
Solution:
Capital Employed = Shareholder’s funds+ Long-term debts
Capital Employed = 10,00,000 + 20,00,000
Capital Employed = 30,00,000
Gross profit = 20% on cost
20,00,000 = 20% on cost
Cost of Revenue from operation = 20,00,000 x 100/20
Cost of Revenue from operation = 1,00,00,000
Revenue from operation = cost of revenue from operation + Profit
Revenue from operation = 1,00,000,00 + 20,00,000
Revenue from operation = 1,20,00,000
Net Assets Turnover operation = Revenue from operation/ Capital Employed
Net Assets Turnover Ratio = 1,20,00,000/30,00,000
Net Assets Turnover Ratio = 4 times
133. From the following Balance Sheet of Akhil ltd. as at 31st march, 2025, calculate (i) Net assets turnover ratio and (ii) fixed assets turnover ratio:
Revenuer from operations for the year was 45,00,000.
Solution:
Capital Employed = share capital + reserve & surplus + 8% Debentures
= 10,00,000 + 3,00,000 + 5,00,000
= 18,00,000
Revenue from operation = 45,00,000
Net Assets Turnover Ratio = Revenue from operation/ Capital Employed
= 45,00,000 / 18,00,000
= 2.5 times
Net Fixed Assets = Property plant & Equipment (Net Depreciation)
= 13,00,000
Revenue from operation = 45,00,000
Net Assets Turnover Ratio = Revenue from operation/ Capital Employed
= 45,00,000 / 13,00,000
= 3.4615 = 3.46 times
GROSS PROFIT RATIO
134. From the following, calculate Gross Profit Ratio:
Gross Profit: 50,000; revenue from operation 5,00,000; sales Return 50,000.
Solution:
Gross Profit Ratio = Gross Profit / revenue from operation x 100
= 50,000 / 5,00,000 x 100
= 10%
135. Compute Gross profit Ratio form the following information:
Cost of revenue from operations (cost of goods sold) 5,40,000;
revenue from operations (Net sales) 6,00,000.
Solution:
Gross profit = revenue from operation – cost of revenue from operation
= 6,00,000 – 5,40,000
= 60,000
Gross Profit Ratio = Gross Profit / revenue from operation
= 60,000 / 6,00,000 x 100
= 10%
136. Computer Gross profit Ratio from the following information:
Revenue from operations, i.e., Net sales = 4,00,000; Gross profit 25% on cost.
Solution;
Gross profit = revenue from operation – cost of revenue from operation
25 /100x = 4,00,000 – x
1/4x + x = 4,00,000
5x / 4 = 4,00,000 x
X = 4,00,000 x 4 / 5
Cost of revenue from operation = 3,20,000
Gross profit = Revenue from operation – cost of revenue from operation
= 4,00,000 – 3,20,000
= 80,000
Gross Profit Ratio = Gross profit / revenue from operation x 100
= 80,000 / 4,00,000 x 100
= 20%
137. Calculate gross profit ratio from the following data:
Cash sales are 20% of Total sales are 5,00,000; purchases are 4,00,000; Excess of closing inventory over opening inventory 25,000.
Solution:
Total sales = cash sales + credit sales
X = 20/100x = 5,00,000
x – 20/100x = 5,00,000
80x /100x = 5,00,000
Total sales = 5,00,000 x 100 / 80
Revenue from operation = 6,25,000
Cost of goods sold = opening inventory + purchases – closing inventory
= purchases – (closing inventory – opening inventory)
= 4,00,000 – 25,000
= 3,75,000
Gross profit = Revenue from operation – cost of goods sold
= 6,25,000 – 3,75,000
= 2,50,000
Gross Profit Ratio = Gross profit / revenue from operation x 100
= 2,50,000 / 6,35,000x 100
= 40%
138. From the following information, calculation Gross profit Ratio:
Credit sales 10,00,000
Purchases 6,00,000
Carriage inwards 20,000
Decrease in inventory 20,000
Return outward 20,000
Wages 1,00,000
Rate of credit sales to cash sale 4:1
Solution:
Revenue from operation = credit sales + cash sales – sales return
= 10,00,000 + 10,00,000 x – 0
= 12,50,000
Cost of goods sold = purchases – Return outward + Carriage inward + wages + Decrease In inventory
= 6,00,000 – 20,000 + 20,000 + 1,00,000 + 20,000
= 7,20,000
Gross profit = Revenue from operation – cost of Goods sold
= 12,50,000 – 7,20,000
= 5,30,000
Gross Profit Ratio = Gross profit / revenue from operation x 100
= 5,30,000 / 12,50,000 x 100
= 42.4 %
139. From the following information, calculate Gross profit Ratio:
Revenue from operations:
Cash 2,00,000 Carriage inwards 8,000
Credit 8,00,000 Salaries 42,000
Purchases: Decreases in inventory 1,22,000
Cash 40,000 Return Outwards 20,000
Credit 3,60,000 Wages 20,000
Solution:
Revenue from operation = Credit sales + Cash sales
= 8,00,000 + 2,00,000
= 10,00,000
Cost of goods sold = purchases (cash + credit) – Return outward + wages + Carriage inward + Decrease In inventory
= (3,60,000 + 40,000) – 20,000 + 20,000 + 8,000 + 1,22,000
= 5,30,000
Gross profit = Revenue from operation – cost of goods sold
= 10,00,000 – 5,30,000
= 4,70,000
Gross Profit Ratio = Gross profit / revenue from operation x 100
= 4,70,000 / 10,00,000 x 100
= 47 %
140. Opening inventory 2,00,000; closing inventory 1,20,000. Inventory Turnover Ratio 8 times; Selling price 25% above cost. Calculate Gross profit Ratio.
Solution:
Inventory Turnover Ratio = Cost of good sold / Avg. Inventory
8 = cost of good sold / 2,00,000 + 1, 20,000 / 2
Cost of Goods sold = 8 (3,20,000) / 2
= 12,80,000
Revenue from operation = cogs + 25% of cogs
= 12,80,000 + x 12,80,000
= 12,80,000 + 3,20,000
= 16,00,000
Gross profit = Revenue from operation – cost of goods sold
= 16,00,000 – 12,80,000
= 3,20,000
Gross Profit Ratio = Gross profit / revenue from operation x 100
= 3,20,000 / 16,00,000 x 100
= 20 %
141. A trade carries an Average inventory of 1,00,000. His inventory Turnover Ratio is 8 times. He sells goods at a profit of 25% of cost. Calculate Gross Profit Ratio.
Solution:
Inventory Turnover Ratio = Cost of good sold / Avg. Inventory
8 = Cost of good sold / 1,00,000
Cost of Goods sold = 8,00,000
Revenue from operation = cogs + 25% of cogs
= 8,00,000 + x 8,00,000
= 10,00,000
Gross profit = Revenue from operation – cost of goods sold
= 10,00,000 – 8,00,000
= 2,00,000
Gross Profit Ratio = Gross profit / revenue from operation x 100
= 2,00,000 / 10,00,000 x 100
= 20 %
142. Calculate Gross profit ratio form the following data:
Average inventory 3,20,000; inventory turnover ratio 8 times; Average trade receivables 4,00,000 trade receivables turnover ratio 6 times; cash sales 25% of Net sales.
Solution:
Inventory Turnover Ratio = Cost of good sold / Avg. Inventory
8 = Cost of good sold / 3,20,000
Cost of Goods sold = 3,20,000 x 8
= 25,60,000
Trade receivables turnover ratio = Net credit revenue from operation / Avg. trade receivable
6 = Net credit revenue from operation / 4,00,000
Net credit revenue from operation = 24,00,000
Revenue from operation = Net credit revenue from operation + cash revenue from operation
X = 24,00,000 + 25x / 100
X – 25x / 100 = 24,00,000
75x / 100 = 24,00,000
Revenue from operation = 24,00,000 x 100 / 75
= 32,00,000
Gross profit = Revenue from operation – cost of goods sold
= 32,00,000 – 25,60,000
= 6,40,000
Gross Profit Ratio = Gross profit / revenue from operation x 100
= 6,40,000 / 32,00,000 x 100
= 20 %
143. (i) Revenue from operation: cash sales 4,20,000; credit sales 6,00,000; Return 20,000 cost of Revenue from Operations or cost of Goods sold 8,00,000. Calculate Gross profit Ratio.
(ii) Average Inventory 1,60,000; Inventory Ratio 6 Times; Selling price 25% above cost. Calculate Gross profit Ratio.
(iii) Opening inventory 1,00,000; Closing Inventory 60,000; Inventory Turnover Ratio 8 times; selling price 25% above cost. Calculate Gross Profit Ratio.
Solution:
Case – 1
Net Revenue from operation = Credit sales + Cash sales – Sales Retrun
= 6,00,000 + 4,20,000 – 20,000
= 10,00,000
Cost of Goods sold = 8,00,000
Gross profit = Net revenue from operation – Cost of goods sold
= 10,00,000 – 8,00,000
= 2,00,000
Gross Profit Ratio = Gross profit / revenue from operation x 100
= 2,00,000 / 10,00,000 x 100
= 20 %
Case – 2
Inventory Turnover Ratio = Cost of good sold / Avg. Inventory
6 = Cost of good sold / 1,60,000
Cost of Goods sold = 9,60,000
Revenue from operation = cogs + 25% of cogs
= 9,60,000 + x 9,60,000
= 9,60,000 + 2,40,000
= 12,00,000
Gross profit = Revenue from operation – cost of goods sold
= 12,00,000 – 9,60,000
= 2,40,000
Gross Profit Ratio = Gross profit / revenue from operation x 100
= 2,40,0000 / 12,00,000 x 100
= 20 %
Case – 3
Inventory Turnover Ratio = Cost of good sold / Op. Inventory + Cl. Inventory / 2
6 = Cost of good sold / 1,00,000 + 60,000 / 2
Cost of Goods sold = 8 ( 1,60,000 ) / 2
= 6,40,000
Revenue from operation = cogs + 25% of cogs
= 6,40,000 + 25% of 6,40,000
= 6,40,000 + 1,60,000
= 8,00,000
Gross profit = Revenue from operation – cost of goods sold
= 8,00,000 – 6,40,000
= 1,60,000
Gross Profit Ratio = Gross profit / revenue from operation x 100
= 1,60,000 / 8,00,000 x 100
= 20 %
144. Gross profit Ratio of a company is 25%. state, giving reason, which of the following transactions will
(a) increase or (b) decrease or (c) not alter the Gross profit Ratio.
(i) Purchases of stock-in-Trade 50,000.
(ii) purchases Return 15,000.
(iii) Cash sale of stock-in-Trade 40,000.
(iv) Stock-in-Trade costing 20,000 withdrawn for personal use.
(v) Stock-in-Trade costing 15,000 distributed as free sample.
Solution: (i) – (v) No Change.
OPERATING RATIO
145. Revenue from operations 12,00,000, cost of revenue from operations 5,00,000. Opening cost 6,00,000. Calculate Ratio.
Solution:
Opening Cost = 6,00,000
Revenue from operation = 12,00,000
Operating Ratio = Opening cost / revenue from operation x 100
= 6,00,000 / 12,00,000 x 100
= 50 %
146. Cost of Revenue from operations (Cost of goods sold) 3,00,000. Operating Expenses 1,20,000. Revenue from Operations: Cash sales 5,00,000. Calculate operating Ratio. (AMOUNT CHANGE)
Solution:
Cost of goods sold + Operating expenses
Operating cost = __________________________________________ X 100
Revenue from Operation
3,00,000 + 1,20,000
= ________________________________ X 100
500,000
Revenue from operation = Cash sales – sales Return
= 5,20,000 – 20,000
= 5,00,000
Operating Ratio = Operation cost / revenue from operation x 100
= 4,20,000 / 5,00,000 x 100
= 84 %
147. Operating Ratio 92%; Operating expenses 94,000; Revenue from operations 6,00,000; sales Return 40,000. Calculate cost of Revenue from operations (Cost of goods sold).
Solution
Operating Ratio = Cost of goods sold Operation Exp. / revenue from operation x 100
92 = Cost of goods sold + 94,000/ 6,00,000 x 100
Cost of Goods sold + 94,000 = 92 x 6,00,000 / 100
Cost of goods sold = 5,52,000 – 94,000
= 4,58,000
148. From the following information, calculate Operating Ratio:
Revenue from Operations Rs.10,00,000; Cost of Revenue form Operations Rs.4,00,000; Selling Expenses Rs.80,000; Administrative Expenses Rs.1,20,000.
Goods were sold at a profit of 25% on cost.
Solution-
Operation of cost = Cost of Revenue from operations + Selling expenses + Administration expenses
= 8,00,000 + 40,000 + 1,20,000
= 9,60,000
Operating Ratio = 9,60,000/ 10,00,000 X 100
= 96%
149. From the following information, calculate operating Ratio:
Cost of Revenue
From operations (cost of goods sold) 52,000
Operating Expenses 18,000
Revenue from Operations:
Gross sales 88,000
Sales Return 8,000
solution:
Revenue from operation = Gross sales – sales Return
= 88,000 – 8,000
= 80,000
Operating Ratio = Cost of good sold + operating Exp. / Revenue from operation x 100
= 52,000 + 18,000 / 80,000 x 100
= 70,000 / 80,000 x 100
= 87.5%
150. Calculate cost of Revenue from operations from the information:
Revenue from operations 12,00,000; Opening Ratio 75%; Operating Expenses 1,00,000.
Solution:
Operating Ratio = Cost of good sold + Operating Exp. / revenue from operation x 100
92 = Cost of revenue from operation + 1,00,000 / 12,00,000 x 100
Cost of Revenue from operation = 75 x 12,00,000 / 100 – 1,00,000
= 8,00,000
151. Calculate Operating Ratio from the following information:
Operating cost 6,80,000; Gross Profit 25%; Operating Expenses 80,000.
Solution:
Operating cost = Cost of Goods sold + Operating Expenses
6,80,000 = Cost of Goods sold + 80,000
Cost of Goods sold = 6,00,000
Gross profit = Revenue from operation – cost of goods sold
25/100x = x – 6,00,000
x – 25/ 100x = 6,00,000
x – 75x/100 = 6,00,000
Revenue from operation = 6,00,000 x 100 / 75
= 8,00,000
Operating Ratio = Cost of good sold + operating Exp. / revenue from operation x 100
= 6,00,000 + 80,000 / 8,00,000 x 100
= 6,80,000 / 8,00,000 x 100
= 85 %
152. (i) Cost of Revenue from operations (cost of goods sold) 2,20,000;
Revenue from operations (Net Sales) 3,20,000; Selling Expenses
12,000; Office Expenses Rs.8,000; Depreciation 6,000. Calculate
Operating Ratio.
(ii) Revenue from operations, cash Sales 4,00,000; Credit sales 1,00,000; Gross Profit 1,00,000; Office and selling Expenses 50,000. Calculate Operating Ratio.
Solution:
Case – 1
Operating expenses = Selling Expenses + Office Expenses + Depreciation
= 12,000 + 8,000 + 6,000
= 26,000
Operating Ratio = Cost of good sold + Operating Exp. / Revenue from operation x 100
= 2,20,000 + 26,000 / 3,20,000 x 100
= 2,46,000 / 3,20,000 x 100
= 76.875%
Case – 2
Revenue from operation = Cash sales + credit sales
= 4,00,000 + 1,00,000
= 5,00,000
Cost of Goods sold = Revenue from operation – Gross profit
= 5,00,000 – 1,00,000
= 4,00,000
Operating Ratio = Cost of good sold + operating Exp. / revenue from operation x 100
= 4,00,000+ 50,000 / 5,00,000 x 100
= 4,50,000 / 5,00,000 x 100
= 90 %
OPERATING PROFIT RATIO
153. Calculate Operating Profit Ratio from the following:
Revenue from Operations (Net sales) 5,00,000
Cost of Revenue from operations (Cost of Goods sold) 2,00,000
Wages 1,00,000
Office and Administrative Expenses 50,000
Interest on Borrowings 5,000
Solution:
Opening Expenses = Office & Administrative Expenses
= 50,000
Gross profit = Revenue from operation – Cost of Goods sold
= 5,00,000 – 2,00,000
= 3,00,000
Opening Profit = Gross Profit – Operating Expenses
= 3,00,000 – 50,000
= 2,50,000
Operating Profit Ratio = Operating profit / Revenue from operation x 100
= 2,50,000 / 5,00,000 x 100
= 50 %
153. Calculate Operating profit ratio from the following information:
Opening inventory 1,00,000
Purchases 10,00,000
Revenue from operations, i.e., Net sales 14,70,000
Administrative and Selling Expenses 1,70,000
Closing inventory 1,50,000
Loss by fire 20,000
Dividend Received 30,000
Solution:
Cost of goods sold = Opening inventory + Purchase – closing inventory
= 1,00,000 + 10,00,000 – 1,50,000
= 9,50,000
Gross profit = Revenue from operation – Cost of goods sold
= 14,70,000 – 9,50,000
= 5,20,000
Operating profit = Gross profit – Administrative & selling Expenses
= 5,20,000 – 1,70,000
= 3,50,000
Operating Profit Ratio = Operating profit / Revenue from operation x 100
= 3,50,000 / 5,20,000 x 100
= 23.81%
154. Calculate Operating profit ratio from the following information:
Opening inventory 1,00,000
Purchases 10,00,000
Revenue from operations, i.e., Net sales 14,70,000
Administrative and Selling Expenses 1,70,000
Closing inventory 1,50,000
Loss by fire 20,000
Dividend Received 30,000
Solution:
Cost of goods sold = Opening inventory + Purchase – closing inventory
= 1,00,000 + 10,00,000 – 1,50,000
= 9,50,000
Gross profit = Revenue from operation – Cost of goods sold
= 14,70,000 – 9,50,000
= 5,20,000
Operating profit = Gross profit – Administrative & selling Expenses
= 5,20,000 – 1,70,000
= 3,50,000
Operating Profit Ratio = Operating profit / Revenue from operation x 100
= 3,50,000 / 14,70,000 x 100
= 23.81%
155. Revenue from operations 9,00,000; Gross profit 25% on cost; Operating Expenses 45,000. Calculate Operating Profit Ratio.
Solution:
Gross profit = Revenue from operation – Cost of goods sold
25 / 100 x = 9,00,000 – x
x + 25 / 100x = 9,00,000
x – 125x / 100 = 9,00,000
Cost of Goods sold = 9,00,000 x 100 / 125
= 7,20,000
Gross profit = 9,00,000 – 7,20,000
= 1,80,000
Opening profit = Gross profit – Opening Expenses
= 1,80,000 – 45,000
= 1,35,000
Operating Profit Ratio = Operating profit /Revenue form operation x 100
= 1,35,000 / 9,00,000 x 100
= 15 %
156. Operating Cost 3,40,000; gross profit ratio 20% operating expenses 20,000. Calculate operating profit ratio.
Solution:
Operating cost = Cost of Goods sold + Operating Expenses
3,40,000 = Cost of Goods sold + 20,000
Cost of Goods sold = 3,40,000 – 20,000
= 3,20,000
Gross profit = Revenue from operation – Cost of goods sold
20/100 x = x – 3,20,000
x – 20x /100 = 3,20,000
80x /100 = 3,20,000
Revenue from operation = 3,20,000 x 100 / 80
= 4,00,000
Gross profit = 4,00,000 – 3,20,000
= 80,000
Opening profit = Gross profit – Opening Expenses
= 80,000 – 20,000
= 60,000
Operating Profit Ratio = Operating profit / Revenue form operation x 100
= 60,000 / 4,00,000 x 100
= 15 %
157. What will be the operating profit Ratio, if operating Ratio is 82.59 % ?
Solution:
Operating Profit Ratio + Operating Ratio = 100
Operating profit Ratio + 82.59 = 100
Operating Profit Ratio = 100 – 82.59
= 17.41 %
158. Calculate Operating profit Ratio in each of the following alternative cases:
Case – 1: Revenue from Operation (Net sales) 20,00,000; Operating Profit 3,00,000.
Case – 2: Revenue from Operation (Net sales) 6,00,000; Operating Cost 5,10,000.
Case – 3: Revenue from Operation (Net sales) 3,60,000; Gross Profit 20% on sales; Operating Expenses 18,000.
Case – 4: Revenue from Operation (Net sales) 4,50,000; Cost of Revenue operations 3,60,000; Operating Expenses 22,500.
Case – 5: Cost of Goods sold, i.e., Cost of Revenue from Operations 4,00,000; Gross Profit 20% on sales; Operating Expenses 25,000.
Solution:
Case – 1
Operating Profit Ratio = Operating profit / Revenue from operation x 100
= 3,00,000 /2,00,000 x 100
= 15 %
Case – 2
Operating profit = Revenue from operation – Operating cost
= 6,00,000 – 5,10,000
= 90,000
Operating Profit Ratio = Operating profit / Revenue from operation x 100
= 90,000 / 6,00,000 x 100
= 15 %
Case – 3
Gross Profit
= x 3,60,000
= 72,000
Operating profit = Gross Profit – Operating Expenses
= 72,000 – 18,000
= 54,000
Operating Profit Ratio = Operating profit / Revenue from operation x 100
= 54,000 / 3,60,000 x 100
= 15 %
Case – 4
Gross profit = Revenue from operation – Cost of Revenue from
operation
= 4,50,000 – 3,60,000
= 90,000
Operating profit = Gross Profit – Operating Expenses
= 90,000 – 22,500
= 67,500
Operating Profit Ratio = Operating profit / Revenue from operation x 100
= 67,500 / 4,50,000 x 100
= 15 %
Case – 5
Gross profit = Revenue from operation – Cost of Revenue from
operation
20/100x = x – 4,00,000
x – 20x/100 = 4,00,000
80x / 100 x = 4,00,000
Revenue from operation = 4,00,000 x 100/ 80
= 5,00,000
Gross profit = 5,00,000 – 4,00,000
= 1,00,000
Opening profit = Gross profit – Opening Expenses
= 1,00,000 – 25,000
= 75,000
Operating Profit Ratio = Operating profit / Revenue from operation x 100
= 75,000 / 5,00,000 x 100
= 15 %
159. Operating profit ratio of star Ltd. is 20%. State, giving reason, which of the following transactions will (i) increase, (ii) decrease, or (iii) not alter the operating profit ratio:
- Purchase of Stock-in-Trade 1,00,000
- Purchase returns 20,000
- Revenue from operations on sale of stock-in-Trade 1,25,000
- Stock-in-Trade costing 25,000 withdrawn for personal use.
Assuming that operating cost is variable, I.e., varies with revenue from operations.
Solution:
- No change.
- No change.
- No change.
- No change.
NET PROFIT RATIO
160. Revenue from operations, i.e., Net sales 12,00,000; Net profit 1,20,000. Calculate Net profit Ratio.
Solution:
Net Profit Ratio = Net profit / Revenue form operation x 100
= 1,20,000/12,00,000 x 100
= 10 %
161. Cash sales 2,20,000; Credit sales 3,00,000; sales Return 20,000; Gross profit 1,00,000; Operating Expenses 25,000; Non-operating incomes 30,000; Non-Operating Expenses 5,000. Calculate Net profit Ratio.
Solution:
Revenue from operation = cash sales + credit sales – sales Return
= 2,20,000 + 3,00,000 – 20,000
= 5,00,000
Net Profit= Gross profit + Non-Operating income – Operating Expenses
– Non-Operating Expenses
= 1,00,000 + 30,000 – 25,000 – 5,000
= 1,00,000
Net Profit Ratio = Net profit / Revenue form operation x 100
= 1,00,000/5,00,000 x 100
= 20 %
162. Revenue from operations, i.e., Net sales 8,20,000; Return 10,000; cost of Revenue from operations (cost of goods sold) 5,20,000; Operating expenses 2,09,000; Interest on Debentures 40,500; Gain (profit) on sale of a Fixed Assets 81,000. Calculate net profit Ratio.
Solution:
Gross profit = Revenue from operation – Cost of goods sold
= 8,20,000 – 5,20,000
= 3,00,000
Net Profit = Gross profit – operating expenses – interest on Debentures
+ gain on sale of fixed Assets
= 3,00,000 – 2,09,000 – 40,500 + 81,000
= 1,31,500
Net Profit Ratio = Net profit / Revenue form operation x 100
= 1,31,500/8,20,000 x 100
= 16.04 %
163. Revenue from operations 4,00,000; Gross profit Ratio 25%; Operating Ratio 90% Non-Operating Expenses 2,000; Non-Operating income 22,000. Calculate Net profit Ratio.
Solution:
Gross profit = 25% of Revenue from operation
= 25/100 x 4,00,000
= 1,00,000
Cast of goods sold = Revenue from operation – Gross profit
= 4,00,000 – 1,00,000
= 3,00,000
Operating Ratio = Cost of goods sold + operating Expense/Revenue form operation x 100
90 = 3,00,000 + Operating Expenses /4,00,000 x 100
Operating Exp. = 90 x 4,00,000 / 100 x 100
= 3,60,000 – 3,00,000
= 60,000
Net Profit = Gross Profit + Non-Operating Income – Operating Exp. –
Non-operating Exp.
= 1,00,000 + 22,000 – 60,000 – 2,000
= 60,000
Net Profit Ratio = Net profit / Revenue form operation x 100
= 60,000 / 4,00,000 x 100
= 15 %
RETURN ON CAPITAL EMPLOYED (OR RETURN ON INVESTMENT)
164. Net Profit before interest and Tax 2,50,000; Capital Employed 10,000. Calculate Return on Investment.
Solution:
Return on Investment = Profit Before Interest & tax & Dividend / Capital Empolyed x 100
= 2,50,000/ 10,00,000 x 100
= 25%
165. Net profit before interest and Tax 6,00,000; Net Fixed Assets 20,00,000; Net working capital 10,00,000; current Assets 11,00,000. Calculate Return on investment.
Solution
Capital Employed = Net fixed Assets + Net working Capital
= 20,00,000 + 10,00,000
= 30,00,000
Return on Investment = Profit Before Interest & tax / Capital Employed x 100
=6,00,000/30,00,000 x 100
= 20 %
166. Net Profit before and Tax 4,00,000; 15% Long-term Debt 8,00,000; Shareholder’s Funds 4,00,000. Calculate return on investment.
Solution:
Capital Employed = Share holder’s Funds + 15% long-term Debt
= 4,00,000 + 8,00,000
= 12,00,000
Return on Investment = Profit Before Interest & tax & Dividend / Capital Employed x 100
= 4,00,000/12,00,000 x 100
= 33.33 %
167. Net profit after interest but before tax 1,40,000; 15% long-term Debts 4,00,000; Shareholder’s Funds 2,40,000; Tax rate 50%. Calculate Return on capital Employed.
Solution:
Interest = 15% of long-term Debt
= 15 x 4,00,000
= 60,000
Net profit before interest & tax = Net profit Assets interest + interest
& Before Tax
= 1,40,000 + 60,000
= 2,00,000
Capital Employed = Share holder’s Funds + long-term Debt
= 2,40,000 + 4,00,000
= 6,40,000
Return on Investment = Profit Before Interest & tax & Dividend / Capital Employedx 100
= 2,00,000 /6,40,000 x 100
= 31.25 %
168. Y Ltd’s profit after interest and tax was 1,00,000. Its current Assets were 4,00,000; current liabilities 2,00,000; Fixed Assets 6,00,000 and 10% long-term Debt 4,00,000. The rate of tax was 20% calculate ‘Return on investment’ of Y Ltd.
Capital Employed = Fixed Assets + Current Assets – Current Liabilities
= 6,00,000 + 4,00,000 – 2,00,000
= 8,00,000
169. Calculate Return on investment (ROI) from the following details; net profit after Tax 6,50,000 Rate of income Tax 50%; 10% Debentures of 100 each 10,00,000; Fixed Assets at cost 22,50,000; Accumulated Depreciation on fixed Assets up to date 2,50,000; Current Assets 12,00,000; Current Liabilities 4,00,000.
Solution:
Capital employed = Fixed Assets – Acc. Depreciation + Current Assets –
Current liabilities
= 22,50,000 – 2,50,000 + 12,00,000 – 4,00,000
= 28,00,000
Let profit before tax & After interest be x
Profit After interest & tax = profit before tax & after – tax interest
6,50,000 = x –50/100 x
50x/100 = 6,50,000
=6,50,000 x 100/50
Profit before tax & after interest = 13,00,000
Profit before tax & interest = profit before tax & after interest +
interest
= 13,00,000 + 10/100x 10,00,000
= 13,00,000 + 1,00,000
= 14,00,000
Return on Investment = Profit Before Interest & tax & Dividend / Capital Employed x 100
= 14,00,000/28,00,000 x 100
= 50 %
170. From the following information, calculate return on investment (or return on capital employed):
Particular
Share capital 5,00,000
Reserves and surplus 2,50,000
Net fixed Assets 22,50,000
Non-current Trade investment 2,50,000
Current Assets 11,00,000
10% Long-term Borrowings 20,00,000
Current Liabilities 8,50,000
Net profit before TAX: 6,00,000
Solution;
Interest = 10% of long-term Borrowings
= 10/100 x 20,00,000
= 20,00,000
Net Profit Before interest & tax = Net profit before tax + interest
= 6,00,000 + 2,00,000
= 8,00,000
Capital employed = Share capital + Reserve & surplus + 10% long-term
Borrowings + Long-term provision
= 5,00,000 + 2,50,000 + 20,00,000 + 0
= 27,50,000
Return on Investment = Profit Before Tax & Interest /Capital Employed x 100
= 8,00,000/27,50,000 x 100
= 29.09 %
171. State, with reason, whether the following transactions will increase, decrease or not change the ‘Return on investment’ Ratio.
- Purchase of Machinery of 10,00,000 by issue of equity share of 10 each at par.
- Charging depreciation of 25,000 on Machinery
- Redemption of debentures by payment of 2,00,000
- Conversion of 9% Debentures of 1,00,000 into 10% Debentures of 100 each at par.
Solution:-
- Decrease.
- Decrease;
- No change.
- Decrease.
MISCELLANEOUS
172. Calculate ‘Quike Ratio’ and ‘Debt-Equity Ratio’ from the following information information:
Total Debt Rs.8,00,000
Inventory Rs.2,20,000
Lont-term Debts RS.6,00,000
Working Capital Rs.2,40,000
Shareholders’ Funds Rs.12,00,000
Solution- Quick Ratio = 1.1 : 1, debt – Equity Ratio = 0.5 : 1.
173. Calculate Revenue from operations of BN Ltd. from the following information:
Current Assets 8,00,000
Quick Ratio is 1.5 : 1
Current Ratio is 2 : 1
Inventory turnover Ratio is 6 times
Goods were sold at a profit of 25% on cost.
Solution:
Current Assets = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
2 = 8,00,000/Current Liabilities
Current Liabilities = 4,00,000
Quick Ratio = Quick Assets / Current Liabilities
1.5 = quick Assets / 4,00,000
Quick Assets = 6,00,000
Quick Assets = Current Assets – Inventory
6,00,000 = 8,00,000 – Inventory
Inventory = 2,00,000
Inventory Turnover Ratio = Cost of Goods Sold / Avg. Inventory
6 = Cost of Goods Sold / 2,00,000
Cost of Gods sold = 12,00,000
Gross profit = Revenue from operation – cost of goods sold
25/100 x 12,00,000 Revenue from operation – 12,00,000
Revenue from operation = 12,00,000 + 3,00,000
= 15,00,000
174. Opening inventory 80,000; Purchase 4,30,900; Direct Expenses 4,000; closing inventory 1,60,000; Administrative Expenses 21,100; selling and distribution Expenses 40,000; Revenue form operations, i.e., Net sales 10,00,000. Calculate inventory turnover Ratio; Gross profit Ratio: and Operating Ratio.
Solution:
Case – 1
Cost of Goods sold = Opening inventory + Purchase + Direct Expenses
– Closing inventory
= 80,000 + 43,0900 + 4,000 – 1,60,000
= 3,54,900
Inventory Turnover Ratio =Cost of Goods Sold / Avg. Inventory
6 = 3,54,900/80,000 + 1,60,000/2
= 3,54,000 x 2 / 2,40,000
= 2.96 times
Case – 2
Gross profit = Revenue from operation – Cost of Goods sold
= 10,00,000 – 3,54,900
= 6,45,100
Gross Profit Ratio = Gross Profit / Revenue from operation x 100
= 6,45,100/10,00,000 x 100
= 64.51 %
Case – 3
Operating Ratio = Cost of Goods sold + Operating Expense / Revenue from operation x 100
= 3,54,900 + 40,000 + 21,100/41000,000 x 100
= 4,16,000 / 10,00,000 x 100
= 41.6 %
175. From the given information calculate:
- Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio,
- Current ratio.
| Credit Revenue from operations Rs.80,00,00 Debtors Rs.25,00,000 Bills receivables Rs.15,00,000 Total Assets Rs.50,00,000 | 10% Debentures Rs.12,00,000 Creditors Rs.13,00,000 Bills Payable Rs.7,00,000 |
Solution-
- Trade Receivable Turnover Ratio
= Net Credit Sales / Average Trade Receivable
= 80,00,000/(25,00,000 + 5,00,000)
= 80,00,000 / 40,00,000
= 2 times
B) Current Ratio
= Current Assets / Current Liabilities
Current Assets = Debtors + Bill Receivable
= 2500,000 + 1500,000
= 40,00,000
Current Liabilities = Creditors + Bill Payable
= 1300,000 + 700,000
= 20,00,000
Current Ratio = 40,00,000 / 20,00,000
= 20%
175. Following information is given about a company: (Old Book)
Revenue from operation, i.e., Net sales 1,50,000
Gross Profit 30,000
Cost of Revenue form operations 1,20,000
(Cost of goods Sold)
Opening inventory 29,000
Closing Inventory 31,000
Debtors 16,000
From the above information, Calculate following ratios:
(i) Gross profit Ratio,
(ii) Inventory turnover Ratio, and
(iii) Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio.
Solution:
Case – 1
Gross Profit Ratio = Gross Profit / Revenue form operation x 100
= 30,000 / 1,50,000 x 100
= 20 %
Case – 2
Inventory Turnover Ratio = Cost of Goods Sold / Ave Intentory
6 = 1,20,000 / 29,000 + 31,000 / 2
= 1,20,000 x 2/ 60,000
= 4 times
Case – 3
Trade receivables turnover ratio = Net Credit Sales / Avg. trade receivables
= 1,50, 000 / 16,000
= 9.375
176. From the following information obtained from the books of kamal Ltd., calculate (i) Gross profit Ratio and (ii) Net profit Ratio:
Revenue from Operation 2,50,000
Purchases 1,05,000
Carriage inwards 4,000
Salaries 30,000
Decrease in inventory 15,000
Return outwards 5,000
Wages 18,000
Solution:
Case – 1
Cost of Goods sold = Purchase – Return outward + wages + Carriage
inwards + Decrease in inventory
= 1,05,000 – 5,000 + 18,000 + 4,000 + 15,000
= 1,37,000
Gross Profit = Revenue from operation – cost of Goods sold
= 2,50,000 – 1,37,000
= 1,13,000
Gross Profit Ratio = Gross Profit / Revenue form ooperation x 100
= 1,13,000/2,50,000 x 100
= 45.20 %
Case – 2
Net profit = Gross profit – salaries
= 11,3,000 – 30,000
= 3,000
Net Profit Ratio = Net profit / Revenue form operation x 100
= 83,000 / 2,50,000 x 100
= 33.20 %
177. From the following information, Calculate:
(i) Return on investment Ratio.
(ii) Net Assets Turnover Ratio.
Interest = 10% Debenture
= x 4,00,000 = 40,000
Net Profit Before interest & tax = Net profit after interest & tax + tax +
interest
= 2,40,000 + 1,60,000 + 40,000
= 4,40,000
Capital Employed = Equity share capital + 15% preference share
capital + reserves & Surplus + 10% Debentures
= 5,00,000 + 1,00,000 + 2,00,000 + 4,00,000
= 12,00,000
Return on Investment = Profit Before Tax & Interest / Capital employed x 100
= 4,40,000 / 12,00,000 x 100
= 36.67 %
Net Assets Turnover Ratio = Revenue form operation / Capital employed
= 24,00,000 / 12,00,000
= 2 times
178. Calculate following ratios on the basis of the following information:
(i) Gross profit Ratio; (ii) Current Ratio; (iii) Acid Test Ratio
(iv) Inventory Turnover Ratio.
Gross profit 50,000
Inventory 15,000
Cash and Cash Equivalents 17,500
Revenue from operations 1,00,000
Trade Receivables 27,500
Current Liabilities 40,000
Case – 1
Gross Profit Ratio = Gross profit / revenue from operation x 100
= 50,000 / 1,00,000 x 100
= 50 %
Case – 2
Current Assets = Inventory + Cash & cash Equivalents + Trade
receivables
= 15,000 + 17,500 + 27,500
= 60,000
Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
= 60,000 / 40,000 x 100
= 1.5:1
Case – 3
Quick Assets = Current Assets – Inventory
= 60,000 – 15,000
= 45,000
Quick Ratio = quick Assets / Current Assets
= 45,000 / 40,000 x 100
= 1.125:1
Case – 4
Cost of goods sold = Revenue from operations – Gross profit
= 1,00,000 – 50,000
= 50,000
Inventory Turnover Ratio = Cost of Goods sold / Avg. Inventory
= 50,000 x 2 / 15,000
= 3.33 times
179. Calculate following ratios on the basis of the given information:
(i) Current Ratio; (ii) Acid Test Ratio; (iii) Operating Ratio; and
(iv) Gross profit Ratio.
Current Assets 3,50,000
Current Liabilities 1,75,000
Inventor 1,50,000
Revenue from operations (sales) 6,00,000
Operating Expenses 2,00,000
Cost of Revenue from operations 3,00,000
Solution:
Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
= 3,50,000 / 1,75,000x 100
= 2:1
Case – 2
Acid Test Ratio = Current Assets – Inventory / Current Liabilities
= 3,50,000 – 1,50,000 / 1,75,000
= 2,00,000 / 1,75,000
= 1.4:1
Case – 3
Operating Ratio = Cost of goods sold + Operating expense/Revenue form operation x 100
= 3,00,000 + 2,00,000 / 5,00,000 x 100
= 5,00,000 / 6,00,000 x 100
= 83.33 %
Case – 4
Gross Profit = Revenue from operation – cost of revenue from operation
= 6,00,000 – 3,00,000
= 3,00,000
Gross Profit Ratio = Gross Proift /Revenue form operation x 100
= 3,00,000 / 6,00,000 x 100
= 50 %
180. From the information given below, calculate any three of the following ratios:
(i) Gross profit Ratio: (ii) Working capital Turnover Ratio;
(iii) Debt to Equity Ratio (iv) Proprietary Ratio
Revenue from operations (Net sales) 5,00,000
Cost of Revenue operations (cost of goods sold) 3,00,000
Current Assets 2,00,000
Current Liabilities 1,40,000
Paid-up share capital 2,50,000
13% Debentures 1,00,000
Case – 1
Gross Profit = Revenue from operation – cost of revenue from operation
= 5,00,000 – 3,00,000
= 2,00,000
Gross Profit Ratio = Gross profit / Revenue form operation x 100
= 40 %
Case – 2
Working Capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities
= 2,00,000 – 1,40,000
= 60,000
Working capital Ratio = 5,00,000 / 60,000
= 8.33 times
Case – 3
Debt to Equity Ratio = Debt / Equity
= 1,00,000 / 2,50,000
= 0.4:1
Case – 4
Total Assets = paid-up share capital + 13% Debentures + Current Liabilities
= 2,50,000 + 1,00,000 + 1,40,000
= 4,90,000
Property Ratio = Share holders funds / total Assets
= 2,50,000 / 4,90,000
= 51:1
181. On the basis of the following information, calculate
(i) Debt to Equity Ratio; (ii) Working capital Turnover Ratio.
Information:
Revenue from operations: (a) Cash sales 40,00,000
(b) Credit sales 20,00,000
Cost of Goods sold 35,00,000
Other current Assets 8,00,000
Current Liabilities 4,00,000
Paid-up share capital 17,00,000
6% Debentures 3,00,000
9% Loan from Bank 7,00,000
Debentures Redemption Reserve 3,00,000
Closing Inventory 1,00,000
Case – 1
Debt – 6% Debentures + 9% loan from Bank
= 3,00,000 + 7,00,000
= 10,00,000
Equity = paid-up capital + Debentures Redemption Reserve
= 17,00,000 + 3,00,000
= 20,00,000
Debt to Equity Ratio = Debt / Equity
= 10,00,000 / 20,00,000
= 0.5:1
Case – 2
Revenue from operation = Cash sales + Credit sales
= 40,00,000 + 20,00,000
= 60,00,000
Current Assets = other current Assets + closing inventory
= 8,00,000 + 1,00,000
= 9,00,000
Working Capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities
= 9,00,000 – 4,00,000
= 5,00,000
Working capital Turnover Ratio = turnover form operation / working capital
= 60,00,000 / 5,00,000
= 12 times
182. From the following, calculate (a) Debt to equity ratio; (b) Total Assets to debt Ratio; and (c) proprietary Ratio:
Equity share capital 75,000
preference share capital 25,000
General Reserve 45,000
Balance in statements of profit & loss 30,000
Debentures 75,000
Trade payables 40,000
Outstanding Expense 10,000
Solution:
Case – 1
Equity = Equity share capital + preference share capital + General
Reserve + Balance in statement of profit & loss
= 75,000 + 25,000 + 45,000 + 30,000
= 1,75,000
Debt to Equity Ratio = Debt / Equity
= 75,000 / 1,75,000
= 0.43:1
Case – 2
Total Assets to Debt Ratio = total Assets / Debt
= 3,00,000 / 75,000
= 4:1
Case – 3
Property Ratio = share holders funds / total Assets
= 1,75,000 / 3,00,000
= 0.58:1
183. From the following information related to Naveen Ltd., calculate (a) Return on investment and (b) Total Assets to Debt Ratio:
Information: Fixed Assets 75,00,000; Current Assets 40,00,000; Current liabilities 27,00,000; 12% Debenture 80,00,000 and Net profit before interest, Tax and Dividend 14,50,000.
Solution:
Capital Employed = Fixed Assets + Current Assets – Current Liabilities
= 75,00,000 + 40,00,000 + 27,00,000
= 88,00,000
Return on Investment = Profit Before Int. Tax & Dividend /Capital Employed x 100
= 14,50,000 / 88,00,000 x 100
= 16.48 %
Case – 2
Total Assets = Fixed Assets + Current Assets
= 75,00,000 + 40,00,000
= 11,50,000
Debt = 12% Debentures
= 80,00,000
Total Assets To Debt Ratio = Total Assets / debt
= 11,50,000 / 80,00,000
= 1.44:1
184. From the following information, calculate:
- Gross Profit Ratio;
- Working capital Turnover Ratio; and
- Property Ratio
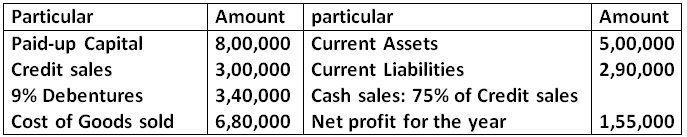
Solution:
Case – 1
Revenue from operation = cash sales + credit sales
= 75/100 x 3,00,000 + 3,00,000
= 2,25,0000 + 3,00,000
= 5,25,000
Gross profit = Revenue from operation – cost of goods sold
= 5,25,000 – 6,80,000
= – 1,55,000
Gross Profit Ratio = Gross profit / revenue form operation x 100
= – 1,55,000 / 5,25,000 x 100
= – 29.52 %
Case – 2
Working capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities
= 5,00,000 – 2,90,000
= 2,10,000
Revenue from operation = 5,25,000
Working capital Turnover Ratio = Turnover form operation / Working capital
= 5,25,000 / 2,10,000
= 2.5 times
Case – 3
Proprietors Funds = Paid up capital + Net Profit for the year
= 8,00,000 + 1,55,000
= 9,55,000
Total Assets = Paid-up Capital + Net Profit for the year + 9%
Debentures + Current Liabilities
= 8,00,000 + 1,55,000 + 3,40,000 + 2,90,000
= 15,85,000
Property Ratio = Property funds / total Assets
= 9,55,000 / 15,85,000 x 100
= 60.25 %